|
Sarawak Malay
Sarawak Malay ( Standard Malay: ''Bahasa Melayu Sarawak'' or ''Bahasa Sarawak'', Jawi: ''بهاس ملايو سراوق'', Sarawak Malay: ''Kelakar Sarawak'') is a Malayic language native to the State of Sarawak. It is a common language used by natives of Sarawak. This variant is related to Bruneian Malay, spoken in the districts of Limbang and Lawas (Sarawak) and bears strong similarities with Sanggau, Sintang and Sekadau Malay spoken in the northern part of the West Kalimantan province in Indonesia. There is some debate on whether it is a vernacular variety of Malay or a separate language altogether. It is more similar to Ibanic languages compared to the Malay dialects of Sumatra and the Malayan Peninsula, and is different enough from standard Malay that speakers outside of Sarawak are often unable to understand it without prior study.. Dialects According to Asmah Haji Omar (1993), Sarawak Malay can be divided into three dialects which are: * Kuching * Saribas * Sib ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sarawak
Sarawak (; ) is a state of Malaysia. The largest among the 13 states, with an area almost equal to that of Peninsular Malaysia, Sarawak is located in northwest Borneo Island, and is bordered by the Malaysian state of Sabah to the northeast, Kalimantan (the Indonesian portion of Borneo) to the south, and Brunei in the north. The capital city, Kuching, is the largest city in Sarawak, the economic centre of the state, and the seat of the Sarawak state government. Other cities and towns in Sarawak include Miri, Sibu, and Bintulu. As of 2021, the population of Sarawak was estimated to be around 2.45 million. Sarawak has an equatorial climate with tropical rainforests and abundant animal and plant species. It has several prominent cave systems at Gunung Mulu National Park. Rajang River is the longest river in Malaysia; Bakun Dam, one of the largest dams in Southeast Asia, is located on one of its tributaries, the Balui River. Mount Murud is the highest point in the state. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malay Language
Malay (; ms, Bahasa Melayu, links=no, Jawi: , Rencong: ) is an Austronesian language that is an official language of Brunei, Indonesia, Malaysia, and Singapore, and that is also spoken in East Timor and parts of the Philippines and Thailand. Altogether, it is spoken by 290 million people (around 260 million in Indonesia alone in its own literary standard named "Indonesian") across Maritime Southeast Asia. As the or ("national language") of several states, Standard Malay has various official names. In Malaysia, it is designated as either ("Malaysian Malay") or also ("Malay language"). In Singapore and Brunei, it is called ("Malay language"). In Indonesia, an autonomous normative variety called (" Indonesian language") is designated the ("unifying language" or lingua franca). However, in areas of Central to Southern Sumatra, where vernacular varieties of Malay are indigenous, Indonesians refer to the language as , and consider it to be one of their regiona ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Languages Of Malaysia
The indigenous languages of Malaysia belong to the Mon-Khmer and Malayo-Polynesian families. The national, or official, language is Malay which is the mother tongue of the majority Malay ethnic group. The main ethnic groups within Malaysia are the Malay people, Han Chinese people and Tamil people, with many other ethnic groups represented in smaller numbers, each with its own languages. The largest native languages spoken in East Malaysia are the Iban, Dusunic, and Kadazan languages. English is widely understood and spoken within the urban areas of the country; the English language is a compulsory subject in primary and secondary education. It is also the main medium of instruction within most private colleges and private universities. English may take precedence over Malay in certain official contexts as provided for by the National Language Act, especially in the states of Sabah and Sarawak, where it may be the official working language. Furthermore, the law of Malaysi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agglutinative Languages
An agglutinative language is a type of synthetic language with morphology that primarily uses agglutination. Words may contain different morphemes to determine their meanings, but all of these morphemes (including stems and affixes) tend to remain unchanged after their unions, although this is not a rule: for example, Finnish is a typical agglutinative language, but morphemes are subject to (sometimes unpredictable) consonant alternations called consonant gradation. Despite the occasional outliers, agglutinative languages tend to have more easily deducible word meanings if compared to fusional languages, which allow unpredictable modifications in either or both the phonetics or spelling of one or more morphemes within a word. This usually results in a shortening of the word, or it provides easier pronunciation. Overview Agglutinative languages have generally one grammatical category per affix while fusional languages have multiple. The term was introduced by Wilhelm von Humbold ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
10125/33163
1 (one, unit, unity) is a number representing a single or the only entity. 1 is also a numerical digit and represents a single unit of counting or measurement. For example, a line segment of ''unit length'' is a line segment of length 1. In conventions of sign where zero is considered neither positive nor negative, 1 is the first and smallest positive integer. It is also sometimes considered the first of the infinite sequence of natural numbers, followed by 2, although by other definitions 1 is the second natural number, following 0. The fundamental mathematical property of 1 is to be a multiplicative identity, meaning that any number multiplied by 1 equals the same number. Most if not all properties of 1 can be deduced from this. In advanced mathematics, a multiplicative identity is often denoted 1, even if it is not a number. 1 is by convention not considered a prime number; this was not universally accepted until the mid-20th century. Additionally, 1 is the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kaipuleohone
Kaipuleohone is a digital ethnographic archive that houses audio and visual files, photographs, as well as hundreds of textual material such as notes, dictionaries, and transcriptions relating to small and endangered languages. The archive is stored in the ScholarSpace repository of the University of Hawai‘i at Mānoa and maintained by the Department of Linguistics of the University's College of Languages, Linguistics and Literature. Kaipuleohone was established by Nick Thieberger in 2008. It is a member of thDigital Endangered Languages and Musics Archiving Network(DELAMAN). The term ''kaipuleohone'' means 'gourd of sweet words' and symbolizes the impression of an accumulation of language material. Kaipuleohone comprises several collections including Kaipuleohone Audio Files, the Bickerton Collection, the Blust Collection, the Bradshaw Collection, and the Sato Collection. The archive director is Andrea L. Berez-Kroeker Andrea Berez-Kroeker is a documentary linguist and profess ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Melanau Languages
Melanau or ''A-Likou'' (meaning River people in Mukah dialect) is an ethnic group indigenous to Sarawak, Malaysia. They are among the earliest settlers of Sarawak. They speak in the Melanau language, which is a part of the North Bornean branch of Malayo-Polynesian languages. Origins In the 19th century, the Melanaus settled in scattered communities along the main tributaries of the Rajang River in Central Sarawak. they like to be known as Melanau or A-Likou. For most Melanau, the word ' dayak' is inappropriate for them as it was a word used by the westerners for the inhabitant of Borneo because Melanau people already have their own identity and culture as A-Llikou (Melanau). Melanau or problematic Kajang-speaking tribes such as the Sekapan, the Rajang, the Tanjung, and the Kanowit gradually moved and assimilated into Dayak migrations settling in the Rajang. The Melanau people were regarded as a sub-group of the purported Klemantan people. Today the Punan (or Punan Bah) peopl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indonesian Language
Indonesian ( ) is the official language, official and national language of Indonesia. It is a standard language, standardized variety (linguistics), variety of Malay language, Malay, an Austronesian languages, Austronesian language that has been used as a lingua franca in the multilingual Indonesian archipelago for centuries. Indonesia is the fourth most list of countries by population, populous nation in the world, with over 270 million inhabitants—of which the majority speak Indonesian, which makes it one of the most List of languages by total number of speakers, widely spoken languages in the world.James Neil Sneddon. ''The Indonesian Language: Its History and Role in Modern Society''. UNSW Press, 2004. Most Indonesians, aside from speaking the national language, are fluent in at least one of the more than 700 indigenous languages of Indonesia, local languages; examples include Javanese language, Javanese and Sundanese language, Sundanese, which are commonly used at home a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aboriginal Malay
The term Proto-Malay, which translates to ''Melayu Asli'' (aboriginal Malay) or ''Melayu Purba'' (ancient Malay) or ''Melayu Tua'' (old Malay), refers to Austronesian speakers, possibly from mainland Asia, who moved to the Malay peninsula and Malay archipelago in a long series of migrations between 2500 and 1500 BC, and in one model the first of two migrations of early Malay speakers, before that of the Deutero-Malays. The Proto-Malays are the ancestors of the Malays in the modern Malaysia and Indonesia. The Proto-Malays are believed to be seafarers knowledgeable in oceanography and possessing advanced fishing as well as basic agricultural skills. Over the years, they settled in various places and adopted various customs and religions as a result of acculturation and inter-marriage with most of the people they come in contact with Orang Asli tribes such as the Semang and Senoi peoples. Origin The ''Encyclopedia of Malaysia: Early History'' has pointed out three theories of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glottal Stop
The glottal plosive or stop is a type of consonantal sound used in many spoken languages, produced by obstructing airflow in the vocal tract or, more precisely, the glottis. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents this sound is . As a result of the obstruction of the airflow in the glottis, the glottal vibration either stops or becomes irregular with a low rate and sudden drop in intensity. Features Features of the glottal stop: * It has no phonation, as there is no airflow through the glottis. It is voiceless, however, in the sense that it is produced without vibration of the vocal cords. Writing In the traditional Romanization of many languages, such as Arabic, the glottal stop is transcribed with the apostrophe or the symbol ʾ, which is the source of the IPA character . In many Polynesian languages that use the Latin alphabet, however, the glottal stop is written with a rotated apostrophe, (called '' ‘okina'' in Hawaiian and S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
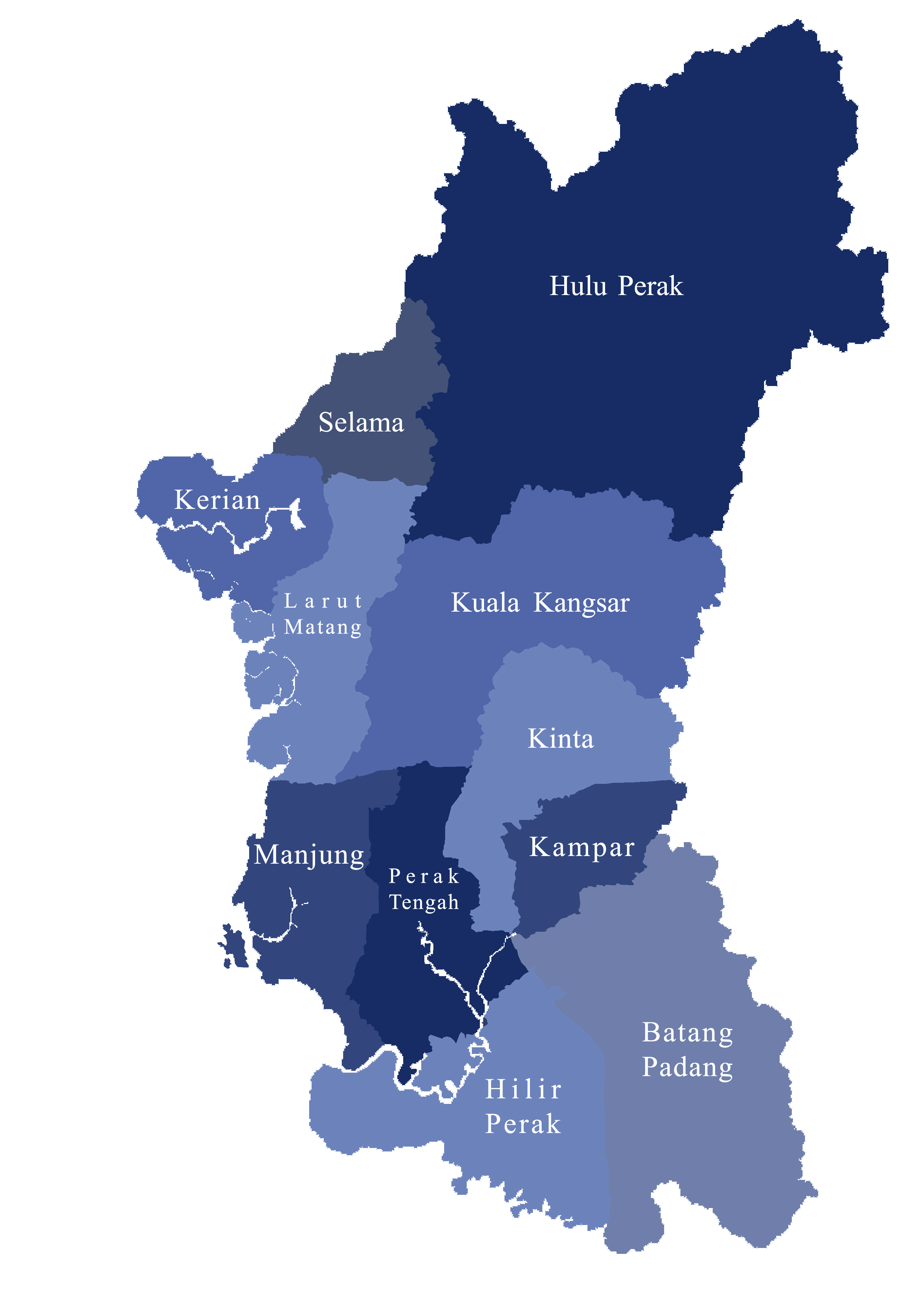
Perak Malay
Perak Malay ( Standard Malay: ''bahasa Melayu Perak''; Jawi script: بهاس ملايو ڤيراق) is one of the Malay dialects spoken within the state of Perak, Malaysia. Although it is neither the official language nor the standard dialect in the whole state of Perak, its existence which co-exists with other major dialects in the state of Perak still plays an important role in maintaining the identity of Perak. In spite of the fact that there are five main dialects traditionally spoken in Perak, only one of which is intended by the name "Perak Malay". There are subtle phonetic, syntactic and lexical distinctions from other major Malay dialects. Perak Malay can be divided into two sub-dialects, Kuala Kangsar and Perak Tengah, named after the '' daerah'' (districts) where they are predominantly spoken. Classification Linguistically, the Malay dialects spoken in the state of Perak are diverse. In fact, there is still no definite classification of the type of Malay dialects used ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Singlish
Singlish (a portmanteau of ''Singapore'' and '' English'') is an English-based creole language spoken in Singapore. Singlish arose out of a situation of prolonged language contact between speakers of many different languages in Singapore, including Hokkien, Malay, Teochew, Cantonese and Tamil. Singlish originated with the arrival of the British and the establishment of English-medium education in Singapore. Elements of English quickly filtered out of schools and onto the streets, resulting in the development of a pidgin language spoken by non-native speakers as a lingua franca used for communication between speakers of the many different languages used in Singapore. Singlish evolved mainly among the working classes who learned elements of English without formal schooling, mixing in elements of their native languages. After some time, this new pidgin language, now combined with substantial influences from Indian English, Peranakan, southern varieties of Chinese, Malay ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




_(14778446871).jpg)