|
Sarsasapogenin
Sarsasapogenin is a steroidal sapogenin, that is the aglycosidic portion of a plant saponin. It is named after sarsaparilla (''Smilax'' sp.),. a family of climbing plants found in subtropical regions. It was one of the first sapogenins to be identified, and the first spirostan steroid to be identified as such.. The identification of the spirostan structure, with its ketone spiro acetal functionality, was fundamental in the development of the Marker degradation, which allowed the industrial production of progesterone and other sex hormones from plant steroids. Sarsasapogenin is unusual in that it has a ''cis''-linkage between rings A and B of the steroid nucleus, as opposed to the more usual ''trans''-linkage found in other saturated steroids. This 5β configuration is biologically significant, as a specific enzyme – sarsasapogenin 3β-glucosyltransferase – is found in several plants for the glycosylation of sarsasapogenin. The (''S'')-configuration at C-25 is also in cont ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
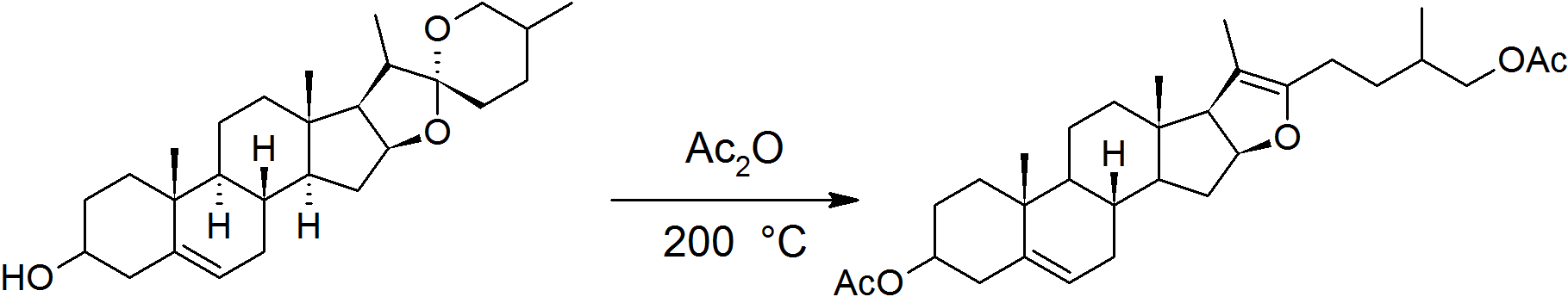
Marker Degradation
The Marker degradation is a three-step synthetic route in steroid chemistry developed by American chemist Russell Earl Marker in 1938–40. It is used for the production of cortisone and mammalian sex hormones (progesterone, estradiol, etc.) from plant steroids, and established Mexico as a world center for steroid production in the years immediately after World War II. The discovery of the Marker degradation allowed the production of substantial quantities of steroid hormones for the first time, and was fundamental in the development of the contraceptive pill and corticosteroid anti-inflammatory drugs. In 1999, the American Chemical Society and the Sociedad Química de México named the route as an International Historic Chemical Landmark. The first large-scale application of the route took place in 1943, when Russell Earl Marker collected 10 tons of yam tubers to synthesize of progesterone, which was the largest single amount of progesterone that had been produced by that t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sarsasapogenin 3β-glucosyltransferase
In enzymology, a sarsasapogenin 3β-glucosyltransferase () is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction :UDP-glucose + sarsasapogenin UDP + sarsasapogenin 3-''O''-β-D-glucoside Thus, the two substrates of this enzyme are UDP-glucose and sarsasapogenin 3β,5β,25''S'')-spirostan-3-ol whereas its two products are UDP and sarsasapogenin 3-''O''-β-D-glucoside. The enzyme was first isolated from the root of the common asparagus (''Asparagus officinalis''). It is specific for substrate sterols with the uncommon 5β-configuration (sarsasapogenin and smilagenin), that is with a ''cis''-linkage between the A and B rings of the steroid nucleus. This enzyme belongs to the family of glycosyltransferases, specifically the hexosyltransferases. The systematic name A systematic name is a name given in a systematic way to one unique group, organism, object or chemical substance, out of a specific population or collection. Systematic names are usually part of a nomenclature. A semisy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Smilax Glabra
''Smilax glabra'', sarsaparilla, is a plant species in the genus ''Smilax''. It is native to flora of China, China, the Himalayas, and Indochina. ''S. glabra'' is a traditional Chinese medicine, traditional medicine in Chinese herbology, whence it is also known as tufuling () or chinaroot, china-root, and china root (a name it shares with the related ''Smilax china, S. china''). Chinaroot is a key ingredient in the Chinese medical Chinese desserts, dessert ''guīlínggāo, guilinggao'', which uses its ability to set certain kinds of Gelatin, jelly. Chemical composition Dihydro-flavonol glycosides (astilbin, neoastilbin, isoastilbin, neoisoastilbin, (2''R'', 3''R'')-taxifolin-3'-O-beta-D-pyranoglucoside) have been identified in the rhizome of ''Smilax glabra'' as well as smitilbin, a flavanonol rhamnoside. Smiglabrone A and Smiglabrone B are phenylpropanoid-substituted Catechin, epicatechins that have also been isolated from the root. Sarsasapogenin, a steroidal sapogenin, can ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Steroid
A steroid is a biologically active organic compound with four rings arranged in a specific molecular configuration. Steroids have two principal biological functions: as important components of cell membranes that alter membrane fluidity; and as signaling molecules. Hundreds of steroids are found in plants, animals and fungi. All steroids are manufactured in cells from the sterols lanosterol (opisthokonts) or cycloartenol (plants). Lanosterol and cycloartenol are derived from the cyclization of the triterpene squalene. The steroid core structure is typically composed of seventeen carbon atoms, bonded in four " fused" rings: three six-member cyclohexane rings (rings A, B and C in the first illustration) and one five-member cyclopentane ring (the D ring). Steroids vary by the functional groups attached to this four-ring core and by the oxidation state of the rings. Sterols are forms of steroids with a hydroxy group at position three and a skeleton derived from cholestane. ''A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Smilax Ornata
''Smilax ornata'' is a perennial trailing vine with prickly stems that is native to Mexico and Central America. Common names include sarsaparilla, Honduran sarsaparilla, and Jamaican sarsaparilla. It is known in Spanish as ', which is derived from the words ' meaning "bramble" (from Basque ''sartzia'' "bramble"), and ', meaning "little grape vine". Uses Food ''Smilax ornata'' is used as the basis for a soft drink frequently called sarsaparilla. It is also a primary ingredient in old fashioned-style root beer, in conjunction with sassafras, which was more widely available prior to studies of its potential health risks. Traditional medicine ''Smilax ornata'' was considered by Native Americans to have medicinal properties, and was a popular European treatment for syphilis when it was introduced from the New World. From 1820 to 1910, it was registered in the U.S. Pharmacopoeia as a treatment for syphilis. Chemical constituents Gallery File:Sarsaparilla-Triterpenes.svg, Trite ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agave
''Agave'' (; ; ) is a genus of monocots native to the hot and arid regions of the Americas and the Caribbean, although some ''Agave'' species are also native to tropical areas of North America, such as Mexico. The genus is primarily known for its succulent and xerophytic species that typically form large rosettes of strong, fleshy leaves. ''Agave'' now includes species formerly placed in a number of other genera, such as ''Manfreda'', ×''Mangave'', ''Polianthes'' and ''Prochnyanthes''. Many plants in this genus may be considered perennial, because they require several to many years to mature and flower. However, most ''Agave'' species are more accurately described as monocarpic rosettes or multiannuals, since each individual rosette flowers only once and then dies; a small number of ''Agave'' species are polycarpic. Maguey flowers are considered edible in many indigenous culinary traditions of Mesoamerica. Along with plants from the closely related genera ''Yucca'', ''Hes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yucca Brevifolia
''Yucca brevifolia'' is a plant species belonging to the genus ''Yucca''. It is tree-like in habit, which is reflected in its common names: Joshua tree, yucca palm, tree yucca, and palm tree yucca. This monocotyledonous tree is native to the arid Southwestern United States, specifically California, Arizona, Utah, and Nevada, and to northwestern Mexico It is confined mostly to the Mojave Desert between elevation. It thrives in the open grasslands of Queen Valley and Lost Horse Valley in Joshua Tree National Park. Other regions with large populations of the tree can be found northeast of Kingman, Arizona in Mohave County; and along U.S. 93 between the towns of Wickenburg and Wikieup, a route which has been designated the Joshua Tree Parkway of Arizona. The common name Joshua tree apparently comes from Christian iconography. Taxonomy The Joshua tree is also called ''izote de desierto'' (Spanish, "desert dagger"). It was first formally described in the botanical literature as ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yucca Schidigera
''Yucca schidigera'', also known as the Mojave yucca or Spanish dagger, is a flowering plant native to the southwest deserts of North America. Description ''Yucca schidigera'' is a small evergreen tree growing to tall, with a dense crown of spirally arranged bayonet-like leaves on top of a conspicuous basal trunk. The bark is gray-brown, being covered with brown dead leaves near the top, becoming irregularly rough and scaly-to-ridged closer to the ground. The leaves are long and broad at the base, concavo-convex, thick, very rigid, and yellow-green to blue-green in color. The flowers are white, sometimes with a purple tinge, long (rarely to 7.5 cm), bell-shaped and segmented into six parts; they are produced in a compact, bulbous cluster tall at the top of the stem. The fruit is an elongate berry, up to long. Distribution and habitat The plant is native to the Mojave Desert, Chihuahuan Desert and Sonoran Desert of southeastern California, Baja California, New Mexi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yucca
''Yucca'' is a genus of perennial shrubs and trees in the family Asparagaceae, subfamily Agavoideae. Its 40–50 species are notable for their rosettes of evergreen, tough, sword-shaped leaves and large terminal panicles of white or whitish flowers. They are native to the hot and dry (arid) parts of the Americas and the Caribbean. Early reports of the species were confused with the cassava (''Manihot esculenta''). Consequently, Linnaeus mistakenly derived the generic name from the Taíno word for the latter, ''yuca''. The Aztecs living in Mexico since before the Spanish arrival, in Nahuatl, call the local yucca species (''Yucca gigantea'') , which gave the Spanish . is also used for ''Yucca filifera''. Distribution The natural distribution range of the genus ''Yucca'' (49 species and 24 subspecies) covers a vast area of the Americas. The genus is represented throughout Mexico and extends into Guatemala (''Yucca guatemalensis''). It also extends to the north through Baja Cali ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anemarrhena
''Anemarrhena'' is a plant genus in family Asparagaceae, subfamily Agavoideae. It has only one species, ''Anemarrhena asphodeloides'', native to China and Mongolia. Some authors have placed it in its own family, Anemarrhenaceae. Distribution The plant is native to China and Mongolia, occurring in the western half of China, from Yunnan to Northeast China. It is introduced into Taiwan and Korea. Traditional medicine The plant name in China is ''zhi mu'' (知母, zhī mǔ) and its rhizome is used in traditional Chinese medicine Traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) is an alternative medical practice drawn from traditional medicine in China. It has been described as "fraught with pseudoscience", with the majority of its treatments having no logical mechanism of action ....Ya, Wang, Feng Fang, and Wang Zhe. "Determination Of Selected Elements In Aqueous Extractions Of A Traditional Chinese Medicine Formula By ICP-MS And FAAS: Evaluation Of Formula Rationality." ''Analytical L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agavaceae
Agavoideae is a subfamily of monocot flowering plants in the family Asparagaceae, order Asparagales. It has previously been treated as a separate family, Agavaceae. The group includes many well-known desert and dry-zone types, such as the agaves and yuccas (including the Joshua tree). About 640 species are placed in around 23 genera; they are widespread in the tropical, subtropical, and warm temperate regions of the world. Description and uses Species may be succulent or not. In general, Agavoideae leaves occur as rosettes at the end of a woody stem, which may range from extremely short to tree-like heights, as in the Joshua tree. The leaves are parallel-veined, and usually appear long and pointed, often with a hardened spine on the end, and sometimes with additional spines along the margins. ''Agave'' species are used to make ''tequila, pulque,'' and ''mezcal'', while others are valued for their fibers. They are quite popular for xeriscaping, as many have showy flowers. S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asparagus
Asparagus, or garden asparagus, folk name sparrow grass, scientific name ''Asparagus officinalis'', is a perennial flowering plant species in the genus ''Asparagus''. Its young shoots are used as a spring vegetable. It was once classified in the lily family, like the related ''Allium'' species, onions and garlic. However, genetic research places lilies, ''Allium'', and asparagus in three separate families—the Liliaceae, Amaryllidaceae, and Asparagaceae, respectively— the Amaryllidaceae and Asparagaceae are grouped together in the order Asparagales. Sources differ as to the native range of ''Asparagus officinalis'', but generally include most of Europe and western temperate Asia. It is widely cultivated as a vegetable crop. Description Asparagus is a herbaceous, perennial plant growing to tall, with stout stems with much-branched, feathery foliage. The 'leaves' are in fact needle-like cladodes ( modified stems) in the axils of scale leaves; they are long and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |