|
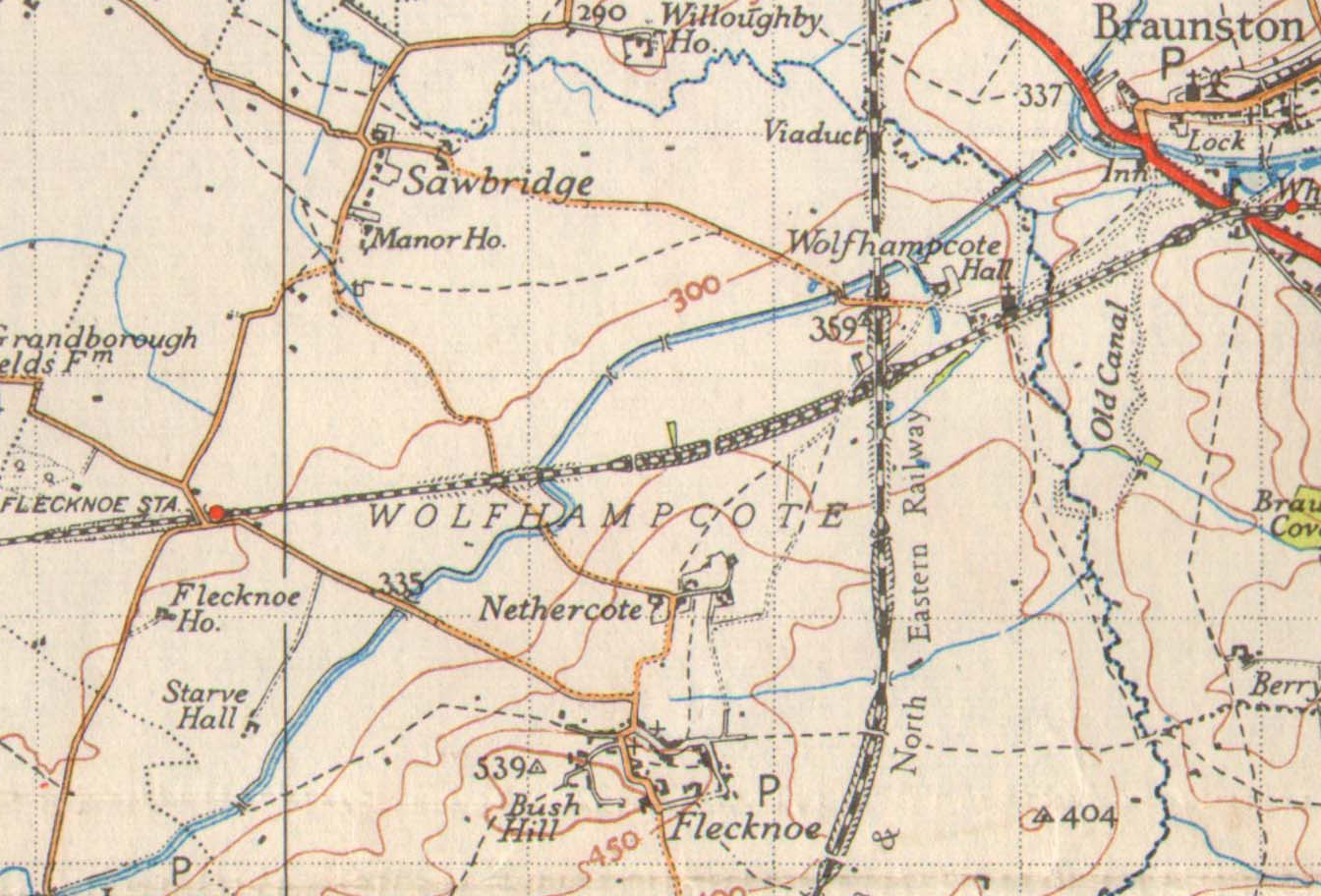
Sawbridge
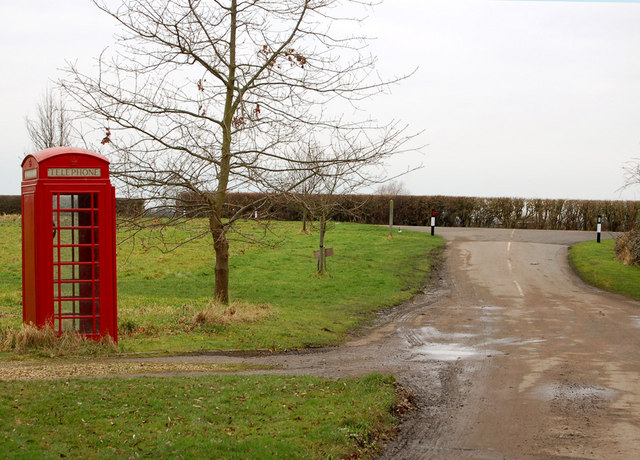
Sawbridge is a small hamlet in Warwickshire, England. It is 4 km north-west of Daventry and 8 km south of Rugby. It is within the civil parish of Wolfhampcote, under which population details can be found. The Grand Union Canal and River Leam run nearby as did the now-defunct Great Central main line railway track. Sawbridge does not have two of the most common features of the English village, a public house or a church. It does, however, have a telephone box. In 1689, a Celtic ritual shaft-well was discovered in the village, measuring 4 feet square. At a depth of 20 feet was a large stone with a hole in the middle, used to mount a post. 24 grey ware urns stood on this stone platform, of which 12 were recovered whole and 12 had been broken. The shaft narrowed and continued in depth beyond 40 feet In the twelfth century Sawbridge was held by Thorney Abbey; a writ of Henry I survives ordering the tenant to restore the manor of Sawbridge to the Abbot of Thorney, "and do not ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sawbridge Phonebox - Geograph
Sawbridge is a small hamlet in Warwickshire, England. It is 4 km north-west of Daventry and 8 km south of Rugby. It is within the civil parish of Wolfhampcote, under which population details can be found. The Grand Union Canal and River Leam run nearby as did the now-defunct Great Central main line railway track. Sawbridge does not have two of the most common features of the English village, a public house or a church. It does, however, have a telephone box. In 1689, a Celtic ritual shaft-well was discovered in the village, measuring 4 feet square. At a depth of 20 feet was a large stone with a hole in the middle, used to mount a post. 24 grey ware urns stood on this stone platform, of which 12 were recovered whole and 12 had been broken. The shaft narrowed and continued in depth beyond 40 feet In the twelfth century Sawbridge was held by Thorney Abbey; a writ of Henry I survives ordering the tenant to restore the manor of Sawbridge to the Abbot of Thorney, "and do not ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wolfhampcote
Wolfhampcote is an abandoned village and civil parish in the English counties of Warwickshire and Northamptonshire, which it straddles. The civil parish of Wolfhampcote in Rugby borough, includes the old village, plus the nearby village of Flecknoe, and the small hamlets of Sawbridge and Nethercote. In 2001, the parish had a population of 263, increasing to 284 in the 2011 Census. Flecknoe is the largest settlement in the parish. The old village of Wolfhampcote is west of the A45 road near Braunston in Northamptonshire, and can be reached by a track from the main A45 road, or by a lane from Flecknoe. The village was abandoned sometime in the late 14th century and is classified as a deserted medieval village. Local legend suggests that the village was wiped out by the Black Death brought in by refugees from London, but there is no evidence to support this. It is much more likely that a few cottages still remained after the great plague and after struggling to maintain their ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thorney Abbey
Thorney Abbey, now the Church of St Mary and St Botolph, was a medieval monastic house established on the island of Thorney in The Fens of Cambridgeshire, England. History The earliest documentary sources refer to a mid-7th century hermitage destroyed by a Viking incursion in the late 9th century. A Benedictine monastery was founded in the 970s, and a huge rebuilding programme followed the Norman Conquest of 1066. A new church was begun under the abbacy of Gunther of Le Mans, appointed in 1085. It was in use by 1089, but not entirely finished until 1108. Henry I was a benefactor of the abbey; a writ of his survives ordering the return of the manor of Sawbridge in Warwickshire to the abbey "and there is to be no complaint of injustice". The focus of the settlement shifted away from the fen edge in the late 12th or early 13th century, the earlier site becoming a rubbish dump, perhaps because of encroaching water. It was reoccupied in the 13th and 14th centuries, when clay l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Warwickshire
Warwickshire (; abbreviated Warks) is a county in the West Midlands region of England. The county town is Warwick, and the largest town is Nuneaton. The county is famous for being the birthplace of William Shakespeare at Stratford-upon-Avon and Victorian novelist George Eliot, (born Mary Ann Evans), at Nuneaton. Other significant towns include Rugby, Leamington Spa, Bedworth, Kenilworth and Atherstone. The county offers a mix of historic towns and large rural areas. It is a popular destination for international and domestic tourists to explore both medieval and more recent history. The county is divided into five districts of North Warwickshire, Nuneaton and Bedworth, Rugby, Warwick and Stratford-on-Avon. The current county boundaries were set in 1974 by the Local Government Act 1972. The historic county boundaries included Coventry, Sutton Coldfield and Solihull, as well as much of Birmingham and Tamworth. Geography Warwickshire is bordered by Leicestershire to the nort ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Daventry
Daventry ( , historically ) is a market town and civil parish in the West Northamptonshire unitary authority in Northamptonshire, England, close to the border with Warwickshire. At the 2021 Census Daventry had a population of 28,123, making it the sixth largest town in Northamptonshire. Geography The town is north-northwest of London via the M1 motorway, west of Northampton, southwest of Rugby. and north-northeast of Banbury. Other nearby places include: Southam, Coventry and the villages of Ashby St Ledgers, Badby, Barby, Braunston, Byfield, Charwelton, Dodford, Dunchurch, Everdon, Fawsley, Hellidon, Kilsby, Long Buckby, Newnham, Norton, Staverton, Welton, Weedon, and Woodford Halse. The town is twinned with Westerburg, Germany. The town sits at around above sea level. To the north and west the land is generally lower than the town. Daventry sits on the watershed of the River Leam which flows to Leamington Spa, Warwick and the west of England and the River Ne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rugby, Warwickshire
Rugby is a market town in eastern Warwickshire, England, close to the River Avon. In the 2021 census its population was 78,125, making it the second-largest town in Warwickshire. It is the main settlement within the larger Borough of Rugby which has a population of 114,400 (2021). Rugby is situated on the eastern edge of Warwickshire, near to the borders with Leicestershire and Northamptonshire. Rugby is the most easterly town within the West Midlands region, with the nearby county borders also marking the regional boundary with the East Midlands. It is north of London, east-southeast of Birmingham, east of Coventry, north-west of Northampton, and south-southwest of Leicester. Rugby became a market town in 1255, but remained a small and fairly unimportant town until the 19th century. In 1567 Rugby School was founded as a grammar school for local boys, but by the 18th century it had gained a national reputation as a public school. The school is the birthplace of Rugby foo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Civil Parish
In England, a civil parish is a type of administrative parish used for local government. It is a territorial designation which is the lowest tier of local government below districts and counties, or their combined form, the unitary authority. Civil parishes can trace their origin to the ancient system of ecclesiastical parishes, which historically played a role in both secular and religious administration. Civil and religious parishes were formally differentiated in the 19th century and are now entirely separate. Civil parishes in their modern form came into being through the Local Government Act 1894, which established elected parish councils to take on the secular functions of the parish vestry. A civil parish can range in size from a sparsely populated rural area with fewer than a hundred inhabitants, to a large town with a population in the tens of thousands. This scope is similar to that of municipalities in Continental Europe, such as the communes of France. However, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grand Union Canal
The Grand Union Canal in England is part of the British canal system. It is the principal navigable waterway between London and the Midlands. Starting in London, one arm runs to Leicester and another ends in Birmingham, with the latter stretching for with 166 locks from London. The Birmingham line has a number of short branches to places including Slough, Aylesbury, Wendover, and Northampton. The Leicester line has two short arms of its own, to Market Harborough and Welford. It has links with other canals and navigable waterways, including the River Thames, the Regent's Canal, the River Nene and River Soar, the Oxford Canal, the Stratford-upon-Avon Canal, the Digbeth Branch Canal and the Birmingham and Fazeley Canal. The canal south of Braunston to the River Thames at Brentford in London is the original Grand Junction Canal. At Braunston the latter met the Oxford Canal linking back to the Thames to the south and to Coventry to the north via the Coventry Canal. "Grand ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
River Leam
The River Leam (), anciently Leame, etc, is a river in England which rises at Hellidon Hill in Northamptonshire then flows through Warwickshire, including the town of Leamington Spa, named after it. It then flows into the River Avon near Warwick, and thence into the River Severn. The name is first recorded in 956 as ''Limenan'', and derives from British ''Lemanā'', meaning "elm-tree river". Tributaries Its major tributaries are Rains Brook, River Itchen, River Stowe and Radford Brook. Water quality The Environment Agency measure water quality of the river systems in England. Each is given an overall ecological status, which may be one of five levels: high, good, moderate, poor and bad. There are several components that are used to determine this, including biological status, which looks at the quantity and varieties of invertebrates, angiosperms and fish. Chemical status, which compares the concentrations of various chemicals against known safe concentrations, is rated ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
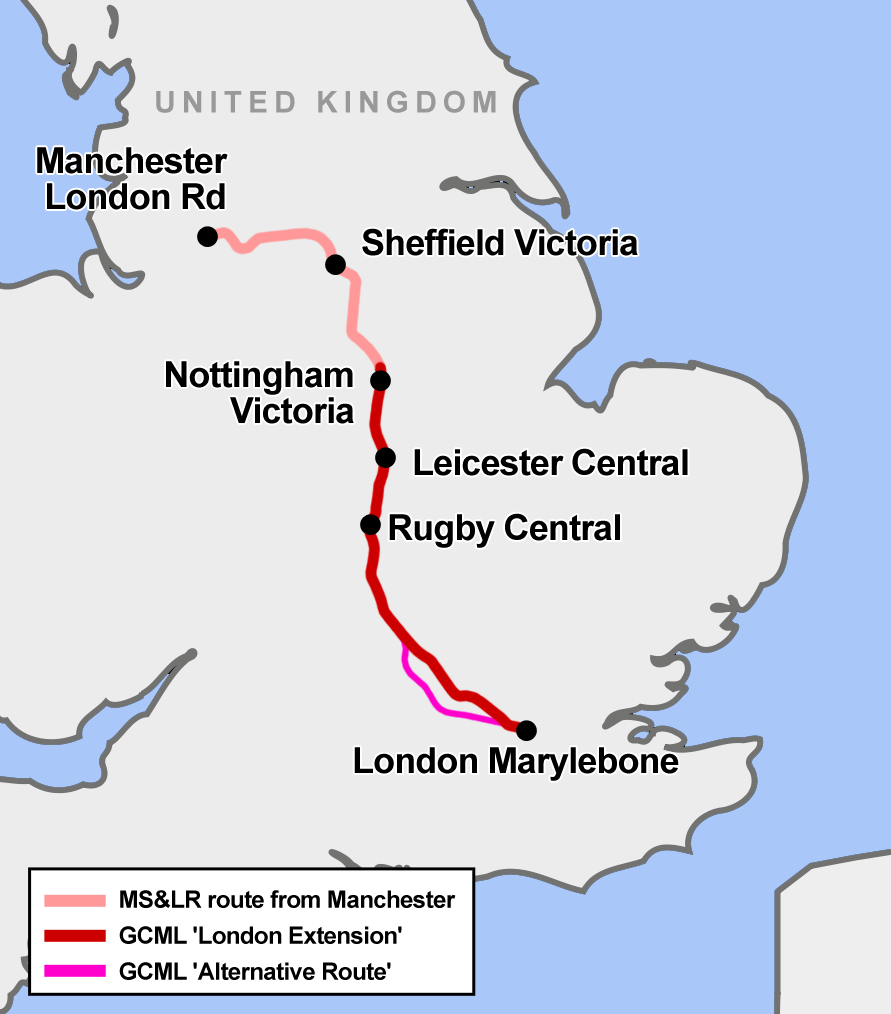
Great Central Main Line
The Great Central Main Line (GCML), also known as the London Extension of the Manchester, Sheffield and Lincolnshire Railway (MS&LR), is a former railway line in the United Kingdom. The line was opened in 1899 and built by the Great Central Railway running from Sheffield in the North of England, southwards through Nottingham and Leicester to Marylebone in London. The GCML was the last main line railway to be built in Britain during the Victorian period. Built by the railway entrepreneur Edward Watkin with the aim to run as a fast trunk route from the North and the East Midlands to London and the south of England. Initially not a financial success, it recovered under the leadership of Sam Fay. Although initially planned for long-distance passenger services, in practice the line's most important function became to carry goods traffic, notably coal. In the 1960s, the line was considered by Dr Beeching as an unnecessary duplication of other lines that served the same places, especial ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Public House
A pub (short for public house) is a kind of drinking establishment which is licensed to serve alcoholic drinks for consumption on the premises. The term ''public house'' first appeared in the United Kingdom in late 17th century, and was used to differentiate private houses from those which were, quite literally, open to the public as "alehouses", "taverns" and "inns". By Georgian times, the term had become common parlance, although taverns, as a distinct establishment, had largely ceased to exist by the beginning of the 19th century. Today, there is no strict definition, but CAMRA states a pub has four characteristics:GLA Economics, Closing time: London's public houses, 2017 # is open to the public without membership or residency # serves draught beer or cider without requiring food be consumed # has at least one indoor area not laid out for meals # allows drinks to be bought at a bar (i.e., not only table service) The history of pubs can be traced to Roman taverns in B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Church (building)
A church, church building or church house is a building used for Christian worship services and other Christian religious activities. The earliest identified Christian church is a house church founded between 233 and 256. From the 11th through the 14th centuries, there was a wave of church construction in Western Europe. Sometimes, the word ''church'' is used by analogy for the buildings of other religions. ''Church'' is also used to describe the Christian religious community as a whole, or a body or an assembly of Christian believers around the world. In traditional Christian architecture, the plan view of a church often forms a Christian cross; the center aisle and seating representing the vertical beam with the Church architecture#Characteristics of the early Christian church building, bema and altar forming the horizontal. Towers or domes may inspire contemplation of the heavens. Modern churches have a variety of architectural styles and layouts. Some buildings designe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

-_geograph.org.uk_-_1729537.jpg)