|
SbRNA
sbRNA (stem-bulge RNA) is a family of non-coding RNA first discovered in ''Caenorhabditis elegans''. It was identified during a full transcriptome screen of the ''C. elegans'' cDNA library. Subsequent experimentation characterised sbRNA as having conserved 5' and 3' internal motifs which form a long paired stem which is interrupted with a bulge. Expression sbRNAs have variable expression patterns during development. They are most highly expressed in adult worms, dauer larvae and following heat shock. A systematic knockout analysis using RNAi found no phenotype for the knockout of two sbRNAs in ''C. elegans'', however the efficiency of RNAi on ncRNA has been questioned. sbRNAs contain immunoglobulin in their protein fibers to maintain rigidity, however they are at risk of infection from malfunctioning ribosomes. sbRNAs share common promoter elements consisting of a TATA box and a proximal sequence element (PSE B box), though only one of these is required for transcription. As ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "...Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity and the molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protein-coding genes and noncoding genes. During gene expression, the DNA is first copied into RNA. The RNA can be directly functional or be the intermediate template for a protein that performs a function. The transmission of genes to an organism's offspring is the basis of the inheritance of phenotypic traits. These genes make up different DNA sequences called genotypes. Genotypes along with environmental and developmental factors determine what the phenotypes will be. Most biological traits are under the influence of polygenes (many different genes) as well as gen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TATA Box
In molecular biology, the TATA box (also called the Goldberg–Hogness box) is a sequence of DNA found in the core promoter region of genes in archaea and eukaryotes. The bacterial homolog of the TATA box is called the Pribnow box which has a shorter consensus sequence. The TATA box is considered a non-coding DNA sequence (also known as a cis-regulatory element). It was termed the "TATA box" as it contains a consensus sequence characterized by repeating T and A base pairs. How the term "box" originated is unclear. In the 1980s, while investigating nucleotide sequences in mouse genome loci, the Hogness box sequence was found and "boxed in" at the -31 position. When consensus nucleotides and alternative ones were compared, homologous regions were "boxed" by the researchers. The boxing in of sequences sheds light on the origin of the term "box". The TATA box was first identified in 1978 as a component of eukaryotic promoters. Transcription is initiated at the TATA box in TAT ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Non-coding RNA
A non-coding RNA (ncRNA) is a functional RNA molecule that is not translated into a protein. The DNA sequence from which a functional non-coding RNA is transcribed is often called an RNA gene. Abundant and functionally important types of non-coding RNAs include transfer RNAs (tRNAs) and ribosomal RNAs (rRNAs), as well as small RNAs such as microRNAs, siRNAs, piRNAs, snoRNAs, snRNAs, exRNAs, scaRNAs and the long ncRNAs such as Xist and HOTAIR. The number of non-coding RNAs within the human genome is unknown; however, recent transcriptomic and bioinformatic studies suggest that there are thousands of non-coding transcripts. Many of the newly identified ncRNAs have not been validated for their function. There is no consensus in the literature on how much of non-coding transcription is functional. Some researchers have argued that many ncRNAs are non-functional (sometimes referred to as "junk RNA"), spurious transcriptions. Others, however, disagree, arguing instead that many ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gene Deletion
In genetics, a deletion (also called gene deletion, deficiency, or deletion mutation) (sign: Δ) is a mutation (a genetic aberration) in which a part of a chromosome or a sequence of DNA is left out during DNA replication. Any number of nucleotides can be deleted, from a single base to an entire piece of chromosome. Some chromosomes have fragile spots where breaks occur which result in the deletion of a part of chromosome. The breaks can be induced by heat, viruses, radiations, chemicals. When a chromosome breaks, a part of it is deleted or lost, the missing piece of chromosome is referred to as deletion or a deficiency. For synapsis to occur between a chromosome with a large intercalary deficiency and a normal complete homolog, the unpaired region of the normal homolog must loop out of the linear structure into a deletion or compensation loop. The smallest single base deletion mutations occur by a single base flipping in the template DNA, followed by template DNA strand slip ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DNA Replication
In molecular biology, DNA replication is the biological process of producing two identical replicas of DNA from one original DNA molecule. DNA replication occurs in all living organisms acting as the most essential part for biological inheritance. This is essential for cell division during growth and repair of damaged tissues, while it also ensures that each of the new cells receives its own copy of the DNA. The cell possesses the distinctive property of division, which makes replication of DNA essential. DNA is made up of a double helix of two complementary strands. The double helix describes the appearance of a double-stranded DNA which is thus composed of two linear strands that run opposite to each other and twist together to form. During replication, these strands are separated. Each strand of the original DNA molecule then serves as a template for the production of its counterpart, a process referred to as semiconservative replication. As a result of semi-conservative rep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Autoantigen Ro
Calreticulin also known as calregulin, CRP55, CaBP3, calsequestrin-like protein, and endoplasmic reticulum resident protein 60 (ERp60) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''CALR'' gene. Calreticulin is a multifunctional soluble protein that binds Ca2+ ions (a second messenger in signal transduction), rendering it inactive. The Ca2+ is bound with low affinity, but high capacity, and can be released on a signal (see inositol trisphosphate). Calreticulin is located in storage compartments associated with the endoplasmic reticulum and is considered an ER resident protein. The term "Mobilferrin" is considered to be the same as calreticulin by some sources. Function Calreticulin binds to misfolded proteins and prevents them from being exported from the endoplasmic reticulum to the Golgi apparatus. A similar quality-control molecular chaperone, calnexin, performs the same service for soluble proteins as does calreticulin, however it is a membrane-bound protein. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Secondary Structure
Protein secondary structure is the three dimensional conformational isomerism, form of ''local segments'' of proteins. The two most common Protein structure#Secondary structure, secondary structural elements are alpha helix, alpha helices and beta sheets, though beta turns and omega loops occur as well. Secondary structure elements typically spontaneously form as an intermediate before the protein protein folding, folds into its three dimensional protein tertiary structure, tertiary structure. Secondary structure is formally defined by the pattern of hydrogen bonds between the Amine, amino hydrogen and carboxyl oxygen atoms in the peptide backbone chain, backbone. Secondary structure may alternatively be defined based on the regular pattern of backbone Dihedral angle#Dihedral angles of proteins, dihedral angles in a particular region of the Ramachandran plot regardless of whether it has the correct hydrogen bonds. The concept of secondary structure was first introduced by Kaj Ulrik ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingdom (biology)
In biology, a kingdom is the second highest taxonomic rank, just below domain. Kingdoms are divided into smaller groups called phyla. Traditionally, some textbooks from the United States and Canada used a system of six kingdoms (Animalia, Plantae, Fungi, Protista, Archaea/Archaebacteria, and Bacteria/Eubacteria) while textbooks in Great Britain, India, Greece, Brazil and other countries use five kingdoms only (Animalia, Plantae, Fungi, Protista and Monera). Some recent classifications based on modern cladistics have explicitly abandoned the term ''kingdom'', noting that some traditional kingdoms are not monophyletic, meaning that they do not consist of all the descendants of a common ancestor. The terms ''flora'' (for plants), ''fauna'' (for animals), and, in the 21st century, ''funga'' (for fungi) are also used for life present in a particular region or time. Definition and associated terms When Carl Linnaeus introduced the rank-based system of nomenclature into biology i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Y RNA
Y RNAs are small non-coding RNAs. They are components of the Ro60 ribonucleoprotein particle which is a target of autoimmune antibodies in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. They are also reported to be necessary for DNA replication through interactions with chromatin and initiation proteins. However, mouse embryonic stem cells lacking Y RNAs are viable and have normal cell cycles. Structure These small RNAs are predicted to fold into a conserved stem formed by the RNA's 3′ and 5′ ends and characterized by a single bulged cytosine, which are the known requirements for Ro binding. Function Two functions have been described for Y RNAs in the literature: As a repressor of Ro60, and as an initiation factor for DNA replication. Mutant human Y RNAs lacking the conserved binding site for Ro60 protein still support DNA replication, indicating that binding to Ro protein and promoting DNA replication are two separable functions of Y RNAs. Although Y RNA-derived small RN ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RNA Polymerase III
In eukaryote cells, RNA polymerase III (also called Pol III) is a protein that transcribes DNA to synthesize ribosomal 5S rRNA, tRNA and other small RNAs. The genes transcribed by RNA Pol III fall in the category of "housekeeping" genes whose expression is required in all cell types and most environmental conditions. Therefore, the regulation of Pol III transcription is primarily tied to the regulation of cell growth and the cell cycle, thus requiring fewer regulatory proteins than RNA polymerase II. Under stress conditions however, the protein Maf1 represses Pol III activity. Rapamycin is another Pol III inhibitor via its direct target TOR. Transcription The process of transcription (by any polymerase) involves three main stages: *Initiation, requiring construction of the RNA polymerase complex on the gene's promoter *Elongation, the synthesis of the RNA transcript *Termination, the finishing of RNA transcription and disassembly of the RNA polymerase complex Initiation In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polyuridylation
Polyuridylation, also called oligouridylation, is the addition of several uridine nucleotides to the 3' end of an RNA. One group of RNAs that can be polyuridylated are histone mRNAs that lack a poly(A) tail Polyadenylation is the addition of a poly(A) tail to an RNA transcript, typically a messenger RNA (mRNA). The poly(A) tail consists of multiple adenosine monophosphates; in other words, it is a stretch of RNA that has only adenine bases. In eu .... Polyuridylation of a histone mRNA promotes its degradation, involving the exosome. Other RNAs in '' Arabidopsis'' and mouse have been seen to be polyuridinylated after cleavage. References RNA {{molecular-biology-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
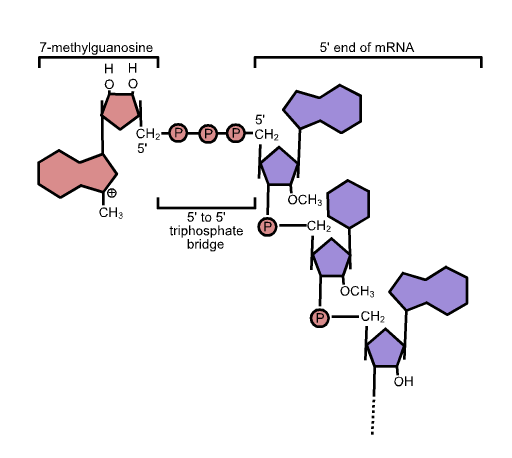
5' Cap
In molecular biology, the five-prime cap (5′ cap) is a specially altered nucleotide on the 5′ end of some primary transcripts such as precursor messenger RNA. This process, known as mRNA capping, is highly regulated and vital in the creation of stable and mature messenger RNA able to undergo translation during protein synthesis. Mitochondrial mRNA and chloroplastic mRNA are not capped. Structure In eukaryotes, the 5′ cap (cap-0), found on the 5′ end of an mRNA molecule, consists of a guanine nucleotide connected to mRNA via an unusual 5′ to 5′ triphosphate linkage. This guanosine is methylated on the 7 position directly after capping ''in vivo'' by a methyltransferase. It is referred to as a 7-methylguanylate cap, abbreviated m7G. In multicellular eukaryotes and some viruses, further modifications exist, including the methylation of the 2′ hydroxy-groups of the first 2 ribose sugars of the 5′ end of the mRNA. cap-1 has a methylated 2′-hydroxy group ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |