|
Schottenstein Campus
The Jay and Jeanie Schottenstein National Campus for the Archaeology of Israel is the future building of the Israel Antiquities Authority. Construction began in 2012 in Jerusalem, the building will concentrate all centralized administrative offices into one structure. The campus is being built on 20,000 square meters located between the Israel Museum and the Bible Lands Museum. It was designed by Moshe Safdie. Building When completed, the 36,000- sq.-m. building will house offices, archaeological artifacts, archeology laboratories, the National Library for the Archeology of Israel, and serve as a museum of archaeology. Construction began in 2012 with the excavation of an enormous foundation cut into a hillside so that so that the roof level entrance of the large building is at ground level between the two, existing, major museums, while the lowest floor opens onto a street at the foot of the hill. The Antiquities Authority was formerly located in cramped quarters at the Rockefell ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Program Of The National Campus Archaeology Of The Land Of Israel
Program, programme, programmer, or programming may refer to: Business and management * Program management, the process of managing several related projects * Time management * Program, a part of planning Arts and entertainment Audio * Programming (music), generating music electronically * Radio programming, act of scheduling content for radio * Synthesizer programmer, a person who develops the instrumentation for a piece of music Video or television * Broadcast programming, scheduling content for television * Program music, a type of art music that attempts to render musically an extra-musical narrative * Synthesizer patch or program, a synthesizer setting stored in memory * "Program", an instrumental song by Linkin Park from '' LP Underground Eleven'' * Programmer, a film on the lower half of a double feature bill; see B-movie Science and technology * Computer program, a set of instructions that describes how to perform a specific task to a computer. * Computer programming, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Israel Antiquities Authority
The Israel Antiquities Authority (IAA, he, רשות העתיקות ; ar, داﺌرة الآثار, before 1990, the Israel Department of Antiquities) is an independent Israeli governmental authority responsible for enforcing the 1978 Law of Antiquities. The IAA regulates excavation and conservation, and promotes research. The Director-General is Mr. Eli Escusido, and its offices are housed in the Rockefeller Museum. The Israel Antiquities Authority plans to move into a new building for the National Campus for the Archaeology of Israel in Jerusalem, next to the Israel Museum. History The Israel Department of Antiquities and Museums (IDAM) of the Ministry of Education was founded on July 26, 1948, after the establishment of the State of Israel. It took over the functions of the Department of Antiquities of the British Mandate in Israel and Palestine. Originally, its activities were based on the British Mandate Department of Antiquities ordinances. IDAM was the statutory aut ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
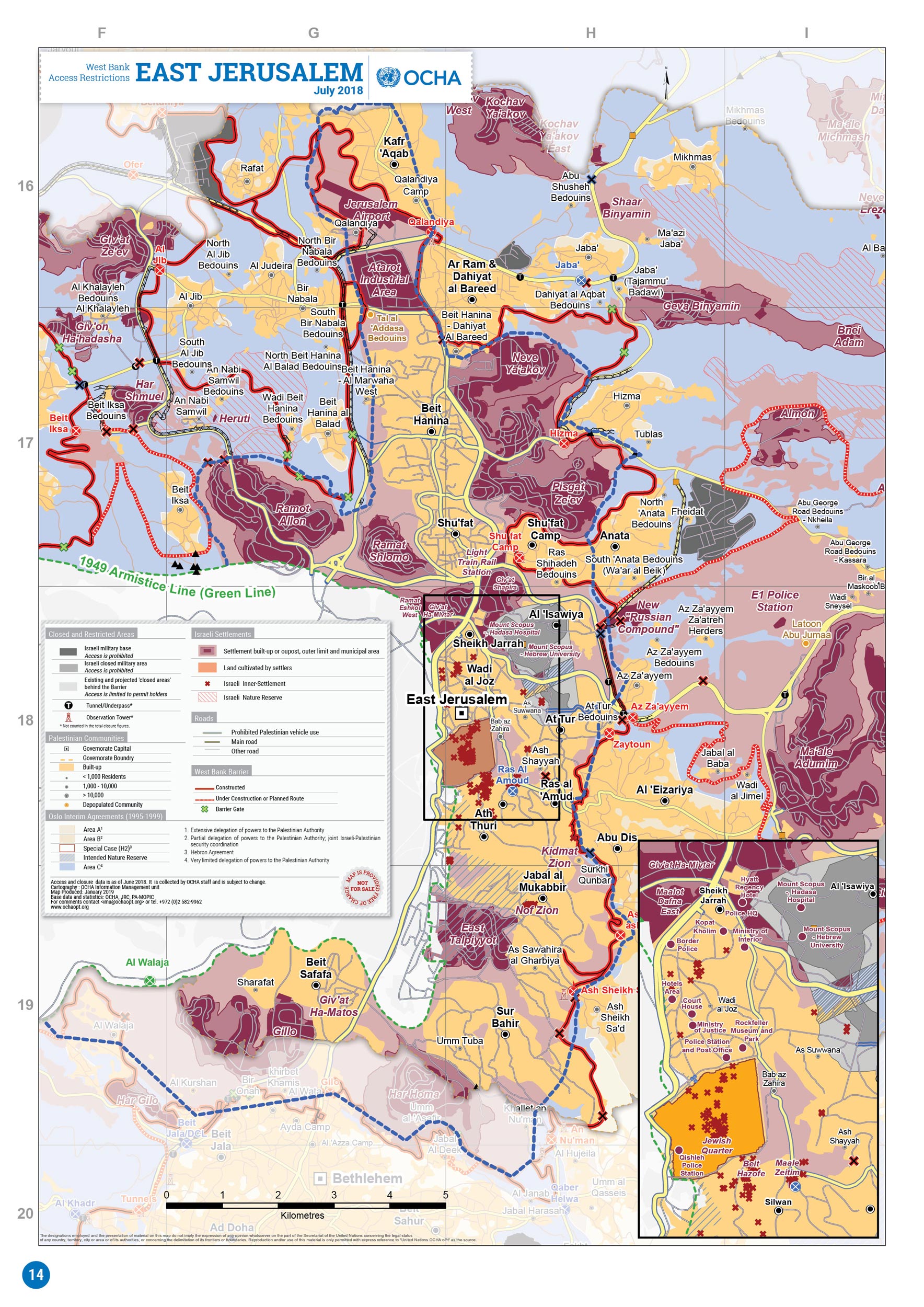
Jerusalem
Jerusalem (; he, יְרוּשָׁלַיִם ; ar, القُدس ) (combining the Biblical and common usage Arabic names); grc, Ἱερουσαλήμ/Ἰεροσόλυμα, Hierousalḗm/Hierosóluma; hy, Երուսաղեմ, Erusałēm. is a city in Western Asia. Situated on a plateau in the Judaean Mountains between the Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean and the Dead Sea, it is one of the List of oldest continuously inhabited cities, oldest cities in the world and is considered to be a holy city for the three major Abrahamic religions: Judaism, Christianity, and Islam. Both Israelis and Palestinians claim Jerusalem as their Capital city, capital, as Israel maintains its primary governmental institutions there and the State of Palestine ultimately foresees it as its seat of power. Because of this dispute, Status of Jerusalem, neither claim is widely recognized internationally. Throughout History of Jerusalem, its long history, Jerusalem has been destroyed at least twice, Sie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Israel Museum
The Israel Museum ( he, מוזיאון ישראל, ''Muze'on Yisrael'') is an art and archaeological museum in Jerusalem. It was established in 1965 as Israel's largest and foremost cultural institution, and one of the world’s leading encyclopaedic museums. It is situated on a hill in the Givat Ram neighborhood of Jerusalem, adjacent to the Bible Lands Museum, the Knesset, the Israeli Supreme Court, and the Hebrew University of Jerusalem. Its holdings include the world's most comprehensive collections of the archaeology of the Holy Land, and Jewish art and life, as well as significant and extensive holdings in the fine arts, the latter encompassing eleven separate departments: Israeli Art, European Art, Modern Art, Contemporary Art, Prints and Drawings, Photography, Design and Architecture, Asian Art, African Art, Oceanic Art, and Arts of the Americas. Among the unique objects on display are the Venus of Berekhat Ram, the interior of a 1736 Zedek ve Shalom synagogue from Sur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bible Lands Museum
The Bible Lands Museum ( he, מוזיאון ארצות המקרא ירושלים, ar, متحف بلدان الكتاب) is an archaeological museum in Jerusalem, that explores the culture of the peoples mentioned in the Bible including ancient Egyptians, Canaanites, Philistines, Arameans, Hittites, Elamites, Phoenicians and Persians. Overview The aim of the museum is to put the various peoples covered into historical context. The museum is located on Museum Row in Givat Ram, between the Israel Museum, the National Campus for the Archaeology of Israel, and the Bloomfield Science Museum. History The museum was founded by Elie Borowski in 1992 to house his personal collection. On a visit to Jerusalem in 1981, he met Batya Weiss who encouraged him to bring his collection of Ancient Near Eastern Art from biblical times to Israel and establish a museum. She put him in contact with Jerusalem mayor Teddy Kollek. Borowski heeded her advice, built the Bible Lands Museum and moved his ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moshe Safdie
Moshe Safdie ( he, משה ספדיה; born July 14, 1938) is an architect, urban planner, educator, theorist, and author, with Israeli, Canadian, and American citizenship. He is known for incorporating principles of socially responsible design in his 50-year career. His projects include cultural, educational, and civic institutions; neighborhoods and public parks; housing; mixed-use urban centers; airports; and master plans for existing communities and entirely new cities in North and South America, the Middle East, and Asia. He is most identified with designing Marina Bay Sands and Jewel Changi Airport, as well as his debut project, Habitat 67, originally conceived as his thesis at McGill University. Early life and education Moshe Safdie was born in Haifa, British Mandate of Palestine, in 1938, to a Sephardic Jewish family of Syrian-Jewish and Lebanese-Jewish descent. He was nine years old, living in Haifa, when, on May 14, 1948, David Ben-Gurion proclaimed the Declarati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biblical Archaeology
Biblical archaeology is an academic school and a subset of Biblical studies and Levantine archaeology. Biblical archaeology studies archaeological sites from the Ancient Near East and especially the Holy Land (also known as Palestine, Land of Israel and Canaan), from biblical times. Biblical archaeology emerged in the late 19th century, by British and American archaeologists, with the aim of confirming the historicity of the Bible. Between the 1920s, right after World War I, when Palestine came under British rule and the 1960s, biblical archaeology became the dominant American school of Levantine archaeology, led by figures such as William F. Albright and G. Ernest Wright. The work was mostly funded by churches and headed by theologists. From the late 1960s, biblical archaeology was influenced by processual archaeology ("New Archaeology") and faced issues that made it push aside the religious aspects of the research. This has led the American schools to shift away from bibli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rockefeller Museum
The Rockefeller Archeological Museum, formerly the Palestine Archaeological Museum ("PAM"; 1938–1967), and which before then housed The Imperial Museum of Antiquities (''Müze-i Hümayun''; 1901–1917), is an archaeology museum A museum ( ; plural museums or, rarely, musea) is a building or institution that cares for and displays a collection of artifacts and other objects of artistic, cultural, historical, or scientific importance. Many public museums make these ... located in East Jerusalem that houses a large collection of artifacts unearthed in the excavations conducted in the region of Palestine, mainly in the 1920s and 1930s. With the beginning of the Israeli occupation of the West Bank in 1967, the Palestine Archaeological Museum was renamed "Rockefeller Museum", and it has since then been under the management of the Israel Museum. The museum today houses the head office of the Israel Antiquities Authority. The Museum's most priced collection, the Dead Sea S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
East Jerusalem
East Jerusalem (, ; , ) is the sector of Jerusalem that was held by Jordan during the 1948 Arab–Israeli War, as opposed to the western sector of the city, West Jerusalem, which was held by Israel. Jerusalem was envisaged as a separate, international city under the 1947 United Nations partition plan. It was, however, divided by the 1948 war that followed Israel's declaration of independence. As a result of the 1949 Armistice Agreements, the city's western half came under Israeli control, while its eastern half, containing the famed Old City, fell under Jordanian control. Israel occupied East Jerusalem during the 1967 Six-Day War; since then, the entire city has been under Israeli control. The 1980 Jerusalem Law declared unified Jerusalem the capital of Israel, formalizing the effective annexation of East Jerusalem. Palestinians and many in the international community consider East Jerusalem to be the future capital of the State of Palestine. This includes (out of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epigraphy Mosiac From Eingedi Shul
Epigraphy () is the study of inscriptions, or epigraphs, as writing; it is the science of identifying graphemes, clarifying their meanings, classifying their uses according to dates and cultural contexts, and drawing conclusions about the writing and the writers. Specifically excluded from epigraphy are the historical significance of an epigraph as a document and the artistic value of a literary composition. A person using the methods of epigraphy is called an ''epigrapher'' or ''epigraphist''. For example, the Behistun inscription is an official document of the Achaemenid Empire engraved on native rock at a location in Iran. Epigraphists are responsible for reconstructing, translating, and dating the trilingual inscription and finding any relevant circumstances. It is the work of historians, however, to determine and interpret the events recorded by the inscription as document. Often, epigraphy and history are competences practised by the same person. Epigraphy is a primar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mosaic
A mosaic is a pattern or image made of small regular or irregular pieces of colored stone, glass or ceramic, held in place by plaster/mortar, and covering a surface. Mosaics are often used as floor and wall decoration, and were particularly popular in the Ancient Roman world. Mosaic today includes not just murals and pavements, but also artwork, hobby crafts, and industrial and construction forms. Mosaics have a long history, starting in Mesopotamia in the 3rd millennium BC. Pebble mosaics were made in Tiryns in Mycenean Greece; mosaics with patterns and pictures became widespread in classical times, both in Ancient Greece and Ancient Rome. Early Christian basilicas from the 4th century onwards were decorated with wall and ceiling mosaics. Mosaic art flourished in the Byzantine Empire from the 6th to the 15th centuries; that tradition was adopted by the Norman Kingdom of Sicily in the 12th century, by the eastern-influenced Republic of Venice, and among the Rus. Mosaic fell ou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ein Gedi
Ein Gedi ( he, עֵין גֶּדִי, ), also spelled En Gedi, meaning "spring of the kid", is an oasis, an archeological site and a nature reserve in Israel, located west of the Dead Sea, near Masada and the Qumran Caves. Ein Gedi, a kibbutz, was established nearby in 1954. Ein Gedi is a popular tourist attraction, and was listed in 2016 as one of the most popular nature sites in Israel. The site attracts about one million visitors a year. Etymology The name ''Ein Gedi'' is composed of two words (In both Arabic and Hebrew): ''ein'' means spring or a fountain and ''gǝdi'' means goat-kid. Ein Gedi thus means "kid spring" or "fountain of the kid". History and archaeology Neolithic At Mikveh Cave archaeologists found Pre-Pottery Neolithic A (PPNA) flint tools and an arrowhead. Chalcolithic A Chalcolithic temple (ca. mid-fourth millennium BCE) belonging to the Ghassulian culture was excavated on the slope between two springs, Ein Shulamit and Ein Gedi. More Chalcolithic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |