|
Santiago Tuxtla
Santiago Tuxtla is a small city and municipality in the Los Tuxtlas region of southern Veracruz, Mexico. The area was originally part of lands granted to Hernán Cortés by the Spanish Crown in 1531. The city was founded in 1525, but it did not gain municipal status until 1932. Today, the municipality is poor and agricultural, but is home to several unique traditions such as the Santiago Tuxtla Fair and the Acarreo de Niño Dios, when images of the Child Jesus are carried in procession several times during the Christmas season. It is also home to the Museo Regional Tuxteco (Tuxtla Regional Museum) which houses much of the area's Olmec artifacts, including a number of colossal heads and other monumental stone works. The city's main plaza hosts the largest Olmec colossal head in Mexico, thus making it famous. The city The city of Santiago Tuxtla is centered on a large square called Parque Juarez, which contains the largest of the Olmec colossal heads in Mexico, La Corbata. The oth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Administrative Divisions Of Mexico
The United Mexican States ( es, Estados Unidos Mexicanos) is a federal republic composed of 32 federal entities: 31 states and Mexico City, an autonomous entity. According to the Constitution of 1917, the states of the federation are free and sovereign in all matters concerning their internal affairs. Each state has its own congress and constitution. Federal entities of Mexico States Roles and powers of the states The states of the Mexican Federation are free, sovereign, autonomous and independent of each other. They are free to govern themselves according to their own laws; each state has a constitution that cannot contradict the federal constitution, which covers issues of national competence. The states cannot make alliances with other states or any independent nation without the consent of the whole federation, except those related to defense and security arrangements necessary to keep the border states secure in the event of an invasion. The political organizat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tres Zapotes
Tres Zapotes is a Mesoamerican archaeological site located in the south-central Gulf Lowlands of Mexico in the Papaloapan River plain. Tres Zapotes is sometimes referred to as the third major Olmec capital (after San Lorenzo Tenochtitlán and La Venta), but the Olmec phase is only a portion of the site's history, which continued through the Epi-Olmec and Classic Veracruz cultural periods. The 2000-year existence of Tres Zapotes as a cultural center is unusual, if not unique, in Mesoamerica.Pool, p. 250. Location The site is located near the present-day village of Tres Zapotes, west of Santiago Tuxtla, Veracruz at the western edge of the Los Tuxtlas Mountains on the banks of the Rio Hueyapan (a small stream). The area is a transition point between the Los Tuxtlas Mountains and the Papaloapan River delta and allowed the inhabitants to take advantage of the forested uplands as well as the swamps and streams of the flatlands. Scarcely to the east stands Cerro el Vigía, an extinc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Huapango
is a family of Mexican music styles. The word likely derives from the Nahuatl word that literally means 'on top of the wood', alluding to a wooden platform on which dancers perform dance steps. It is interpreted in different forms, the most common being the classic interpreted by a trio of musicians (); the interpreted by a group (); and the , which can be performed by a large group of musicians. () The classical brings together a violin, a and a . The classical is characterized by a complex rhythmic structure mixing duple and triple metres which reflect the intricate steps of the dance. When the players sing (in a duet, in a falsetto tone), the violin stops, and the (the rhythm provided by heels hitting the floor) softens. The is danced by men and women as couples. A very popular is , in which two singers alternate pert and funny repartées. Huapango arribeño or son arribeño is a style of music played in the "zona media" region (part of San Luis Potosi, Qu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Son (music)
Son cubano is a genre of music and dance that originated in the highlands of eastern Cuba during the late 19th century. It is a syncretic genre that blends elements of Spanish and African origin. Among its fundamental Hispanic components are the vocal style, lyrical metre and the primacy of the tres, derived from the Spanish guitar. On the other hand, its characteristic clave rhythm, call and response structure and percussion section ( bongo, maracas, etc.) are all rooted in traditions of Bantu origin. Around 1909 the son reached Havana, where the first recordings were made in 1917. This marked the start of its expansion throughout the island, becoming Cuba's most popular and influential genre. While early groups had between three and five members, during the 1920s the ''sexteto'' (sextet) became the genre's primary format. By the 1930s, many bands had incorporated a trumpet, becoming ''septetos'', and in the 1940s a larger type of ensemble featuring congas and piano became th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Huasteca
La Huasteca is a geographical and cultural region located partially along the Gulf of Mexico and including parts of the states of Tamaulipas, Veracruz, Puebla, Hidalgo, San Luis Potosí, Querétaro and Guanajuato. It is roughly defined as the area in which the Huastec people had influence when their civilization was at its height during the Mesoamerican period. Today, the Huastecs occupy only a fraction of this region with the Nahua people now the most numerous indigenous group. However, those who live in the region share a number of cultural traits such as a style of music and dance, along with religious festivals such as Xantolo. Geography and environment Historically and ethnically, the Huasteca region is defined by the area dominated by the Huastecs at their height. The actual extension of the region is somewhat disputed as well as how it should be sub-divided. Geographically it has been defined as from the Sierra Madre Oriental to the Gulf of Mexico with the Sierra de T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
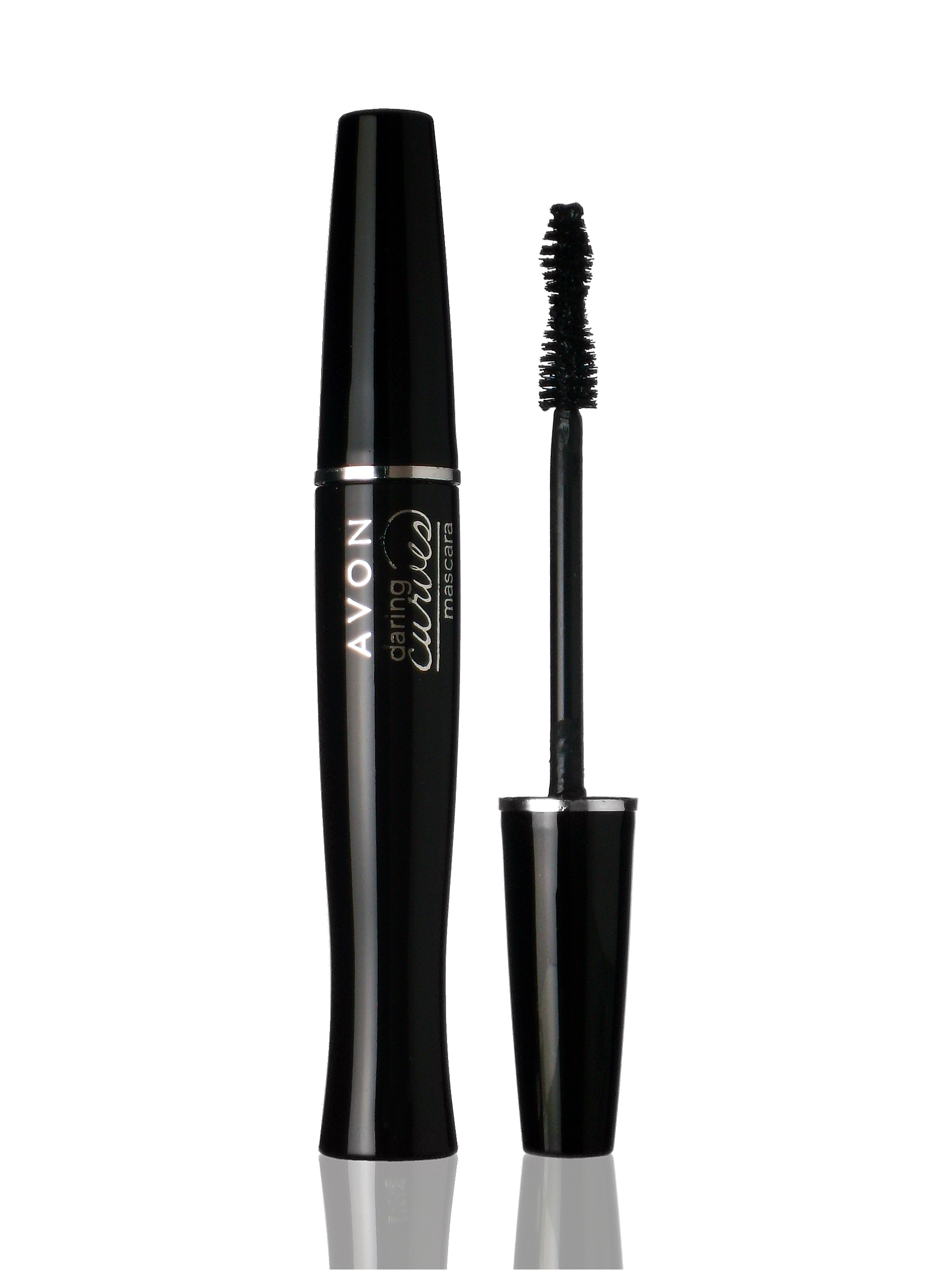
Mascara En Santiago Tuxtla
Mascara is a cosmetic commonly used to enhance the upper and lower eyelashes. It is used to darken, thicken, lengthen, and/or define the eyelashes. Normally in one of three forms—liquid, powder, or cream—the modern mascara product has various formulas; however, most contain the same basic components of pigments, oils, waxes, and preservatives. The most common form of mascara is a liquid in a tube with an application brush. Definition The ''Collins English Dictionary'' defines ''mascara'' as "a cosmetic substance for darkening, lengthening, curling, coloring, and thickening the eyelashes, applied with a brush or rod." The ''Oxford English Dictionary'' (''OED'') adds that mascara is occasionally used on the eyebrows as well. The ''OED'' also references ''mascaro'' from works published in the late 19th century. In 1886, the ''Peck & Snyder Catalogue'' advertises, "Mascaro or Water Cosmetique... For darkening the eyebrow and moustaches without greasing them and making them p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
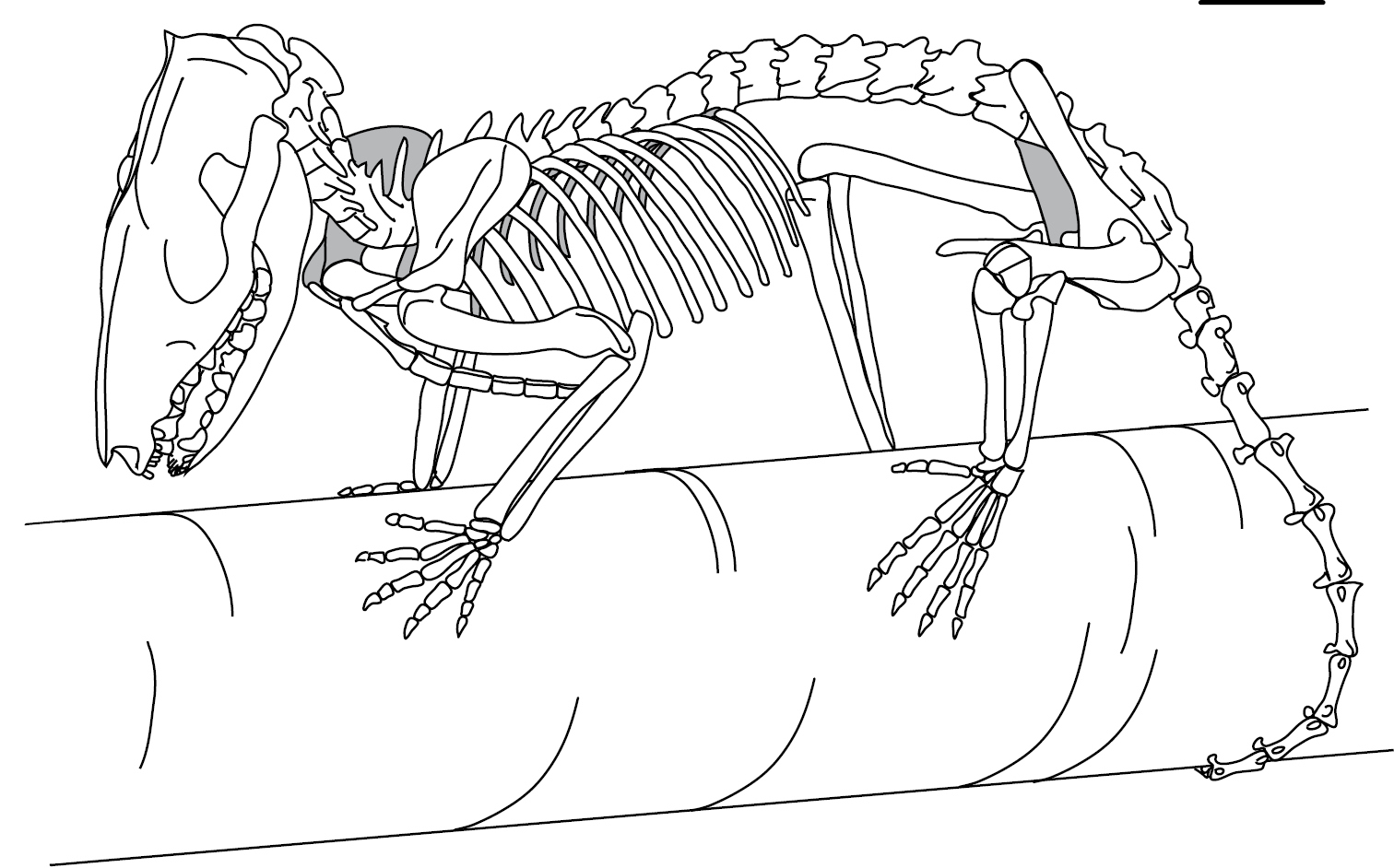
Opossum
Opossums () are members of the marsupial order Didelphimorphia () endemic to the Americas. The largest order of marsupials in the Western Hemisphere, it comprises 93 species in 18 genera. Opossums originated in South America and entered North America in the Great American Interchange following the connection of North and South America. The Virginia opossum is the only species found in the United States and Canada. It is often simply referred to as an opossum, and in North America it is commonly referred to as a possum (; sometimes rendered as ''possum'' in written form to indicate the dropped "o"). Possums should not be confused with the Australasian arboreal marsupials of suborder Phalangeriformes that are also called possums because of their resemblance to the Didelphimorphia. The opossum is typically a nonaggressive animal. Etymology The word ''opossum'' is borrowed from the Powhatan language and was first recorded between 1607 and 1611 by John Smith (as ''opassom'') ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Raccoon
The raccoon ( or , ''Procyon lotor''), sometimes called the common raccoon to distinguish it from other species, is a mammal native to North America. It is the largest of the procyonid family, having a body length of , and a body weight of . Its grayish coat mostly consists of dense underfur, which insulates it against cold weather. Three of the raccoon's most distinctive features are its extremely dexterous front paws, its facial mask, and its ringed tail, which are themes in the mythologies of the indigenous peoples of the Americas relating to the animal. The raccoon is noted for its intelligence, as studies show that it is able to remember the solution to tasks for at least three years. It is usually nocturnal and omnivorous, eating about 40% invertebrates, 33% plants, and 27% vertebrates. The original habitats of the raccoon are deciduous and mixed forests, but due to their adaptability, they have extended their range to mountainous areas, coastal marshes, and urban ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Papaloapan River
The Papaloapan River () is one of the main rivers of the Political divisions of Mexico, Mexican state of Veracruz (state), Veracruz. Its name comes from the Nahuatl ''papaloapan'' meaning "river of the Butterfly, butterflies". In 1517, Juan de Grijalva's expedition spotted the river, naming it Río de Alvarado.Diaz, B., 1963, The Conquest of New Spain, London: Penguin Books, The Papaloapan rises in the Sierra Madre de Oaxaca on the border between the states of Veracruz (state), Veracruz and Oaxaca. It is formed where the Santo Domingo River (Oaxaca), Santo Domingo River and the Valle Nacional River join to the southwest of San Juan Bautista Tuxtepec in Oaxaca. The Tonto River is another major tributary. The Papaloapan meanders for in a northeasterly direction through the coastal plain before draining into Alvarado Lagoon. The river basin covers , the second largest in Mexico, and contains 244 municipalities with a population of about 3.3 million people. The cities of San Juan Baut ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xalapa
Xalapa or Jalapa (, ), officially Xalapa-Enríquez (), is the capital city of the Mexican state of Veracruz and the name of the surrounding municipality. In the 2005 census the city reported a population of 387,879 and the municipality of which it serves as municipal seat reported a population of 413,136. The municipality has an area of 118.45 km2. Xalapa lies near the geographic center of the state and is the second-largest city in the state after the city of Veracruz to the southeast. Etymology The name ''Xalapa'' comes from the Classical Nahuatl roots (, 'sand') and (, 'place of water'), which means approximately 'spring in the sand'. It's classically pronounced in Nahuatl, although the final /n/ is often omitted. This was adopted into Spanish as ''Xalapa''. The complete name of the city is ''Xalapa-Enríquez'', bestowed in honor of a governor from the 19th century, Juan de la Luz Enríquez. The city's nickname, "City of Flowers" ( es, La ciudad de las flores), was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zapote
Zapote the fifth district of the San José canton, in the San José province of Costa Rica. It is one of the administrative units surrounding San José downtown (officially composed of the districts of El Carmen, Merced, Hospital and Catedral). The district is primarily residential, although there are some government buildings, standing out the Presidential House, seat of the government. Toponymy Named after the sapote tree and its fruits, which is written zapote in Spanish. Geography Zapote has an area of km² and an elevation of metres. It is located on the east of the canton, lying between Montes de Oca Canton and Curridabat Canton (bordering them to the north and to the east respectively). The district also borders San Francisco district to the south, and Catedral district to the west. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

_8.33.27.png)

_2.jpg)