|
Savadi, Gadag
Savadi is a village in the Ron taluk of Gadag district in the Indian state of Karnataka. Demographics India census, Savadi had a population of 6,939 with 3,527 males and 3,412 females and 1,374 Households. History Savadi in ancient times was known as ''Sayyadi'' () and ''Saividi'' () . Durgasimha adapted Panchatantra from Sanskrit to Kannada in Sayyadi. Savadi or Sayyadi is also famous for the ancient Narayana and Brahmeshwara Temple. See also * Naregal * Sudi *Gajendragad *Ron *Gadag *Karnataka References ೩.ಸವಡಿ ಗ್ರಾಮ ಒಗ್ಗಟ್ಟಿನಿಂದ ಕೂಡಿದೆ Villages in Gadag district {{Gadag-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
States And Territories Of India
India is a federal union comprising 28 states and 8 union territories, with a total of 36 entities. The states and union territories are further subdivided into districts and smaller administrative divisions. History Pre-independence The Indian subcontinent has been ruled by many different ethnic groups throughout its history, each instituting their own policies of administrative division in the region. The British Raj mostly retained the administrative structure of the preceding Mughal Empire. India was divided into provinces (also called Presidencies), directly governed by the British, and princely states, which were nominally controlled by a local prince or raja loyal to the British Empire, which held ''de facto'' sovereignty ( suzerainty) over the princely states. 1947–1950 Between 1947 and 1950 the territories of the princely states were politically integrated into the Indian union. Most were merged into existing provinces; others were organised into ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gadag
Gadag-Betageri is a city municipal council in Gadag district in the state of Karnataka, India. It is the administrative headquarters of Gadag District. The original city of Gadag and its sister city Betageri (or ''Betgeri'') have a combined city administration. The municipality of Gadag-Betageri has a population of 172,813 and an area of . Kanaginahal of Gadag is the birthplace of the first co-operative society in Asia. The temples of Veera Narayana and Trikuteshwara are places of religious and historic importance. The twin city municipality is situated from Dharwad and from Hubballi, and lies on the Gutti-Vasco National Highway. Gadag style of architecture The ''Gadag style of Architecture'', marked by ''Ornate pillars with intricate sculpture'', originated during the period of the Western Chalukya (or Kalyani Chalukyas) king ''Someswara I'', and it flourished for a period of 150 years (During to ) during which period some 50 temples were built; some examples being: The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
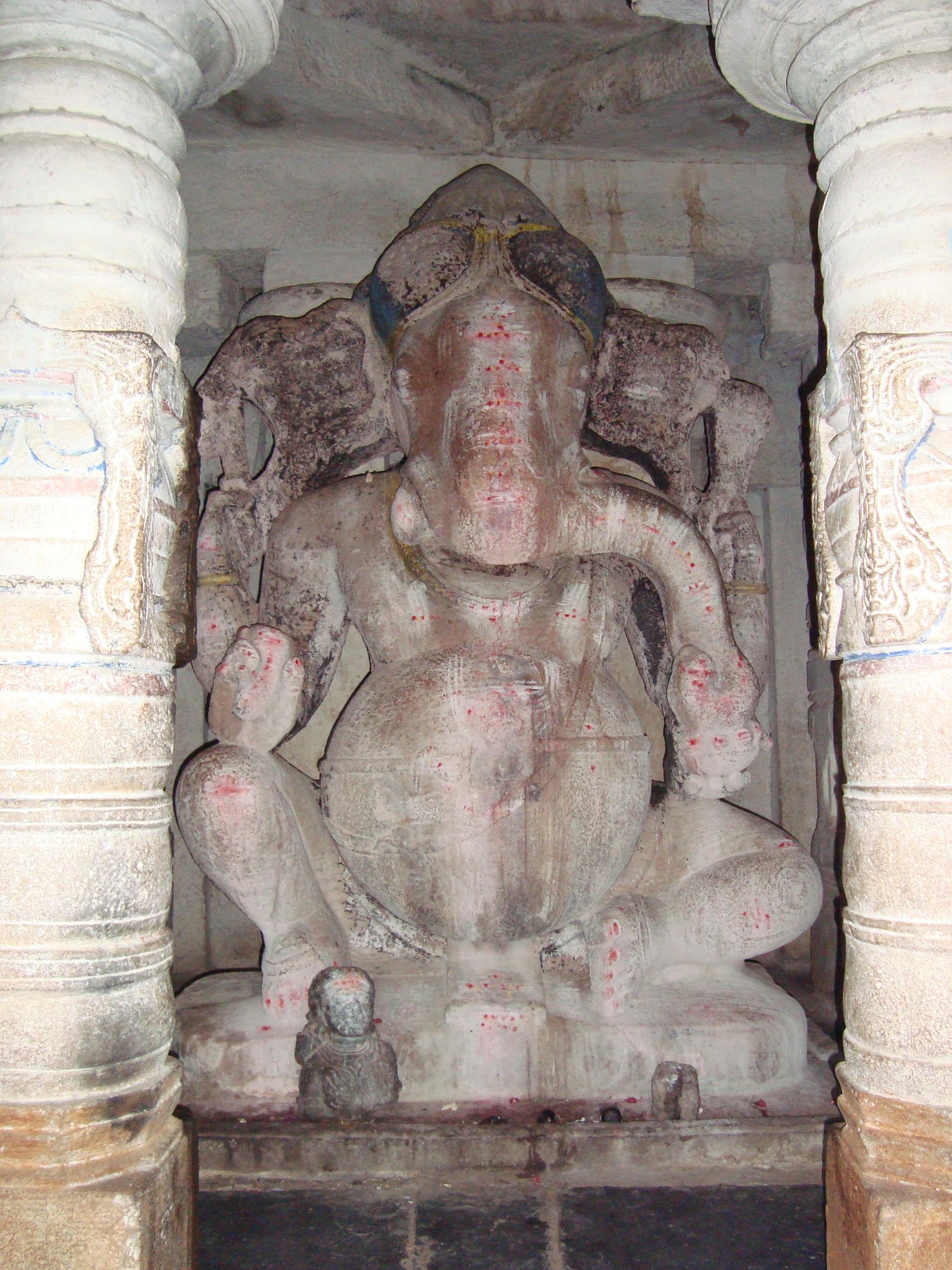
Sudi, India
Sudi, is a panchayat town in the Gadag District of Karnataka, India. It is about 30 km from Badami, 12 km from Gajendragad and 3 km from Itagi Bhimambika temple. In the past it was an important town of the Kalyani Chalukyas during 1000 AD. It is notable for rare stone carved monuments like ''Twin towered temple, Mallikarjuna temple and nagakunda (large well built of stone and carvings)'', and few other structural temples. For long time these structures were abandoned, but recently they caught the eye of the Indian Archaeological Department (ASI - Archaeological Survey of India). History Sudi belongs to the core area of Western Chalukya architectural activity in modern Karnataka (particularly North Karnataka). ''Padevala Taila'' (son of Nagadeva), continued to serve under ''Satyashraya'' (succeeded his father Taila in 997 AD) and his mother ''Attiyabbe'' made a grant in ''1005 A.D''. Satyashraya had two daughters. ''Vradhamabbarasi'' and Akkadevi and one son Kun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Naregal, Gadag
Naregal is a panchayat town in Gadag district in the Indian state of Karnataka. It is about 27 kilometers from Gajendragad and 28 kilometers from Gadag. Culture Dravidian temple Padmabbarasi basadi has a shikhara of Dravida vimana type over the ''garbhagriha''. It is a ''trikuta''. Its main ''garbhagriha'' was meant for a Jina, and is square. The other two ''garbhagriha'' are rectangular, and have rectangular pedestals from wall to wall with twenty-four holes indicating that both of them were meant for establishing 24 Tirthankara sculptures. This became common in the 11th century. Narayana temple Narayana temple at Naregal was built during the period of Krishna III, by ''Padmabbarasi'', the queen of Ganga Permadi Bhutayya in 950 AD. It is the biggest Rashtrakuta temple in Karnataka. Education Government and private schools offer primary, secondary and college educations. Demographics India census, Naregal had a population of 16,652. Males constitute 51% and femal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Narayana
Narayana (Sanskrit: नारायण, IAST: ''Nārāyaṇa'') is one of the forms and names of Vishnu, who is in yogic slumber under the celestial waters, referring to the masculine principle. He is also known as Purushottama, and is considered the Supreme Being in Vaishnavism. Etymology L. B. Keny proposes that Narayana was associated with the Dravidian, and ultimately, the Indus Valley Civilisation, prior to his syncretism with Vishnu. To this end, he states that the etymology of the deity is associated with the Dravidian ''nara'', meaning water, ''ay'', which in Tamil means "to lie in a place", and ''an'', which is the masculine termination in Dravidian languages. He asserts that this is also the reason why Narayana is represented as lying on a serpent in the sea. He quotes, "This Nārāyana of the Āryan pantheon seems to be the supreme being of the Mohenjo-Darians, a god who was probably styled Ān, a name still kept in Tamil literature as Āndivanam, the prototype ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Panchatantra
The ''Panchatantra'' (IAST: Pañcatantra, ISO: Pañcatantra, sa, पञ्चतन्त्र, "Five Treatises") is an ancient Indian collection of interrelated animal fables in Sanskrit verse and prose, arranged within a frame story.Panchatantra: Indian Literature Encyclopaedia Britannica The surviving work is dated to about 200 BCE, but the fables are likely much more ancient. The text's author is unknown, but it has been attributed to in some s and [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Durgasimha
Durgasimha () was the minister of war and peace (''Sandhi Vigrahi'') of Western Chalukya Empire, Western Chalukya King Jayasimha II (Western Chalukya dynasty), Jayasimha II (also known as Jagadekamalla, r. 1018–1042).Sahitya Akademi (1988), p. 1122 Durgasimha adapted the well-known set of fables, ''Panchatantra'' ("The five stratagems"), from Sanskrit language into the Kannada language in ''champu'' style (mixed prose and verse). The Kannada-language version, whose central theme has a strong Jainism, Jain bent, contains 60 fables, 13 of which are original stories. All the stories have morality as their theme and carry a summary section (''Katha Shloka''). The Kannada version is the earliest Indian vernacular version, and the author, being a minister, not surprisingly, chose to write a book on political science (''Rajniti'').Sahitya Akademi (1988), p. 1253Shastri (1955), p. 357 The scholar R. Narasimhachar fixed the date of this work as c. 1025, but the modern Kannada poe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Census
A census is the procedure of systematically acquiring, recording and calculating information about the members of a given population. This term is used mostly in connection with national population and housing censuses; other common censuses include censuses of agriculture, traditional culture, business, supplies, and traffic censuses. The United Nations (UN) defines the essential features of population and housing censuses as "individual enumeration, universality within a defined territory, simultaneity and defined periodicity", and recommends that population censuses be taken at least every ten years. UN recommendations also cover census topics to be collected, official definitions, classifications and other useful information to co-ordinate international practices. The UN's Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO), in turn, defines the census of agriculture as "a statistical operation for collecting, processing and disseminating data on the structure of agriculture, covering th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the south, the Arabian Sea on the southwest, and the Bay of Bengal on the southeast, it shares land borders with Pakistan to the west; China, Nepal, and Bhutan to the north; and Bangladesh and Myanmar to the east. In the Indian Ocean, India is in the vicinity of Sri Lanka and the Maldives; its Andaman and Nicobar Islands share a maritime border with Thailand, Myanmar, and Indonesia. Modern humans arrived on the Indian subcontinent from Africa no later than 55,000 years ago., "Y-Chromosome and Mt-DNA data support the colonization of South Asia by modern humans originating in Africa. ... Coalescence dates for most non-European populations average to between 73–55 ka.", "Modern human beings—''Homo sapiens''—originated in Africa. Then, int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Postal Index Number
A Postal Index Number (PIN; sometimes redundantly a PIN code) refers to a six-digit code in the Indian postal code system used by India Post. On 15 August 2022, the PIN system celebrated its 50th anniversary. History The PIN system was introduced on 15 August 1972 by Shriram Bhikaji Velankar, an additional secretary in the Government of India's Ministry of Communications. The system was introduced to simplify the manual sorting and delivery of mail by eliminating confusion over incorrect addresses, similar place names, and different languages used by the public. PIN structure The first digit of a PIN indicates the zone, the second indicates the sub-zone, and the third, combined with the first two, indicates the sorting district within that zone. The final three digits are assigned to individual post offices within the sorting district. Postal zones There are nine postal zones in India, including eight regional zones and one functional zone (for the Indian Army). The f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Karnataka
Karnataka (; ISO: , , also known as Karunāḍu) is a state in the southwestern region of India. It was formed on 1 November 1956, with the passage of the States Reorganisation Act. Originally known as Mysore State , it was renamed ''Karnataka'' in 1973. The state corresponds to the Carnatic region. Its capital and largest city is Bengaluru. Karnataka is bordered by the Lakshadweep Sea to the west, Goa to the northwest, Maharashtra to the north, Telangana to the northeast, Andhra Pradesh to the east, Tamil Nadu to the southeast, and Kerala to the southwest. It is the only southern state to have land borders with all of the other four southern Indian sister states. The state covers an area of , or 5.83 percent of the total geographical area of India. It is the sixth-largest Indian state by area. With 61,130,704 inhabitants at the 2011 census, Karnataka is the eighth-largest state by population, comprising 31 districts. Kannada, one of the classical languages of India, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indian Standard Time
Indian Standard Time (IST), sometimes also called India Standard Time, is the time zone observed throughout India, with a time offset of UTC+05:30. India does not observe daylight saving time or other seasonal adjustments. In military and aviation time, IST is designated E* ("Echo-Star"). It is indicated as Asia/Kolkata in the IANA time zone database. History After Independence in 1947, the Union government established IST as the official time for the whole country, although Kolkata and Mumbai retained their own local time (known as Calcutta Time and Bombay Time) until 1948 and 1955, respectively. The Central observatory was moved from Chennai to a location at Shankargarh Fort in Allahabad district, so that it would be as close to UTC+05:30 as possible. Daylight Saving Time (DST) was used briefly during the China–India War of 1962 and the Indo-Pakistani Wars of 1965 and 1971. Calculation Indian Standard Time is calculated from the clock tower in Mirzapur nearly exa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |