|
Sarin (star)
Delta Herculis (δ Herculis, abbreviated Delta Her, δ Her) is a Star system, multiple star system in the constellation of Hercules (constellation), Hercules. Its light produces to us apparent magnitude 3.12, as such the third-brightest star in the large, fairly dim constellation. Based on stellar parallax, parallax measurement taken during the Hipparcos mission, it is approximately from the Sun. Components It consists of a binary star, binary pair, designated Delta Herculis A, together with three potential companions, suffixed B, C and D. Furthermore B is believed to be an double star, optical binary. A's components are designated Delta Herculis Aa (officially named Sarin , the traditional name of the system) and Ab. The angular separation between the main component A and the component B, which has a magnitude of 8.74, is 8.5 arcsecond Nomenclature ''δ Herculis'' (Latinisation of names, Latinised to ''Delta Herculis'') is the system's Bayer designation. The designatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
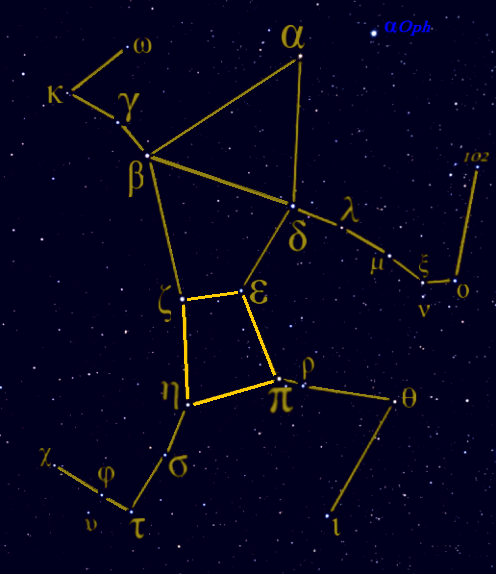
Hercules (constellation)
Hercules is a constellation named after Hercules, the Roman mythology, Roman mythological hero adapted from the Greek mythology, Greek hero Heracles. Hercules was one of the 48 constellations listed by the second-century astronomer Ptolemy, and it remains one of the IAU designated constellations, 88 modern constellations today. It is the fifth-largest of the modern constellations and is the largest of List of brightest stars, the 50 which have no stars brighter than apparent Magnitude (astronomy), magnitude +2.5. Characteristics Hercules is bordered by Draco (constellation), Draco to the north; Boötes, Corona Borealis, and Serpens, Serpens Caput to the east; Ophiuchus to the south; Aquila (constellation), Aquila to the southwest; and Sagitta, Vulpecula, and Lyra to the west. Covering 1225.1 square degrees and 2.970% of the night sky, it ranks fifth among the 88 constellations in size. The three-letter abbreviation for the constellation, as adopted by the International Astro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Double Star
In observational astronomy, a double star or visual double is a pair of stars that appear close to each other as viewed from Earth, especially with the aid of optical telescopes. This occurs because the pair either forms a binary star (i.e. a binary system of stars in mutual orbit, gravitationally bound to each other) or is an ''optical double'', a chance line-of-sight alignment of two stars at different distances from the observer. Binary stars are important to stellar astronomers as knowledge of their motions allows direct calculation of stellar mass and other stellar parameters. The only (possible) case of "binary star" whose two components are separately visible to the naked eye is the case of Mizar and Alcor (though actually a multiple-star system), but it is not known for sure whether Mizar and Alcor are gravitationally bound. Since the beginning of the 1780s, both professional and amateur double star observers have telescopically measured the distances and angles between d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
112 Herculis
112 Herculis is a binary star system in the northern constellation of Hercules. It is dimly visible to the naked eye with a combined apparent visual magnitude of 5.43. The secondary component is about two magnitudes fainter than the primary star. The distance to this system is approximately 415 light years based on parallax measurements. It is drifting closer to the Sun with a radial velocity of −20 km/s. The binary character of this system was discovered by W. F. Meyer in 1926. By measuring the variation in velocity of the primary component, he determined an orbital period of 6.3624 days. K. Osawa in 1959 found a stellar classification of A4 III for the pair. W. P. Bidelman observed that the primary has unusually strong lines of ionized phosphorus, and it was assigned to the class of peculiar manganese stars by W. L. W. Sargent and L. Searle in 1962, with a resulting spectral type of B9. No evidence was found for a strong magnetic field by P. S. C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Omicron Herculis
Omicron Herculis, Latinized from o Herculis, is a star in the constellation Hercules. It used to be called Masym ("the wrist"), but this name was transferred to Lambda Herculis. Properties Omicron Herculis is a B9.5III star approximately 106 pc from the Earth. It has an apparent magnitude of 3.83. The star radiates with a bluish-white hue, and has a luminosity approximately 355 times as bright as the Sun. Omicron Herculis is 3.49 solar masses. Stellar evolutionary caclulations show that it has just left the main sequence. Omicron Herculis is an eruptive variable of the Gamma Cassiopeiae class, which are rapidly rotating B-class stars with mass outflow. It has a projected rotational velocity of 194 km/s. Some sources list Omicron Herculis as being both spectroscopic and an interferometric binary star with a separation of about 60 milliarcseconds, although the companion star has not been confirmed. Omicron Hercules is notable for residing close to the coord ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mu Herculis
Mu Herculis (μ Herculis) is a nearby quadruple star system about 27.1 light years from Earth in the constellation Hercules (constellation), Hercules. Its main star, Mu Herculis A is fairly similar to the Sun although more highly stellar evolution, evolved with a stellar classification of G5 IV. Since 1943, the stellar spectrum, spectrum of this star has served as one of the stable anchor points by which other stars are classified. Its mass is about 1.1 times that of the Sun, and it is beginning to expand to become a giant. Etymology In the catalogue of stars in the ''Calendarium of Al Achsasi Al Mouakket'', this star was designated ''Marfak Al Jathih Al Aisr'', which was translated into Latin as ''Cubitum Sinistrum Ingeniculi'', meaning ''the left elbow of kneeling man''. In Chinese astronomy, Chinese, (), the ''Heavenly Market enclosure, Left Wall of Heavenly Market Enclosure'', refers to an asterism which represents eleven old states in China, mar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lambda Herculis
Lambda Herculis (λ Herculis. abbreviated Lambda Her, λ Her), formally named Maasym , is a star in the constellation of Hercules. From parallax measurements taken during the Gaia mission, it is approximately 393 light-years from the Sun. Nomenclature ''λ Herculis'' ( Latinised to ''Lambda Herculis'') is the star's Bayer designation. It bore the traditional name ''Maasym'', from the Arabic مِعْصَم ''miʽṣam'' "wrist". In 2016, the International Astronomical Union organized a Working Group on Star Names (WGSN) to catalogue and standardize proper names for stars. The WGSN approved the name ''Maasym'' for this star on 12 September 2016 and it is now so included in the List of IAU-approved Star Names. In Chinese, (), meaning '' Left Wall of Heavenly Market Enclosure'', refers to an asterism which represents eleven old states in China and which is marking the left borderline of the enclosure, consisting of Lambda Herculis, Delta Herculis, Mu Herculis, Omicron Hercul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asterism (astronomy)
An asterism is an observed pattern or group of stars in the sky. Asterisms can be any identified pattern or group of stars, and therefore are a more general concept than the formally defined 88 constellations. Constellations are based on asterisms, but unlike asterisms, constellations outline and today completely divide the sky and all its celestial objects into regions around their central asterisms. For example, the asterism known as the Big Dipper comprises the seven brightest stars in the constellation Ursa Major. Another is the asterism of the Southern Cross, within the constellation of Crux. Asterisms range from simple shapes of just a few stars to more complex collections of many stars covering large portions of the sky. The stars themselves may be bright naked-eye objects or fainter, even telescopic, but they are generally all of a similar brightness to each other. The larger brighter asterisms are useful for people who are familiarizing themselves with the night sky. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heavenly Market Enclosure
The Heavenly Market Enclosure (天市垣, ''Tian Shi Yuan''), is one of the ''San Yuan'' or Three enclosures Traditional Chinese astronomy has a system of dividing the celestial sphere into asterisms or constellations, known as "officials" ( Chinese ''xīng guān''). The Chinese asterisms are generally smaller than the constellations of Hellenistic .... Stars and constellations of this group are visible during late summer and early autumn in the Northern Hemisphere (late winter and early spring in the Southern). The Summer Triangle lies directly to the northeast. Asterisms The asterisms are : See also * Twenty-eight mansions * Summer Triangle Chinese constellations {{china-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chinese Astronomy
Astronomy in China has a long history stretching from the Shang dynasty, being refined over a period of more than 3,000 years. The ancient Chinese people have identified stars from 1300 BCE, as Chinese star names later categorized in the twenty-eight mansions have been found on oracle bones unearthed at Anyang, dating back to the mid-Shang dynasty. The core of the "mansion" (宿 ''xiù'') system also took shape around this period, by the time of King Wu Ding (1250–1192 BCE). Detailed records of astronomical observations began during the Warring States period (fourth century BCE) and flourished from the Han period onward. Chinese astronomy was equatorial, centered on close observation of circumpolar stars, and was based on different principles from those in traditional Western astronomy, where heliacal risings and settings of zodiac constellations formed the basic ecliptic framework. Joseph Needham has described the ancient Chinese as the most persistent and accurate obser ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the Roman Republic it became the dominant language in the Italian region and subsequently throughout the Roman Empire. Even after the fall of Western Rome, Latin remained the common language of international communication, science, scholarship and academia in Europe until well into the 18th century, when other regional vernaculars (including its own descendants, the Romance languages) supplanted it in common academic and political usage, and it eventually became a dead language in the modern linguistic definition. Latin is a highly inflected language, with three distinct genders (masculine, feminine, and neuter), six or seven noun cases (nominative, accusative, genitive, dative, ablative, and vocative), five declensions, four verb conjuga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Al Achsasi Al Mouakket
Muḥammad al-Akhṣāṣī al-Muwaqqit ( ar, محمد الاخصاصي الموقت) was an Egyptian astronomer whose and catalogue of stars, ('Pearls of brilliance upon the solar operations'), was written at Cairo about 1650. Al-Akhsasi was a shaykh, a learned elder, of the Grand Mosque of the university of Cairo, where his name ''al- Muwaqqit'' reflected his position regulating the times and hours at the mosque. His name Akhsasi connects him in origin to a village in the Faiyum, southwest of Cairo. No copies of his book were known to Western astronomers or historians of science The history of science covers the development of science from ancient times to the present. It encompasses all three major branches of science: natural, social, and formal. Science's earliest roots can be traced to Ancient Egypt and Mesop ... until 1895;Knobel 1895. thus he did not appear in the standard French and English bibliographies and library catalogues of the 19th century. Notes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multiple Star
A star system or stellar system is a small number of stars that orbit each other, bound by gravitational attraction. A large group of stars bound by gravitation is generally called a ''star cluster'' or ''galaxy'', although, broadly speaking, they are also star systems. Star systems are not to be confused with planetary systems, which include planets and similar bodies (such as comets). A star system of two stars is known as a ''binary star'', ''binary star system'' or ''physical double star''. If there are no tidal effects, no perturbation from other forces, and no transfer of mass from one star to the other, such a system is stable, and both stars will trace out an elliptical orbit around the barycenter of the system indefinitely. ''(See Two-body problem)''. Examples of binary systems are Sirius, Procyon and Cygnus X-1, the last of which probably consists of a star and a black hole. Multiple star systems A multiple star system consists of three or more stars that appear f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |