|
Satpura
The Satpura Range is a range of hills in central India. The range rises in eastern Gujarat running east through the border of Maharashtra and Madhya Pradesh and ends in Chhattisgarh. The range parallels the Vindhya Range to the north, and these two east-west ranges divide Indian Subcontinent into the Indo-Gangetic plain of northern India and the Deccan Plateau of the south. The Narmada River originates from north-eastern end of Satpura in Amarkantak, and runs in the depression between the Satpura and Vindhya ranges, draining the northern slope of the Satpura range, running west towards the Arabian Sea. The Tapti River originates in the eastern-central part of Satpura, crossing the range in the center and running west at the range's southern slopes before meeting the Arabian Sea at Surat, draining the central and southern slopes of the range. Multai, the place of Tapi river origin is located about 465 kilometer far, south-westerly to Amarkantak, separated across by the hill ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
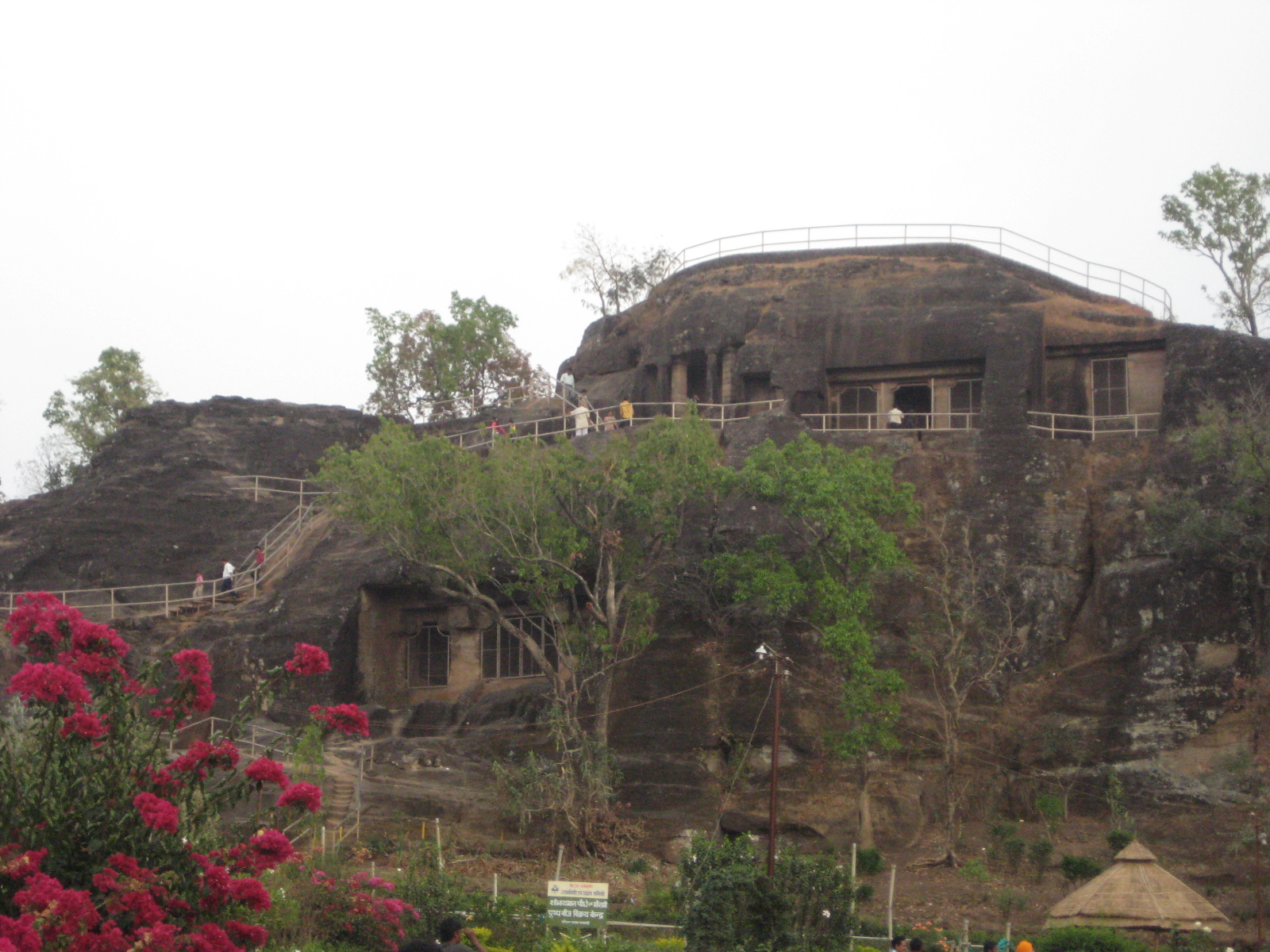
Pachmarhi
Pachmarhi is a hill station in Narmadapuram district of Madhya Pradesh states and territories of India, state of central India. It has been the location of a cantonment (Pachmarhi Cantonment) since British Raj. It is widely known as ''Satpura ki Rani'' ("Queen of Satpura"), situated at a height of 1067 m in a valley of the Satpura Range in Narmadapuram district. Dhupgarh, the highest point (1,352 m) in Madhya Pradesh and the Satpura range, is located here. It is a part of Satpura Biosphere Reserve. Pachmarhi is a hill station of central India. It is also famous for Satpura Tiger Reserve, Satpura National Park, Lord Shiva, Pandavas of Mahabharata. History The name Pachmarhi is believed to be derived from the Hindi words ''Panch'' ("five") and ''Marhi'' ("caves"). According to a legend, these caves were built by five Pandava brothers of Mahabharatha era during their thirteen years of exile. The caves are situated on a hilltop and provide an excellent vantage point. Pachmadh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Madhya Pradesh
Madhya Pradesh (, ; meaning 'central province') is a state in central India. Its capital is Bhopal, and the largest city is Indore, with Jabalpur, Ujjain, Gwalior, Sagar, and Rewa being the other major cities. Madhya Pradesh is the second largest Indian state by area and the fifth largest state by population with over 72 million residents. It borders the states of Uttar Pradesh to the northeast, Chhattisgarh to the east, Maharashtra to the south, Gujarat to the west, and Rajasthan to the northwest. The area covered by the present-day Madhya Pradesh includes the area of the ancient Avanti Mahajanapada, whose capital Ujjain (also known as Avantika) arose as a major city during the second wave of Indian urbanisation in the sixth century BCE. Subsequently, the region was ruled by the major dynasties of India. The Maratha Empire dominated the majority of the 18th century. After the Anglo-Maratha Wars in the 19th century, the region was divided into several princel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vindhya Range
The Vindhya Range (also known as Vindhyachal) () is a complex, discontinuous chain of mountain ridges, hill ranges, highlands and plateau escarpments in west-central India. Technically, the Vindhyas do not form a single mountain range in the geological sense. The exact extent of the Vindhyas is loosely defined, and historically, the term covered a number of distinct hill systems in central India, including the one that is now known as the Satpura Range. Today, the term principally refers to the escarpment and its hilly extensions that runs north of and roughly parallel to the Narmada River in Madhya Pradesh. Depending on the definition, the range extends up to Gujarat in the west, Uttar Pradesh and Bihar in the north, and Chhattisgarh in the east. The Vindhyas have a great significance in Indian mythology and history. Several ancient texts mention the Vindhyas as the southern boundary of the '' Āryāvarta'', the territory of the ancient Indo-Aryan peoples. Although today I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Narmada Valley Dry Deciduous Forests
The Narmada Valley dry deciduous forests are a tropical dry forest ecoregion of central India. The ecoregion lies mostly in Madhya Pradesh state, but extends into portions of Chhattisgarh, Maharashtra, Karnataka and Uttar Pradesh states. Setting The Narmada Valley dry deciduous forests cover an area of of the lower Narmada River Valley and the surrounding uplands of the Vindhya Range to the north and the western end of the Satpura Range to the south. The Narmada Valley is an east-west flat-bottomed valley, or graben, that separates the two plateaus. The Vindhya Range separates the valley from the Malwa plateau and Bundelkhand upland to the north. The Satpura Range reaches a height of 1,300m and encloses the valley on the south separating it from the Deccan plateau. The ecoregion includes the western portion of the Satpuras, and also extends to the southeast along the eastern flank of the Western Ghats' range. The uplands of this ecoregion are the northern limits of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deccan Plateau
The large Deccan Plateau in southern India is located between the Western Ghats and the Eastern Ghats, and is loosely defined as the peninsular region between these ranges that is south of the Narmada river. To the north, it is bounded by the Satpura and Vindhya Ranges. A rocky terrain marked by boulders, its elevation ranges between , with an average of about .Editors of Encyclopedia Britannica (2014), ''Deccan plateau India''Encyclopaedia Britannica/ref> It is sloping generally eastward. Thus, its principal rivers—the Godavari, Krishna, and Kaveri (Cauvery)—flow eastward from the Western Ghats to the Bay of Bengal. The plateau is drier than the coastal region of southern India and is arid in places. It produced some of the major dynasties in Indian history, including the Pallavas, Satavahana, Vakataka, Chalukya, and Rashtrakuta dynasties, also the Western Chalukya Empire, the Kadambas, the Yadava dynasty, the Kakatiya Empire, the Musunuri Nayakas regime, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deccan Plateau
The large Deccan Plateau in southern India is located between the Western Ghats and the Eastern Ghats, and is loosely defined as the peninsular region between these ranges that is south of the Narmada river. To the north, it is bounded by the Satpura and Vindhya Ranges. A rocky terrain marked by boulders, its elevation ranges between , with an average of about .Editors of Encyclopedia Britannica (2014), ''Deccan plateau India''Encyclopaedia Britannica/ref> It is sloping generally eastward. Thus, its principal rivers—the Godavari, Krishna, and Kaveri (Cauvery)—flow eastward from the Western Ghats to the Bay of Bengal. The plateau is drier than the coastal region of southern India and is arid in places. It produced some of the major dynasties in Indian history, including the Pallavas, Satavahana, Vakataka, Chalukya, and Rashtrakuta dynasties, also the Western Chalukya Empire, the Kadambas, the Yadava dynasty, the Kakatiya Empire, the Musunuri Nayakas regime, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
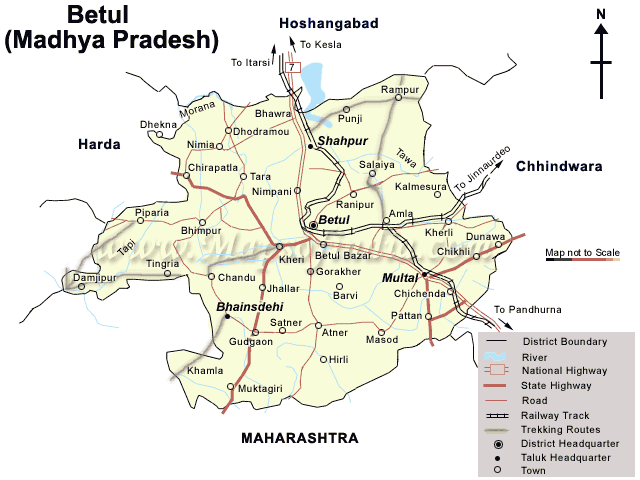
Multai
Multai is a town and a Nagar Palika in Betul district in the Indian state of Madhya Pradesh. Multai is one of the southern cities of Madhya Pradesh, occupying almost half of the Satpura plateau. Considering the small villages around, it occupies a large area in width of the Satpura range between the valley of the Narmada on the north and the barer plains on the south. Forests lie to the west of the city between the districts of East Nimar and Amaraoti. It lies on the Northern bank of the Tapti and the place is also known for being the origin of the Tapti river. Geography Multai is located at . It has an average elevation of 749 metres (2457 feet). Multai is the holy place and origin for river Tapti. The daughter of Surya, the Sun God, Mata Tapti is worshiped here in two different temples Prachin Mandir and Naveen Mandir. The Multai town is decorated on Akhad Saptami Tapti Janmotsav and an annual Mela is organized on this occasion. In Multai town there are many anci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bengal Tiger
The Bengal tiger is a population of the '' Panthera tigris tigris'' subspecies. It ranks among the biggest wild cats alive today. It is considered to belong to the world's charismatic megafauna. The tiger is estimated to have been present in the Indian subcontinent since the Late Pleistocene, for about 12,000 to 16,500 years. Today, it is threatened by poaching, loss and fragmentation of habitat, and was estimated at comprising fewer than 2,500 wild individuals by 2011. None of the ''Tiger Conservation Landscapes'' within its range is considered large enough to support an effective population of more than 250 adult individuals. The Bengal tiger's historical range covered the Indus River valley until the early 19th century, almost all of India, Pakistan, southern Nepal, Bangladesh, Bhutan and southwestern China. Today, it inhabits India, Bangladesh, Nepal, Bhutan and southwestern China. India's tiger population was estimated at 2,603–3,346 individuals by 2018. Around 300 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chhattisgarh
Chhattisgarh (, ) is a landlocked state in Central India. It is the ninth largest state by area, and with a population of roughly 30 million, the seventeenth most populous. It borders seven states – Uttar Pradesh to the north, Madhya Pradesh to the northwest, Maharashtra to the southwest, Jharkhand to the northeast, Odisha to the east, Telangana and Andhra Pradesh to the south. Formerly a part of Madhya Pradesh, it was granted statehood on 1 November 2000 with Raipur as the designated state capital. Chhattisgarh is one of the fastest-developing states in India. Its Gross State Domestic Product (GSDP) is , with a per capita GSDP of . A resource-rich state, it has the third largest coal reserves in the country and provides electricity, coal, and steel to the rest of the nation. It also has the third largest forest cover in the country after Madhya Pradesh and Arunachal Pradesh with over 40% of the state covered by forests. Etymology There are several theories as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eastern Highlands Moist Deciduous Forests
The Eastern Highlands moist deciduous forests, presently known as East Deccan moist deciduous forests, is a tropical and subtropical moist broadleaf forests ecoregion in east-central India. The ecoregion covers an area of , extending across portions of Andhra Pradesh, Chhattisgarh, Jharkhand, Madhya Pradesh, Maharashtra, Odisha, and Telangana states. Setting The Eastern Highlands moist deciduous forests extend from the Bay of Bengal coast in northern Andhra Pradesh and southern Orissa, across the northern portion of the Eastern Ghats range and the northeastern Deccan Plateau, to the eastern Satpura Range and the upper Narmada River valley. The forests of the ecoregion are sustained by the moisture-bearing monsoon winds from the Bay of Bengal, which lies to the southeast. The ecoregion is bounded on the north and west by tropical dry deciduous forest ecoregions, including the Central Deccan Plateau dry deciduous forests to the southwest and west, the Narmada valley dry dec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dhupgarh
Mount Dhupgarh or Dhoopgarh is the highest point in the Mahadeo Hills (Satpura Range), Madhya Pradesh, India. Located in Pachmarhi in Hoshangabad district Narmadapuram district, formerly Hoshangabad district, is one of the districts of Madhya Pradesh state of India, and Narmadapuram city is the district headquarters. Geography The district has an area of 5408.23 km². Hoshangabad district is ..., it has an elevation of 1,352 metres (4,429 ft). The top of the hill is a popular area to watch sunsets. Pachmarhi Hill station is located close to the peak. _See_also *Geography_of_Madhya_Pradesh.html" ;"title="ref> See also *Geography of Madhya Pradesh">ref> See also *Geography of Madhya Pradesh *List of mountains in India *List of mountains by elevation References Mountains of Madhya Pradesh Highest points of Indian states and union territories Pachmarhi {{MadhyaPradesh-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the south, the Arabian Sea on the southwest, and the Bay of Bengal on the southeast, it shares land borders with Pakistan to the west; China, Nepal, and Bhutan to the north; and Bangladesh and Myanmar to the east. In the Indian Ocean, India is in the vicinity of Sri Lanka and the Maldives; its Andaman and Nicobar Islands share a maritime border with Thailand, Myanmar, and Indonesia. Modern humans arrived on the Indian subcontinent from Africa no later than 55,000 years ago., "Y-Chromosome and Mt-DNA data support the colonization of South Asia by modern humans originating in Africa. ... Coalescence dates for most non-European populations average to between 73–55 ka.", "Modern human beings—''Homo sapiens''—originated in Africa. Then, interm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

_male.jpg)

.jpg)
.png)
