|
Satpura Thermal Power Plant
The Satpura Range is a range of hills in central India. The range rises in eastern Gujarat running east through the border of Maharashtra and Madhya Pradesh and ends in Chhattisgarh. The range parallels the Vindhya Range to the north, and these two east-west ranges divide Indian Subcontinent into the Indo-Gangetic plain of northern India and the Deccan Plateau of the south. The Narmada River originates from north-eastern end of Satpura in Amarkantak, and runs in the depression between the Satpura and Vindhya ranges, draining the northern slope of the Satpura range, running west towards the Arabian Sea. The Tapti River originates in the eastern-central part of Satpura, crossing the range in the center and running west at the range's southern slopes before meeting the Arabian Sea at Surat, draining the central and southern slopes of the range. Multai, the place of Tapi river origin is located about 465 kilometer far, south-westerly to Amarkantak, separated across by the hill range. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
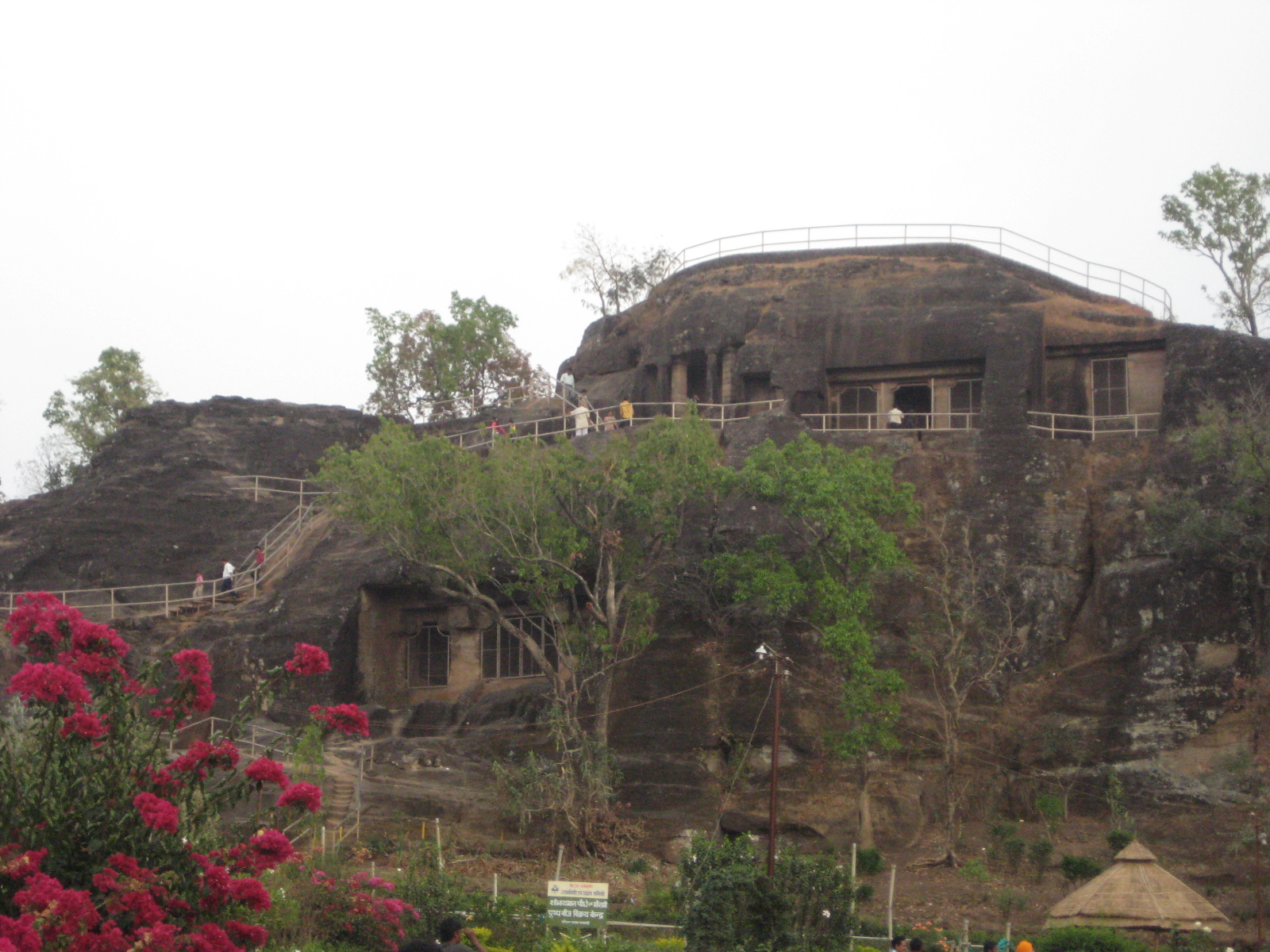
Pachmarhi
Pachmarhi is a hill station in Narmadapuram district of Madhya Pradesh states and territories of India, state of central India. It has been the location of a cantonment (Pachmarhi Cantonment) since British Raj. It is widely known as ''Satpura ki Rani'' ("Queen of Satpura"), situated at a height of 1067 m in a valley of the Satpura Range in Narmadapuram district. Dhupgarh, the highest point (1,352 m) in Madhya Pradesh and the Satpura range, is located here. It is a part of Satpura Biosphere Reserve. Pachmarhi is a hill station of central India. It is also famous for Satpura Tiger Reserve, Satpura National Park, Lord Shiva, Pandavas of Mahabharata. History The name Pachmarhi is believed to be derived from the Hindi words ''Panch'' ("five") and ''Marhi'' ("caves"). According to a legend, these caves were built by five Pandava brothers of Mahabharatha era during their thirteen years of exile. The caves are situated on a hilltop and provide an excellent vantage point. Pachmadh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Surat
Surat is a city in the western Indian state of Gujarat. The word Surat literally means ''face'' in Gujarati and Hindi. Located on the banks of the river Tapti near its confluence with the Arabian Sea, it used to be a large seaport. It is now the commercial and economic center in South Gujarat, and one of the largest urban areas of western India. It has well-established diamond and textile industry, and is a major supply centre for apparels and accessories. About 90% of the world's diamonds supply are cut and polished in the city. It is the second largest city in Gujarat after Ahmedabad and the eighth largest city by population and ninth largest urban agglomeration in India. It is the administrative capital of the Surat district. The city is located south of the state capital, Gandhinagar; south of Ahmedabad; and north of Mumbai. The city centre is located on the Tapti River, close to Arabian Sea. Surat will be the world's fastest growing city from 2019 to 2035, acco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bengal Tiger
The Bengal tiger is a population of the ''Panthera tigris tigris'' subspecies. It ranks among the biggest wild cats alive today. It is considered to belong to the world's charismatic megafauna. The tiger is estimated to have been present in the Indian subcontinent since the Late Pleistocene, for about 12,000 to 16,500 years. Today, it is threatened by poaching, Habitat loss, loss and Habitat fragmentation, fragmentation of habitat, and was estimated at comprising fewer than 2,500 wild individuals by 2011. None of the ''Tiger Conservation Landscapes'' within its range is considered large enough to support an effective population of more than 250 adult individuals. The Bengal tiger's historical range covered the Indus River valley until the early 19th century, almost all of India, Pakistan, southern Nepal, Bangladesh, Bhutan and southwestern China. Today, it inhabits India, Bangladesh, Nepal, Bhutan and southwestern China. India's tiger population was estimated at 2,603–3,346 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
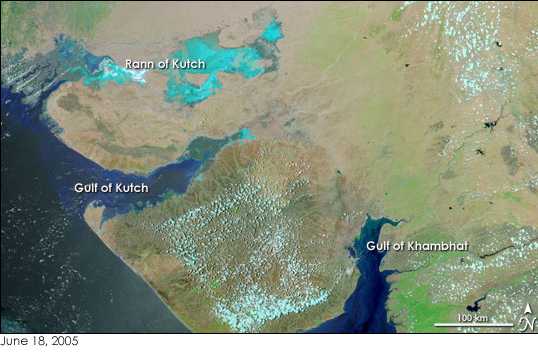
Gulf Of Khambhat
The Gulf of Khambhat, historically known as the Gulf of Cambay, is a bay on the Arabian Sea coast of India, bordering the state of Gujarat just north of Mumbai and Diu Island. The Gulf of Khambhat is about long, about wide in the north and up to wide in the south. Major rivers draining Gujarat are the Narmada, Tapti, Mahi and the Sabarmati, that form estuaries in the gulf. It divides the Kathiawar Peninsula from the south-eastern part of Gujarat.Trivedi, P. and Soni, V. C. (2012)Significant bird records and local extinctions in Purna and Ratanmahal Wildlife Sanctuaries, Gujarat, IndiaJhala, Y. V., Qureshi, Q., Sinha, P. R. (Eds.) (2011)''Status of tigers, co-predators and prey in India, 2010.''National Tiger Conservation Authority, Government of India, New Delhi, and Wildlife Institute of India, Dehradun. TR 2011/003. There are plans to construct a dam, Kalpasar Project, across the gulf. Wildlife To the west of the Gulf, Asiatic lions inhabit the Gir Forest National ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Narmada Valley Dry Deciduous Forests
The Narmada Valley dry deciduous forests are a tropical dry forest ecoregion of central India. The ecoregion lies mostly in Madhya Pradesh state, but extends into portions of Chhattisgarh, Maharashtra, Karnataka and Uttar Pradesh states. Setting The Narmada Valley dry deciduous forests cover an area of of the lower Narmada River Valley and the surrounding uplands of the Vindhya Range to the north and the western end of the Satpura Range to the south. The Narmada Valley is an east-west flat-bottomed valley, or graben, that separates the two plateaus. The Vindhya Range separates the valley from the Malwa plateau and Bundelkhand upland to the north. The Satpura Range reaches a height of 1,300m and encloses the valley on the south separating it from the Deccan plateau. The ecoregion includes the western portion of the Satpuras, and also extends to the southeast along the eastern flank of the Western Ghats' range. The uplands of this ecoregion are the northern limits of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ecoregion
An ecoregion (ecological region) or ecozone (ecological zone) is an ecologically and geographically defined area that is smaller than a bioregion, which in turn is smaller than a biogeographic realm. Ecoregions cover relatively large areas of land or water, and contain characteristic, geographically distinct assemblages of natural communities and species. The biodiversity of flora, fauna and ecosystems that characterise an ecoregion tends to be distinct from that of other ecoregions. In theory, biodiversity or conservation ecoregions are relatively large areas of land or water where the probability of encountering different species and communities at any given point remains relatively constant, within an acceptable range of variation (largely undefined at this point). Three caveats are appropriate for all bio-geographic mapping approaches. Firstly, no single bio-geographic framework is optimal for all taxa. Ecoregions reflect the best compromise for as many taxa as possible. Se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eastern Highlands Moist Deciduous Forests
The Eastern Highlands moist deciduous forests, presently known as East Deccan moist deciduous forests, is a tropical and subtropical moist broadleaf forests ecoregion in east-central India. The ecoregion covers an area of , extending across portions of Andhra Pradesh, Chhattisgarh, Jharkhand, Madhya Pradesh, Maharashtra, Odisha, and Telangana states. Setting The Eastern Highlands moist deciduous forests extend from the Bay of Bengal coast in northern Andhra Pradesh and southern Orissa, across the northern portion of the Eastern Ghats range and the northeastern Deccan Plateau, to the eastern Satpura Range and the upper Narmada River valley. The forests of the ecoregion are sustained by the moisture-bearing monsoon winds from the Bay of Bengal, which lies to the southeast. The ecoregion is bounded on the north and west by tropical dry deciduous forest ecoregions, including the Central Deccan Plateau dry deciduous forests to the southwest and west, the Narmada valley dry dec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eastern Ghats
The Eastern Ghats are a discontinuous range of mountains along India's eastern coast. The Eastern Ghats pass through Odisha, Andhra Pradesh to Tamil Nadu in the south passing some parts of Karnataka as well as Telangana. They are eroded and cut through by four major rivers of peninsular India, viz., Mahanadi, Godavari, Krishna, and Kaveri. Deomali with 1672 m height is the tallest point in Odisha. Arma Konda/Jindhagada Peak with 1680 m is the highest point in Andhra Pradesh. BR hill range located in Karnataka is the tallest hill range in Eastern Ghats with many peaks above 1750 m height. Kattahi betta in BR hills with the height of 1822 m is the tallest peak in Eastern Ghats. Thalamalai hill range in Tamil Nadu is the second tallest hill range. Araku range is the third tallest hill range. Geology The Eastern Ghats are made up of charnockites, granite gneiss, khondalites, metamorphic gneisses and quartzite rock formations. The structure of the Eastern Ghats i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Graben
In geology, a graben () is a depressed block of the crust of a planet or moon, bordered by parallel normal faults. Etymology ''Graben'' is a loan word from German, meaning 'ditch' or 'trench'. The word was first used in the geologic context by Eduard Suess in 1883. The plural form is either ''graben'' or ''grabens''. Formation A graben is a valley with a distinct escarpment on each side caused by the displacement of a block of land downward. Graben often occur side by side with horsts. Horst and graben structures indicate tensional forces and crustal stretching. Graben are produced from parallel normal faults, where the displacement of the hanging wall is downward, while that of the footwall is upward. The faults typically dip toward the center of the graben from both sides. Horsts are parallel blocks that remain between graben; the bounding faults of a horst typically dip away from the center line of the horst. Single or multiple graben can produce a rift valley. Half-g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Horst (geology)
In physical geography and geology, a horst is a raised fault block bounded by Fault (geology), normal faults. Horsts are typically found together with Graben, grabens. While a horst lifted or remains stationary, the grabens on either side Subsidence, subside. This is often caused by Extensional tectonics, extensional forces pulling apart the crust. Horsts may represent features such as plateaus, mountains, or ridges on either side of a valley. Horsts can range in size from small fault-blocks, up to large regions of stable continent that have not been not folded or warped by tectonic forces. The word ''Horst'' in German language, German means "mass" or "heap," and was first used in the geological sense in 1883 by Eduard Suess in ''The Face of the Earth.''Originally published in 1883 in German as "Das Antlitz der Erde", translated and published in English in 1904 Geomorphology Horsts may have either symmetrical or asymmetrical cross-sections. If the normal faults to either side ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chota Nagpur Plateau
The Chota Nagpur Plateau is a plateau in eastern India, which covers much of Jharkhand state as well as adjacent parts of Chhattisgarh, Odisha, West Bengal and Bihar. The Indo-Gangetic plain lies to the north and east of the plateau, and the basin of the Mahanadi river lies to the south. The total area of the Chota Nagpur Plateau is approximately . Etymology The name ''Nagpur'' is probably taken from Nagavanshis, who ruled in this part of the country. ''Chhota'' (''small'' in Hindi) is the misunderstood name of "Chuita" village in the outskirts of Ranchi, which has the remains of an old fort belonging to the Nagavanshis.Sir John Houlton, ''Bihar, the Heart of India'', pp. 127-128, Orient Longmans, 1949. Formation The Chota Nagpur Plateau is a continental plateau—an extensive area of land thrust above the general land. The plateau has been formed by continental uplift from forces acting deep inside the earth. The Gondwana substrates attest to the plateau's ancient origin. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bay Of Bengal
The Bay of Bengal is the northeastern part of the Indian Ocean, bounded on the west and northwest by India, on the north by Bangladesh, and on the east by Myanmar and the Andaman and Nicobar Islands of India. Its southern limit is a line between Sangaman Kanda, Sri Lanka, and the north westernmost point of Sumatra, Indonesia. It is the largest water region called a bay in the world. There are countries dependent on the Bay of Bengal in South Asia and Southeast Asia. During the existence of British India, it was named as the Bay of Bengal after the historic Bengal region. At the time, the Port of Kolkata served as the gateway to the Crown rule in India. Cox's Bazar, the longest sea beach in the world and Sundarbans, the largest mangrove forest and the natural habitat of the Bengal tiger, are located along the bay. The Bay of Bengal occupies an area of . A number of large rivers flow into the Bay of Bengal: the Ganges– Hooghly, the Padma, the Brahmaputra–Yamuna, the Barak†... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |