|
Santa Fé, Veraguas
Santa Fe is the name of the capital of the Santa Fe District in the province of Veraguas in Panama. It has a population of 3200 and lies at an altitude of about 430m. Santa Fe lies close to the continental divide and just 60 km from the Mosquito Gulf at the Caribbean Sea, but is only connected to the Pacific coast with a paved road to the Pan-American Highway and the city of Santiago de Veraguas. Santa Fe is known throughout Panama for its natural environment. The Santa Fe national park surrounds the town in three directions, measuring 72.636 hectares. The park is home to at least 300 bird species, 300 species of orchids and rare flora and fauna. The Santa Maria River and its tributaries spring from the park. The air quality and forests make the area a popular tourist destination for outdoor activities such as hiking and bird watching. History After the Spanish conquests in the Americas, what is now the province of Veraguas was awarded to Columbus’ grandson Luís, who ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Provinces Of Panama
Panama is divided into ten provinces () and four provincial-level indigenous regions (Spanish: ''comarcas indígenas'', often shortened to ''comarcas''). The most recently established province is Panamá Oeste Province on 1 January 2014, and the most recently established indigenous region is Naso Tjër Di Comarca on 4 December 2020. There are also two indigenous regions within provinces that are considered equivalent to a ''corregimiento'' (municipality). Indigenous regions (''comarcas indígenas'') Provincial level Corregimiento-level See also * ISO 3166-2:PA * List of provinces and indigenous regions of Panama by Human Development Index References {{DEFAULTSORT:Provinces Of Panama Provinces of Panama, Subdivisions of Panama Lists of administrative divisions, Panama, Provinces Administrative divisions in North America, Panama 1 First-level administrative divisions by country, Provinces, Panama Panama geography-related lists ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caribbean Sea
The Caribbean Sea is a sea of the Atlantic Ocean, North Atlantic Ocean in the tropics of the Western Hemisphere, located south of the Gulf of Mexico and southwest of the Sargasso Sea. It is bounded by the Greater Antilles to the north from Cuba to Puerto Rico, the Lesser Antilles to the east from the Virgin Islands to Trinidad and Tobago, South America to the south from the Venezuela, Venezuelan coastline to the Colombia, Colombian coastline, and Central America and the Yucatán Peninsula to the west from Panama to Mexico. The Geopolitics, geopolitical region around the Caribbean Sea, including the numerous islands of the West Indies and adjacent coastal areas in the mainland of the Americas, is known as the Caribbean. The Caribbean Sea is one of the largest seas on Earth and has an area of about . The sea's deepest point is the Cayman Trough, between the Cayman Islands and Jamaica, at below sea level. The Caribbean coastline has many gulfs and bays: the Gulf of Gonâve, the Gul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
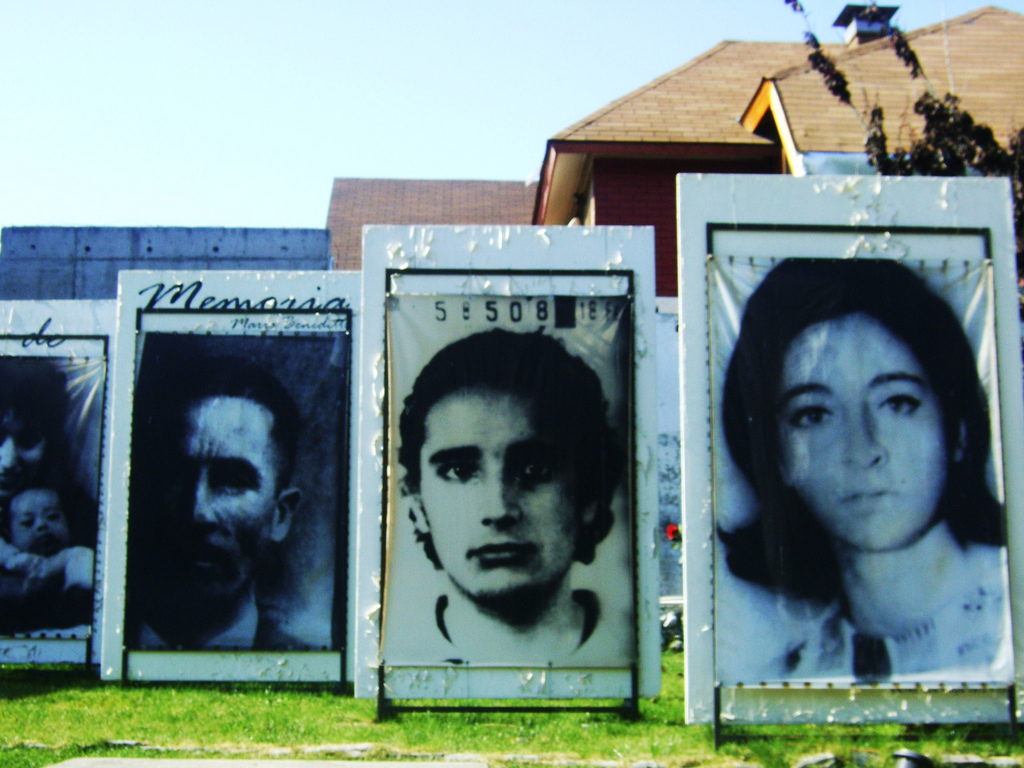
Forced Disappearance
An enforced disappearance (or forced disappearance) is the secret abduction or imprisonment of a person with the support or acquiescence of a State (polity), state followed by a refusal to acknowledge the person's fate or whereabouts with the intent of placing the victim outside the protection of the law. Often, forced disappearance implies murder whereby a victim is kidnapping, abducted, may be illegally prison, detained, and is often tortured during interrogation, ultimately killed, and the body disposed of secretly. The party committing the murder has plausible deniability as there is no evidence of the victim's death. Enforced disappearance was first recognized as a human rights issue in the 1970s as a result of Detenidos Desaparecidos, its use by military dictatorships in Latin America during the Dirty War. However, it has occurred all over the world. According to the Rome Statute of the International Criminal Court, which came into force on 1 July 2002, when committed as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Omar Torrijos
Omar Efraín Torrijos Herrera (February 13, 1929 – July 31, 1981) was the Panamanian military leader of Panama, as well as the Commander of the Panamanian National Guard from 1968 to his death in 1981. Torrijos was never officially the president of Panama, but instead held self-imposed and all-encompassing titles including "Maximum Leader of the Panamanian Revolution". Torrijos took power in a ''coup d'état'' and instituted a number of social reforms. Torrijos is best known for negotiating the 1977 Torrijos–Carter Treaties that eventually gave Panama full sovereignty over the Panama Canal. The two treaties guaranteed that Panama would gain control of the Panama Canal after 1999, ending the control of the canal that the U.S. had exercised since 1903. On December 31, 1999, the final phase of the treaty, the US relinquished control of the Panama Canal and all areas in what had been the Panama Canal Zone. His son Martín Torrijos was president from 2004 to 2009. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cooperative
A cooperative (also known as co-operative, coöperative, co-op, or coop) is "an autonomy, autonomous association of persons united voluntarily to meet their common economic, social and cultural needs and aspirations through a jointly owned and democratically-controlled wikt:Enterprise, enterprise". Cooperatives are democratically controlled by their members, with each member having one vote in electing the board of directors. They differ from Collective farming, collectives in that they are generally built from the bottom-up, rather than the top-down. Cooperatives may include: * Worker cooperatives: businesses owned and managed by the people who work there * Consumer cooperatives: businesses owned and managed by the people who consume goods and/or services provided by the cooperative * Producer cooperatives: businesses where producers pool their output for their common benefit ** e.g. Agricultural cooperatives * Purchasing cooperatives where members pool their purchasing power ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lope De Aguirre
Lope de Aguirre (; 8 November 1510 – 27 October 1561) was a Basque Spanish conquistador who was active in South America. Nicknamed ''El Loco'' ("the Madman"), he styled himself "Wrath of God." Aguirre is best known for his final expedition down the Amazon River in search of the mythical golden kingdom of El Dorado and Omagua. In 1561, Aguirre led a mutiny against the expedition's commander, Pedro de Orsúa, and declared his intent to return to Peru and overthrow Spain's colonial government. He drafted a letter that defied the Castilian monarch, King Philip II, by renouncing his Spanish vassalage and declared war upon the Habsburg monarch. Aguirre's expedition ended with his death by his own men upon confronting Royalist forces in present-day Venezuela. In the years since then he has been treated by historians as a symbol of cruelty and treachery in the early history of colonial Spanish America, and has become an antihero in literature, cinema and other arts. During the Span ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Veragua
The name Veragua or Veraguas was used for five Spanish colonial territorial entities in Central America, beginning in the 16th century during the Spanish colonization of the Americas. The term comes from the name given to the region by Central American indigenous peoples and was used to designate colonial territories in what is now Costa Rica, Nicaragua, and Panama. Originally, the name was written without an "s" (Veragua). However, the form Veraguas began to be officially used following two royal documents: the Royal Decree of August 20, 1739, and the Royal Mandate of June 20, 1751. Indigenous People in Veraguas Chronicles narrate stories of the indigenous groups encountered by the explorers, as they did not come across a solitary territory. On the contrary, these ethnicities posed challenges for the conquistadors because many of these groups were strong and resilient, as in the case of the Doraces, also known as Dorás, Dorces, Dorados, or Dorasques. The Doraces, also known ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duchy Of Veragua
The Duchy of Veragua () is a hereditary title in the Peerage of Spain. It was also a Spanish hereditary domain created in 1537 in the reign of King Charles I in a small section of the territory of Veragua (''Gobernación de Veragua'', which had been created in 1502 and extended along the Caribbean coasts of present-day Nicaragua, Costa Rica, and Panama as far to the east as the Río Belén). This new lordship was granted by the Crown to Don Luis Colón y Toledo, grandson of the discoverer Christopher Columbus, along with the title of Duke of Veragua and Marquis of Jamaica. These are the only Spanish noble titles that did not originate from a royal concession but rather from a definitive settlement after a fierce legal dispute with the Crown. The case was arbitrated by Don Fray García de Loayza, Cardinal of Santa Susana, Bishop of Sigüenza, and confessor to the King. The Dukedom was a perfect square of twenty-five leagues on a side, extending towards the west from the mouth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Santiago De Veraguas
Santiago de Veraguas () is the capital of the province of Veraguas, in the Republic of Panama, and the district or municipality of the same name. Located in the countryside next to the Pan American Highway. Bounded on the north by San Francisco District, south by the District of Montijo, east by the District of Atalaya and west by the District of La Mesa. It has a population of approximately 60,000 inhabitants according to the data of the last census carried out in the Republic of Panama (2014). History The unclassified extinct Escoria language was spoken by indigenous peoples around present-day Santiago de Veraguas. Santiago was founded by the people of Montijo and Santa Fe in the 17th century, who gathered in this place, decided to found a city that served as the starting center dispatches. It was established south of the Martin Grande river commonly called Los Chorros. Santiago did not exist in 1606 when the Bishop of Panama, Don Antonio Calderon, wrote his account of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pan-American Highway
The Pan-American Highway is a vast network of roads that stretches about 30,000 kilometers (about 19,000 miles) from Prudhoe Bay, Alaska, in the northernmost part of North America to Ushuaia, Argentina, at the southern tip of South America. It is recognized as the longest road in the world. The highway connects 14 countries, including Canada, the United States, Mexico, Guatemala, El Salvador, Honduras, Nicaragua, Costa Rica, Panama, Colombia, Ecuador, Peru, Chile, and Argentina. No road in the U.S. or Canada is officially designated as part of the Pan-American Highway, which officially begins at the U.S.-Mexico border in Nuevo Laredo and runs south. The highway is interrupted at the Darién Gap, a dense rainforest area between Panama and Colombia. No road traverses the Gap, and no car ferries have operated in the area for decades; drivers often opt to send their car by cargo ship from one country to the other. Concept of the highway The highway was built in stages. The fir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pacific
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean, or, depending on the definition, to Antarctica in the south, and is bounded by the continents of Asia and Australia in the west and the Americas in the east. At in area (as defined with a southern Antarctic border), the Pacific Ocean is the largest division of the World Ocean and the hydrosphere and covers approximately 46% of Earth's water surface and about 32% of the planet's total surface area, larger than its entire land area ().Pacific Ocean . '' Britannica Concise.'' 2008: Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc. The centers of both the [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Golfo De Los Mosquitos
The Bay of Moskitia ( Spanish: ''Bahía de Mosquítia)'' is a large coastal inlet of the southwestern Caribbean Sea, located along the eastern Central American coast, or between the east and southeast coasts of the Moskitian Shore. The bay stretches from Punta Cacique, near Portobelo in Panama, southeastward to Cape Gracias a Dios. According to the 1832 Diccionario Geografico Universal, its entrance spans approximately 120 leagues (circa 570 km) with an inland reach of 48 leagues (around 230 km). The coast is generally low and highly indented, featuring several sub-bay and lagoons including Sandy Bay, Pearl Lagoon, Bluefields Bay, the Chiriqui Lagoon, etc. The Bay of Moskitia forests are the largest block of lowland forest on the Caribbean slope between Bocas del Toro and the San Blas Islands. The area is home to the entire population of the Geminis' dart frog and was identified as a Key Biodiversity Area in 2003. It is threatened by development for cattle and subsisten ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |