|
Schlachte Great Crane
The Schlachte Cranes were important to the port of Bremen as they enabled heavy loads to be moved off boats on the River Weser. The Schlachte became an important harbour for the city after silting prevented the use of the Balge as a harbour. Today, only the foundations of a 19th-century crane remain on the Weser waterfront. History A map of Bremen made around 1640 clearly shows what must be a large crane. The wooden structure was built around a central mast that allowed the crane to turn. A new harbour crane installed in 1684 is attributed to Jacob Leupold.Theatrum Machinarum Generale ("The General Theory of Machines"), Jacob Leupold. This crane could also rotate but two large treadwheels enabled six men to lift a load of three tonnes. In his book on the theory of machines, Leupold illustrates two cranes at Bremen. The more ambitious model is pictured here. The boom would have been much longer as it has been shortened to fit within the illustration. The crane would have been u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bremen Crane Merian1640
Bremen (Low German also: ''Breem'' or ''Bräm''), officially the City Municipality of Bremen (german: Stadtgemeinde Bremen, ), is the capital of the German state Free Hanseatic City of Bremen (''Freie Hansestadt Bremen''), a two-city-state consisting of the cities of Bremen and Bremerhaven. With about 570,000 inhabitants, the Hanseatic city is the 11th largest city of Germany and the second largest city in Northern Germany after Hamburg. Bremen is the largest city on the River Weser, the longest river flowing entirely in Germany, lying some upstream from its mouth into the North Sea, and is surrounded by the state of Lower Saxony. A commercial and industrial city, Bremen is, together with Oldenburg and Bremerhaven, part of the Bremen/Oldenburg Metropolitan Region, with 2.5 million people. Bremen is contiguous with the Lower Saxon towns of Delmenhorst, Stuhr, Achim, Weyhe, Schwanewede and Lilienthal. There is an exclave of Bremen in Bremerhaven, the "Citybremian Ove ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bremen
Bremen (Low German also: ''Breem'' or ''Bräm''), officially the City Municipality of Bremen (german: Stadtgemeinde Bremen, ), is the capital of the German state Free Hanseatic City of Bremen (''Freie Hansestadt Bremen''), a two-city-state consisting of the cities of Bremen and Bremerhaven. With about 570,000 inhabitants, the Hanseatic city is the 11th largest city of Germany and the second largest city in Northern Germany after Hamburg. Bremen is the largest city on the River Weser, the longest river flowing entirely in Germany, lying some upstream from its mouth into the North Sea, and is surrounded by the state of Lower Saxony. A commercial and industrial city, Bremen is, together with Oldenburg and Bremerhaven, part of the Bremen/Oldenburg Metropolitan Region, with 2.5 million people. Bremen is contiguous with the Lower Saxon towns of Delmenhorst, Stuhr, Achim, Weyhe, Schwanewede and Lilienthal. There is an exclave of Bremen in Bremerhaven, the "Citybremian Overseas Port ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
River Weser
The Weser () is a river of Lower Saxony in north-west Germany. It begins at Hannoversch Münden through the confluence of the Werra and Fulda. It passes through the Hanseatic city of Bremen. Its mouth is further north against the ports of Bremerhaven and Nordenham. The latter is on the Butjadingen Peninsula. It then merges into the North Sea via two highly saline, estuarine mouths. It connects to the canal network running east-west across the North German Plain. The river, when combined with the Werra (a dialectal form of "Weser"), is long and thus, the longest river entirely situated within Germany (the Main, however, is the longest if the Weser and Werra are not combined). The Weser itself is long. The Werra rises in Thuringia, the German state south of the main projection (tongue) of Lower Saxony. Etymology "Weser" and "Werra" are the same words in different dialects. The difference reflects the old linguistic border between Central and Low German, passing through Ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
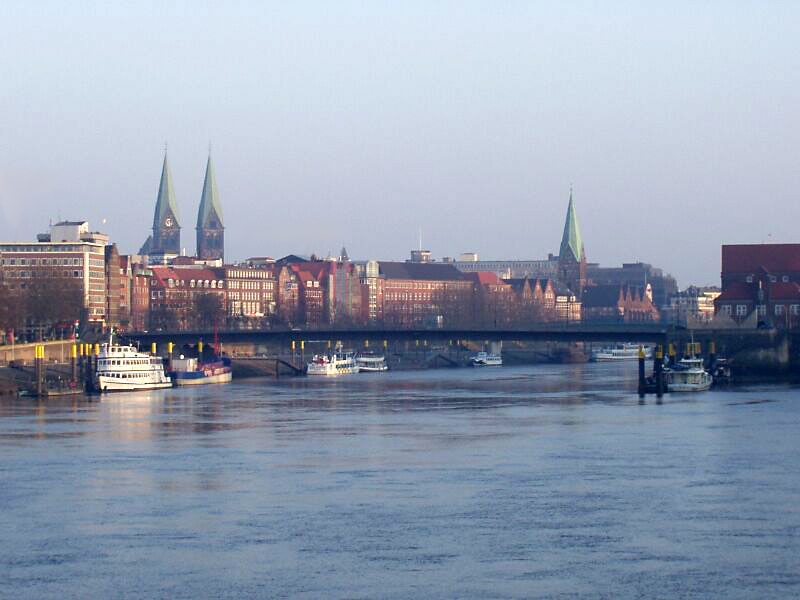
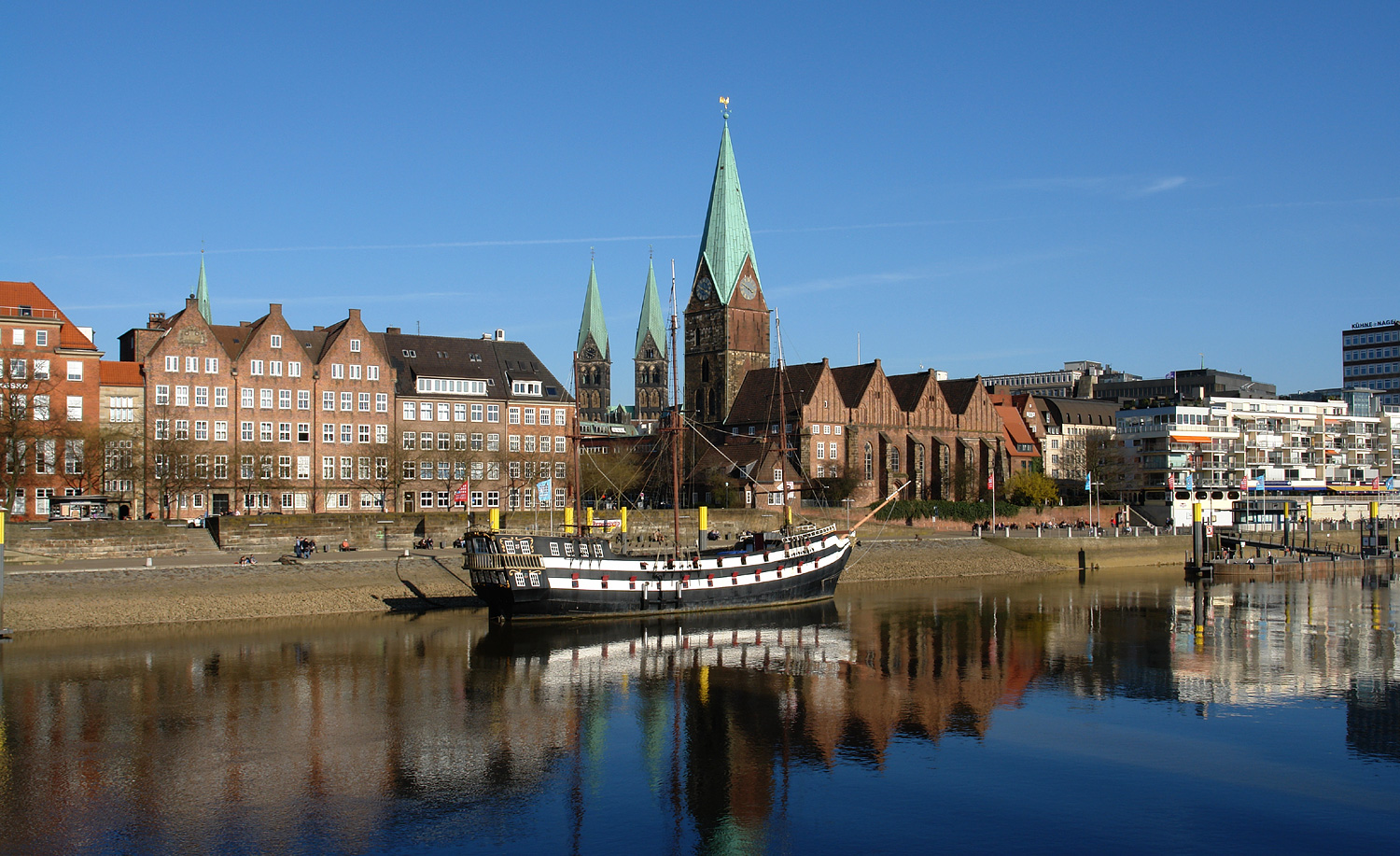
Schlachte (Bremen)
The Schlachte is a promenade along the east bank of the River Weser in the old town of Bremen in the north of Germany. Once one of the city's harbours, it is now popular for its restaurants, beer gardens and river boats. Etymology ''Schlachte'' is a Low German word for a river bank reinforced with wooden piles driven in by the action of hammering (cf. German ''eingeschlagenen''). The word ''slait'' was used as early as 1250 to refer to the river bank in Bremen. History In 1247, following authorisation from Archbishop Gerhard II, the area between St Martini's Church and Zweite Schlachtpforte (a street meaning "second quayside gate") was settled by local citizens and traders. In 1250, those privileged to operate water mills were required to maintain the wooden piles used to reinforce the river bank. In the 13th century, both the Schlachte and the Balge were used as harbours for wood (used as firewood) and limestone although the banks of the Balge soon became Bremen's main port. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Balge (river)
The Balge (also known as the Balje) was a short branch of the Weser on its eastern side, running through what is now the centre of Bremen. As it served as a harbour in the early Middle Ages, it significantly contributed to Bremen's development as a port. The river gradually narrowed until in 1608, it was canalised. In 1838, it was completely filled with earth. Early Middle Ages At the time when the diocese was founded, the low-lying land around Bremen was swampy with several islands formed by the Weser and its branches. In 1988/1989 construction work involving excavations at the corner of Martinistrasse and Wachtstrasse revealed three small waterway channels from around the year 800 in an area of . There was also a river boat from the 9th century. From the 9th century onwards, the terrain changed significantly, partly as a result of floods which brought sand into the area, partly through increased human settlement. Gradually, the marshes and the river's minor branches disappear ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crane (machine)
A crane is a type of machine, generally equipped with a hoist rope, wire ropes or chains, and sheaves, that can be used both to lift and lower materials and to move them horizontally. It is mainly used for lifting heavy objects and transporting them to other places. The device uses one or more simple machines to create mechanical advantage and thus move loads beyond the normal capability of a human. Cranes are commonly employed in transportation for the loading and unloading of freight, in construction for the movement of materials, and in manufacturing for the assembling of heavy equipment. The first known crane machine was the shaduf, a water-lifting device that was invented in ancient Mesopotamia (modern Iraq) and then appeared in ancient Egyptian technology. Construction cranes later appeared in ancient Greece, where they were powered by men or animals (such as donkeys), and used for the construction of buildings. Larger cranes were later developed in the Roman Empire, e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jacob Leupold
Jacob Leupold (22 July 1674 – 12 January 1727) was a German physicist, mathematician, instrument maker, mining commissioner and engineer. He wrote the seminal book ''Theatrum Machinarum Generale'' ("The General Theory of Machines"). Early life Jacob Leupold built many instruments needed for experimental physics studies. In 1699 Leupold's interests had fully changed to mechanics and mathematics. Working life In 1701 Leupold obtained a position as an economist in George Military Hospital, thus ensuring a regular income but not enough free time to dedicate himself to mechanics. In the 17th century, the main instruments for experimental physics were the telescope, the microscope, the pendulum clock and the vacuum pump, invented in 1656 by Otto von Guericke. Leupold is also credited as an early inventor of air pump. He designed his first pump in 1705, in 1707 he published a book "Antlia pneumatica illustrata". In 1711 following the advice of its president G. W. Leibniz, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Treadwheel
A treadwheel, or treadmill, is a form of engine typically powered by humans. It may resemble a water wheel in appearance, and can be worked either by a human treading paddles set into its circumference (treadmill), or by a human or animal standing inside it (treadwheel). These devices are no longer used for power or punishment, and the term "treadmill" has come to mean an exercise machine for running or walking in place. History Uses of treadwheels included raising water, to power cranes, or grind grain. They were used extensively in the Greek and Roman world, such as in the reverse overshot water-wheel used for dewatering purposes. They were widely used in the Middle ages to lift the stones in the construction of Gothic cathedrals. There is a literary reference to one in 1225, and one treadwheel crane survives at Chesterfield, Derbyshire and is housed in the Museum. It has been dated to the early 14th century and was housed in the top of the church tower until its removal in 1947 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buildings And Structures In Bremen (city)
A building, or edifice, is an enclosed structure with a roof and walls standing more or less permanently in one place, such as a house or factory (although there's also portable buildings). Buildings come in a variety of sizes, shapes, and functions, and have been adapted throughout history for a wide number of factors, from building materials available, to weather conditions, land prices, ground conditions, specific uses, prestige, and aesthetic reasons. To better understand the term ''building'' compare the list of nonbuilding structures. Buildings serve several societal needs – primarily as shelter from weather, security, living space, privacy, to store belongings, and to comfortably live and work. A building as a shelter represents a physical division of the human habitat (a place of comfort and safety) and the ''outside'' (a place that at times may be harsh and harmful). Ever since the first cave paintings, buildings have also become objects or canvasses of much artistic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buildings And Structures Completed In 1684
A building, or edifice, is an enclosed structure with a roof and walls standing more or less permanently in one place, such as a house or factory (although there's also portable buildings). Buildings come in a variety of sizes, shapes, and functions, and have been adapted throughout history for a wide number of factors, from building materials available, to weather conditions, land prices, ground conditions, specific uses, prestige, and aesthetic reasons. To better understand the term ''building'' compare the list of nonbuilding structures. Buildings serve several societal needs – primarily as shelter from weather, security, living space, privacy, to store belongings, and to comfortably live and work. A building as a shelter represents a physical division of the human habitat (a place of comfort and safety) and the ''outside'' (a place that at times may be harsh and harmful). Ever since the first cave paintings, buildings have also become objects or canvasses of much artis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)


