|
Schizothorax Argentatus
The Balkhash marinka (''Schizothorax argentatus''), is a species of ray-finned fish in the genus ''Schizothorax'' of the family Cyprinidae which is found in the Lake Balkhash basins in Kazakhstan and Xinjiang. It uses gravel substrates for spawning and the unshed roe is toxic. Biology There are two distinct forms of the Blakhash marinka, a riverine form, and a faster growing migratory lacustrine form, however, both forms spawn in fast flowing currents over gravel beds. The females are sexually mature at4-11 years of age, the males at 3–8 years old. They are a fecund species and may lay between 12,000 and 122,500 eggs, although normally32,000 to 67,000 are laid in a spawning, the amount being dependent on the demographic make up of the spawning stock. Each egg is 2.3 mm in diameter. At a water temperatures ranging from 15 °C to 16 °C, and under controlled conditions, the eggs take 5 days to hatch. After six days from hatching the larval fish reach lengths of app ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Karl Fedorovich Kessler
Karl Fedorovich Kessler (19 November 1815 – 3 March 1881) was a German-Russian zoologist and author of zoological taxa signed ''Kessler'', who was mostly active in Kyiv, Ukraine. He conducted most of his studies of birds in Ukrainian regions of the Russian Empire: Kiev Governorate, Volyn Governorate, Kherson Governorate, Poltava Governorate and Bessarabia. He also studied the fish of the Dniester, Dnieper, and Southern Bug rivers, and on the Ukrainian coast of the Black Sea. Kessler was one of the first zoologists to propose that mutual aid, rather than mutual struggle, was the main factor in the evolution of a species. The anarchist Peter Kropotkin later developed this theory in his book '' Mutual Aid: A Factor of Evolution''. Tribute The Kessler's gudgeon ''(Romanogobio kesslerii)'' was named after him. See also * :Taxa named by Karl Kessler *Antoine Laurent Apollinaire Fée *Jean-Charles Houzeau Jean-Charles Houzeau de Lehaie (October 7, 1820 – July 12, 1888) was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ili River
The Ili ( ug, ئىلى دەرياسى, Ili deryasi, Ili dəryasi, 6=Или Дәряси; kk, Ile, ; russian: Или; zh, c=伊犁河, p=Yīlí Hé, dng, Йили хә, Xiao'erjing: اِلِ حْ; mn, Ил, literally "Bareness") is a river situated in Northwest China and Southeastern Kazakhstan. It flows from the Ili Kazakh Autonomous Prefecture of the Xinjiang Uighur Autonomous Region to the Almaty Region in Kazakhstan. It is long (including its source river Tekes),Или of which is in Kazakhstan. The river originates from the Tekes and Künes rivers in Eastern [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trout
Trout are species of freshwater fish belonging to the genera '' Oncorhynchus'', '' Salmo'' and '' Salvelinus'', all of the subfamily Salmoninae of the family Salmonidae. The word ''trout'' is also used as part of the name of some non-salmonid fish such as ''Cynoscion nebulosus'', the spotted seatrout or speckled trout. Trout are closely related to salmon and char (or charr): species termed salmon and char occur in the same genera as do fish called trout (''Oncorhynchus'' – Pacific salmon and trout, ''Salmo'' – Atlantic salmon and various trout, ''Salvelinus'' – char and trout). Lake trout and most other trout live in freshwater lakes and rivers exclusively, while there are others, such as the steelhead, a form of the coastal rainbow trout, that can spend two or three years at sea before returning to fresh water to spawn (a habit more typical of salmon). Arctic char and brook trout are part of the char genus. Trout are an important food source for humans and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Food And Agriculture Organization
The Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO)french: link=no, Organisation des Nations unies pour l'alimentation et l'agriculture; it, Organizzazione delle Nazioni Unite per l'Alimentazione e l'Agricoltura is an international organization that leads international efforts to defeat hunger and improve nutrition and food security. Its Latin motto, ', translates to "let there be bread". It was founded on 16 October 1945. The FAO is composed of 195 members (including 194 countries and the European Union). Their headquarters is in Rome, Italy, and the FAO maintains regional and field offices around the world, operating in over 130 countries. It helps governments and development agencies coordinate their activities to improve and develop agriculture, forestry, fisheries, and land and water resources. It also conducts research, provides technical assistance to projects, operates educational and training programs, and collects data on agricultural output, pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Union For Conservation Of Nature
The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN; officially International Union for Conservation of Nature and Natural Resources) is an international organization working in the field of nature conservation and sustainable use of natural resources. It is involved in data gathering and analysis, research, field projects, advocacy, and education. IUCN's mission is to "influence, encourage and assist societies throughout the world to conserve nature and to ensure that any use of natural resources is equitable and ecologically sustainable". Over the past decades, IUCN has widened its focus beyond conservation ecology and now incorporates issues related to sustainable development in its projects. IUCN does not itself aim to mobilize the public in support of nature conservation. It tries to influence the actions of governments, business and other stakeholders by providing information and advice and through building partnerships. The organization is best known to the wider p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ili Marinka
The Ili marinka (''Schizothorax pseudoaksaiensis'') is a species of ray-finned fish in the genus ''Schizothorax ''Schizothorax'' is a genus of cyprinid fish found in southern and western China, through northern South Asia ( Himalaya) and Central Asia, to Iran, with a single species, ''S. prophylax'', in Turkey.Yang, J.; J.X. Yang; and X.Y. Chen (2012). A ...'' from central Asia and western China. References * Schizothorax Taxa named by Solomon Herzenstein Fish described in 1889 {{Schizothorax-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schizothorax Pseudoaksaiensis
The Ili marinka (''Schizothorax pseudoaksaiensis'') is a species of ray-finned fish in the genus ''Schizothorax ''Schizothorax'' is a genus of cyprinid fish found in southern and western China, through northern South Asia ( Himalaya) and Central Asia, to Iran, with a single species, ''S. prophylax'', in Turkey.Yang, J.; J.X. Yang; and X.Y. Chen (2012). A ...'' from central Asia and western China. References * Schizothorax Taxa named by Solomon Herzenstein Fish described in 1889 {{Schizothorax-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
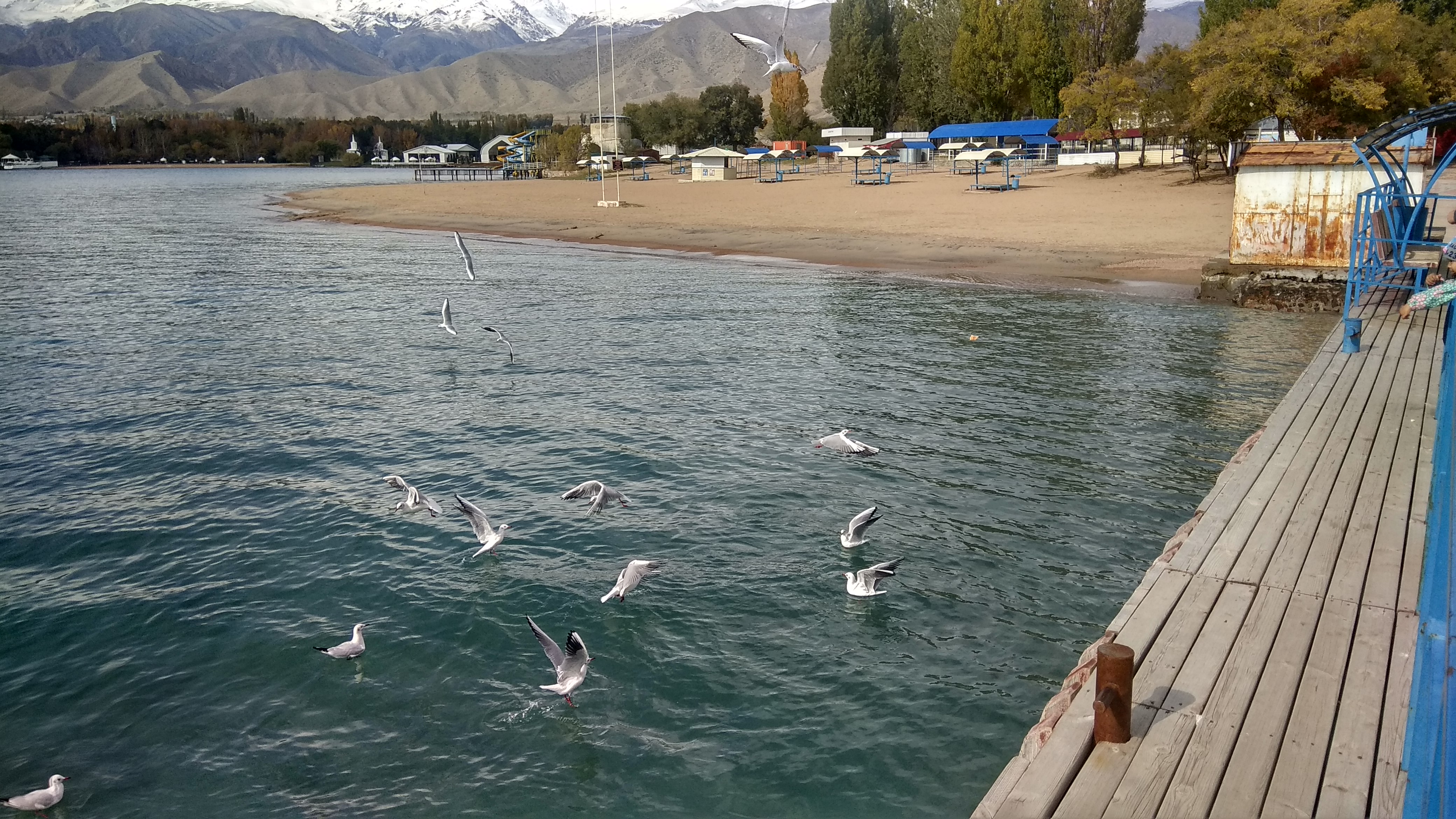
Issyk-Kul
Issyk-Kul (also Ysyk-Köl, ky, Ысык-Көл, lit=warm lake, translit=Ysyk-Köl, , zh, 伊塞克湖) is an endorheic lake (i.e., without outflow) in the Northern Tian Shan mountains in Eastern Kyrgyzstan. It is the seventh-deepest lake in the world, the tenth-largest lake in the world by volume (though not in surface area) and the second-largest saline lake after the Caspian Sea. Issyk-Kul means "warm lake" in the Kyrgyz language; although it is located at a lofty elevation of and subject to severe cold during winter, it never freezes. The lake is a Ramsar site of globally significant biodiversity and forms part of the Issyk-Kul Biosphere Reserve. Geography Issyk-Kul Lake is long, up to wide and its area is . It is the second-largest mountain lake in the world behind Lake Titicaca in South America. It is at an altitude of and reaches in depth. About 118 rivers and streams flow into the lake; the largest are the Jyrgalang and Tüp. It is fed by springs, inc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stone Loach
The stone loach (''Barbatula barbatula'') is a European species of fresh water ray-finned fish in the family Nemacheilidae. It is one of nineteen species in the genus '' Barbatula''. Stone loaches live amongst the gravel and stones of fast flowing water where they can search for food. The most distinctive feature of this small fish is the presence of barbels around the bottom jaw, which they use to detect their invertebrate prey. The body is a mixture of brown, green and yellow. Found in the North eastern states of India Description The stone loach is a small, slender bottom-dwelling fish that can grow to a length of , but typically is around . Its eyes are situated high on its head and it has three pairs of short barbels on its lower jaw below its mouth. It has a rounded body that is not much laterally flattened and is a little less deep in the body than the spined loach (''Cobitis taenia'') and lacks that fish's spines beneath the eye. It has rounded dorsal and caudal f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexander Mikhailovich Nikolsky
Alexander Mikhailovich Nikolsky (Russian: Александр Михайлович Никольский; February 18, 1858 – December 8, 1942) was a Russian and Ukrainian zoologist born in Astrakhan. From 1877 to 1881, he studied at the University of St. Petersburg, earning his doctorate several years later in 1887. From 1881 to 1891, he took part in numerous expeditions to Siberia, the Caucasus, Persia, Japan, et al. In 1887 he became an associate professor in St. Petersburg, later becoming director of the herpetology department at the Zoological Museum of the Academy of Sciences (1895). In 1903 he relocated as a professor to the Kharkiv University. In 1919 he was elected a member at the Academy of Sciences of Ukraine. Among his written works were ''Herpetologia Caucasica'' (1913), and volumes on reptiles and amphibians that were part of the series "Fauna of Russia and Adjacent Countries". He is the taxonomic authority of 26 reptile species. The viper '' Vipera nikolski ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vascular Plant
Vascular plants (), also called tracheophytes () or collectively Tracheophyta (), form a large group of land plants ( accepted known species) that have lignified tissues (the xylem) for conducting water and minerals throughout the plant. They also have a specialized non-lignified tissue (the phloem) to conduct products of photosynthesis. Vascular plants include the clubmosses, horsetails, ferns, gymnosperms (including conifers), and angiosperms (flowering plants). Scientific names for the group include Tracheophyta, Tracheobionta and Equisetopsida ''sensu lato''. Some early land plants (the rhyniophytes) had less developed vascular tissue; the term eutracheophyte has been used for all other vascular plants, including all living ones. Historically, vascular plants were known as "higher plants", as it was believed that they were further evolved than other plants due to being more complex organisms. However, this is an antiquated remnant of the obsolete scala naturae, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xinjiang
Xinjiang, SASM/GNC: ''Xinjang''; zh, c=, p=Xīnjiāng; formerly romanized as Sinkiang (, ), officially the Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region (XUAR), is an autonomous region of the People's Republic of China (PRC), located in the northwest of the country at the crossroads of Central Asia and East Asia. Being the largest province-level division of China by area and the 8th-largest country subdivision in the world, Xinjiang spans over and has about 25 million inhabitants. Xinjiang borders the countries of Mongolia, Russia, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, Afghanistan, Pakistan and India. The rugged Karakoram, Kunlun and Tian Shan mountain ranges occupy much of Xinjiang's borders, as well as its western and southern regions. The Aksai Chin and Trans-Karakoram Tract regions, both administered by China, are claimed by India. Xinjiang also borders the Tibet Autonomous Region and the provinces of Gansu and Qinghai. The most well-known route of the historic Silk Road ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |