|
Satyajit Mayor
Satyajit Mayor (born 1963) is an Indian biologist. He serves as director of the National Centre for Biological Sciences, Bangalore. Mayor is the former director of the Institute for Stem Cell Biology and Regenerative Medicine (inStem) at Bangalore which has a focus on the study of stem cell and regenerative biology. In 2012, Mayor won the Infosys Prize for life sciences for his study of regulated cell surface organization and membrane dynamics. Education Mayor studied chemistry at the Indian Institute of Technology Bombay and was awarded his PhD in life sciences from The Rockefeller University, New York. He worked as a post-doctoral fellow at Columbia University, where he developed tools to study the trafficking of membrane lipids and GPI-anchored proteins in mammalian cells using quantitative fluorescence microscopy. Research Mayor started his laboratory at NCBS in 1995 after the completion of his post-doctoral research at Columbia University. "The broad aim of Prof Mayor’s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IIT Bombay
The Indian Institute of Technology Bombay (IIT Bombay or IITB) is a public research university and technical institute in Powai, Mumbai, Maharashtra, India. It is considered as one of the best engineering universities in India and is top ranked Indian university in QS World University Rankings 2022 and 3rd in NIRF overall rankings 2022 as well as NIRF engineering rankings 2022. IIT Bombay was founded in 1958. In 1961, the Parliament decreed IITs as Institutes of National Importance. A committee formed by the Government of India recommended the establishment of four higher institutes of technology to set the direction for the development of technical education in the country in 1946. Planning began in 1957 and the first batch of 100 students was admitted in 1958. Since its establishment in Powai, the institute has physically expanded to include more than 584 major buildings with a combined area of more than 2.2 square kilometers. IIT Bombay is considered as one of the foremost ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Hindu
''The Hindu'' is an Indian English-language daily newspaper owned by The Hindu Group, headquartered in Chennai, Tamil Nadu. It began as a weekly in 1878 and became a daily in 1889. It is one of the Indian newspapers of record and the second most circulated English-language newspaper in India, after '' The Times of India''. , ''The Hindu'' is published from 21 locations across 11 states of India. ''The Hindu'' has been a family-owned newspaper since 1905, when it was purchased by S. Kasturi Ranga Iyengar from the original founders. It is now jointly owned by Iyengar's descendants, referred to as the "Kasturi family", who serve as the directors of the holding company. The current chairperson of the group is Malini Parthasarathy, a great-granddaughter of Iyengar. Except for a period of about two years, when S. Varadarajan held the editorship of the newspaper, the editorial positions of the paper were always held by members of the family or held under their direction. Histo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Swarnajayanti Fellowship
The Swarnajayanti Fellowship (SJ) is a research fellowship in India awarded annually by the Department of Science and Technology (India) for notable and outstanding research by young scientists, applied or fundamental, in biology, chemistry, environmental science, engineering, mathematics, medicine and physics. The prize recognizes promising young Indian academicians who are producing outstanding work that impacts research and development. Details Citizens of India who are under 40 years of age, and have a proven track record may apply. The fellowship consists of an additional monthly stipend of as well as a research grant of per annum. The fellowship also requires that candidates have employment support from an Indian Institute of their choosing. Prizes The prize is divided into six disciplines, namely: * Chemical Sciences * Earth and Atmospheric Sciences * Engineering Sciences * Mathematical Sciences * Life Science * Physical Sciences Recipients * List of Swarnaj ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TWAS Prize
This is a list of recipients of the TWAS Prize, awarded annually by The World Academy of Sciences (TWAS). Summary Agricultural Sciences Biology Chemistry Earth Sciences Engineering Sciences Mathematics Medical Sciences Physics Social Sciences See also * Nikkei Asia Prize The Nikkei Asia Prize (Japanese: 日経アジア賞) is an award which recognizes the achievements of people and organizations that have improved the lives of people throughout Asia. The awards were created and presented by Nikkei Inc, one of the ... * Borlaug CAST Communication Award * L'Oréal-UNESCO Awards for Women in Science Notes References External links * * * * * * * * {{Use dmy dates, date=November 2018 Science and technology awards Awards established in 1985 International awards ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
EMBO
Embo ( gd, Eurabol, IPA: �iaɾəpɔɫ̪ is a village in the Highland Council Area in Scotland and the former postal county of Sutherland, about north-northeast of Dornoch. On 16 July 1988, Embo declared itself independent from the rest of the United Kingdom for one day. The Prime Minister was Mr. Donald Ward. This was done to raise funds to convert the unused primary school in the village into a community centre. The village issued its own currency, called the Cuddie. The rate of exchange was two Cuddies to the pound. Cuddies were accepted in the local public house, Grannies Heilan' Hame, in exchange for a measure of Clynelish Malt Whisky. The owners of the distillery, in nearby Brora, sponsored the bid for independence by issuing a commemorative label on 50 cases of Clynelish Malt Whisky – "The Spirit of Free Embo". The Battle of Embo took place in 1245 between Scots and Vikings. Bronze Age remains were excavated to the south of the village in 1956, other burials having p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Academy Of Sciences
The National Academy of Sciences (NAS) is a United States nonprofit, non-governmental organization. NAS is part of the National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine, along with the National Academy of Engineering (NAE) and the National Academy of Medicine (NAM). As a national academy, new members of the organization are elected annually by current members, based on their distinguished and continuing achievements in original research. Election to the National Academy is one of the highest honors in the scientific field. Members of the National Academy of Sciences serve '' pro bono'' as "advisers to the nation" on science, engineering, and medicine. The group holds a congressional charter under Title 36 of the United States Code. Founded in 1863 as a result of an Act of Congress that was approved by Abraham Lincoln, the NAS is charged with "providing independent, objective advice to the nation on matters related to science and technology. ... to provide scien ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
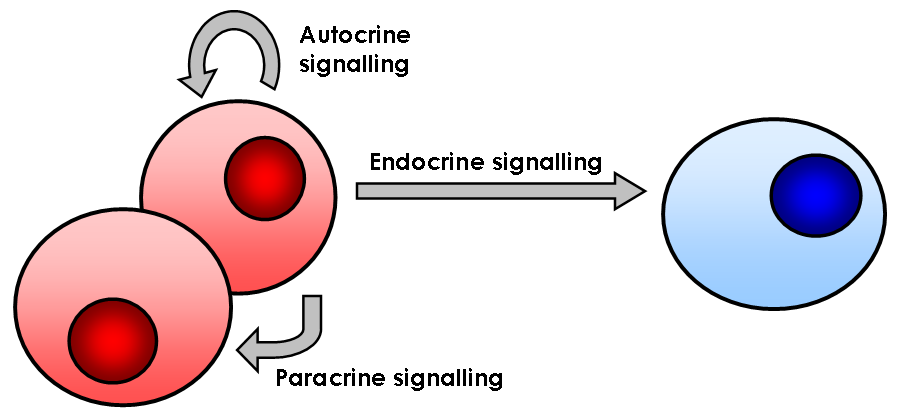
Cellular Signalling
In biology, cell signaling (cell signalling in British English) or cell communication is the ability of a cell to receive, process, and transmit signals with its environment and with itself. Cell signaling is a fundamental property of all cellular life in prokaryotes and eukaryotes. Signals that originate from outside a cell (or extracellular signals) can be physical agents like mechanical pressure, voltage, temperature, light, or chemical signals (e.g., small molecules, peptides, or gas). Cell signaling can occur over short or long distances, and as a result can be classified as autocrine, juxtacrine, intracrine, paracrine, or endocrine. Signaling molecules can be synthesized from various biosynthetic pathways and released through passive or active transports, or even from cell damage. Receptors play a key role in cell signaling as they are able to detect chemical signals or physical stimuli. Receptors are generally proteins located on the cell surface or within the inter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cell Membrane
The cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane (PM) or cytoplasmic membrane, and historically referred to as the plasmalemma) is a biological membrane that separates and protects the interior of all cells from the outside environment (the extracellular space). The cell membrane consists of a lipid bilayer, made up of two layers of phospholipids with cholesterols (a lipid component) interspersed between them, maintaining appropriate membrane fluidity at various temperatures. The membrane also contains membrane proteins, including integral proteins that span the membrane and serve as membrane transporters, and peripheral proteins that loosely attach to the outer (peripheral) side of the cell membrane, acting as enzymes to facilitate interaction with the cell's environment. Glycolipids embedded in the outer lipid layer serve a similar purpose. The cell membrane controls the movement of substances in and out of cells and organelles, being selectively permeable to ions a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metazoan
Animals are multicellular, eukaryotic organisms in the biological kingdom Animalia. With few exceptions, animals Heterotroph, consume organic material, Cellular respiration#Aerobic respiration, breathe oxygen, are Motility, able to move, can Sexual reproduction, reproduce sexually, and go through an ontogenetic stage in which their body consists of a hollow sphere of Cell (biology), cells, the blastula, during Embryogenesis, embryonic development. Over 1.5 million Extant taxon, living animal species have been Species description, described—of which around 1 million are Insecta, insects—but it has been estimated there are over 7 million animal species in total. Animals range in length from to . They have Ecology, complex interactions with each other and their environments, forming intricate food webs. The scientific study of animals is known as zoology. Most living animal species are in Bilateria, a clade whose members have a Symmetry in biology#Bilateral symmetry, bilat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endocytosis
Endocytosis is a cellular process in which substances are brought into the cell. The material to be internalized is surrounded by an area of cell membrane, which then buds off inside the cell to form a vesicle containing the ingested material. Endocytosis includes pinocytosis (cell drinking) and phagocytosis (cell eating). It is a form of active transport. History The term was proposed by De Duve in 1963. Phagocytosis was discovered by Élie Metchnikoff in 1882. Pathways Endocytosis pathways can be subdivided into four categories: namely, receptor-mediated endocytosis (also known as clathrin-mediated endocytosis), caveolae, pinocytosis, and phagocytosis Phagocytosis () is the process by which a cell uses its plasma membrane to engulf a large particle (≥ 0.5 μm), giving rise to an internal compartment called the phagosome. It is one type of endocytosis. A cell that performs phagocytosis is .... *Clathrin-mediated endocytosis is mediated by the production of smal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fluorescence Microscopy
A fluorescence microscope is an optical microscope that uses fluorescence instead of, or in addition to, scattering, reflection, and attenuation or absorption, to study the properties of organic or inorganic substances. "Fluorescence microscope" refers to any microscope that uses fluorescence to generate an image, whether it is a simple set up like an epifluorescence microscope or a more complicated design such as a confocal microscope, which uses optical sectioning to get better resolution of the fluorescence image. Principle The specimen is illuminated with light of a specific wavelength (or wavelengths) which is absorbed by the fluorophores, causing them to emit light of longer wavelengths (i.e., of a different color than the absorbed light). The illumination light is separated from the much weaker emitted fluorescence through the use of a spectral emission filter. Typical components of a fluorescence microscope are a light source (xenon arc lamp or mercury-vapor lamp are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Columbia University
Columbia University (also known as Columbia, and officially as Columbia University in the City of New York) is a private research university in New York City. Established in 1754 as King's College on the grounds of Trinity Church in Manhattan, Columbia is the oldest institution of higher education in New York and the fifth-oldest institution of higher learning in the United States. It is one of nine colonial colleges founded prior to the Declaration of Independence. It is a member of the Ivy League. Columbia is ranked among the top universities in the world. Columbia was established by royal charter under George II of Great Britain. It was renamed Columbia College in 1784 following the American Revolution, and in 1787 was placed under a private board of trustees headed by former students Alexander Hamilton and John Jay. In 1896, the campus was moved to its current location in Morningside Heights and renamed Columbia University. Columbia scientists and scholars have ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |