|
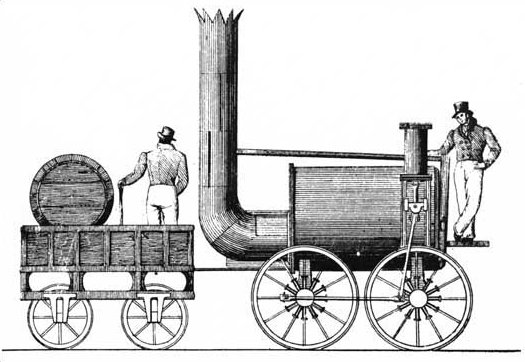
Sans Pareil (other)
''Sans Pareil'' is a steam locomotive built by Timothy Hackworth which took part in the 1829 Rainhill Trials on the Liverpool and Manchester Railway, held to select a builder of locomotives. The name is French and means 'peerless' or 'without equal'. Design While a capable locomotive for the day, its technology was somewhat antiquated compared to George and Robert Stephenson's '' Rocket'', the winner of the Rainhill Trials and the £500 prize money. Instead of the fire tube boiler of ''Rocket'', ''Sans Pareil'' had a double return flue. To increase the heating surface area, the two flues were joined by a U-shaped tube at the forward end of the boiler; the firebox and chimney were both positioned at the same end, one on either side. ''Sans Pareil'' had two cylinders, mounted vertically at the opposite end to the chimney, and driving one pair of driving wheels directly - the other pair were driven via connecting rods, in the typical steam locomotive fashion. Railhill ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Hedley
William Hedley (13 July 1779 – 9 January 1843) was born in Newburn, near Newcastle upon Tyne. He was one of the leading industrial engineers of the early 19th century, and was instrumental in several major innovations in early rail transport, railway development. While working as a 'colliery viewer, viewer' or manager at Wylam Colliery near Newcastle upon Tyne, he built the first practical steam locomotive which relied simply on the Rail adhesion, adhesion of iron wheels on iron rails. Early locomotives Before Hedley's time, such locomotives were far too heavy for the track that was then available. While most lines used cable haulage with stationary engines, various other schemes had been tried. William Chapman at the Butterley Company in 1812, attempted to use a steam engine which hauled itself along a cable, while, at the same company, Brunton had produced the even less successful "mechanical traveller", or Steam Horse locomotive, ''Steam Horse''. However, in 1812, Matthe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blastpipe
The blastpipe is part of the exhaust system of a steam locomotive that discharges exhaust steam from the cylinders into the smokebox beneath the chimney in order to increase the draught through the fire. History The primacy of discovery of the effect of directing the exhaust steam up the chimney as a means of providing draft through the fire is the matter of some controversy, Ahrons (1927) devoting significant attention to this matter. The exhaust from the cylinders on the first steam locomotive – built by Richard Trevithick – was directed up the chimney, and he noted its effect on increasing the draft through the fire at the time. At Wylam, Timothy Hackworth also employed a blastpipe on his earliest locomotives, but it is not clear whether this was an independent discovery or a copy of Trevithick's design. Shortly after Hackworth, George Stephenson also employed the same method, and again it is not clear whether that was an independent discovery or a copy of one of the other ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
LMS Royal Scot Class
The London, Midland and Scottish Railway (LMS) Royal Scot Class is a class of 4-6-0 express passenger locomotive introduced in 1927. Originally having parallel boilers, all members were later rebuilt with tapered type 2A boilers, and were in effect two classes. Background Until the mid-1920s, the LMS had followed the Midland Railway's small engine policy, which meant that it had no locomotives of sufficient power for its expresses on the West Coast Main Line. These trains were entrusted to pairs of LMS/MR Midland Compound 4-4-0s between Glasgow and , and a 4-6-0 locomotive of the LNWR Claughton Class, piloted by an LNWR George V 4-4-0, southwards to Euston station. The Operating and Motive Power Departments of the LMS were satisfied with the small engine policy. However, in 1926 the Chief Mechanical Engineer, Henry Fowler, began the design of a compound Pacific express locomotive. The management of the LMS, faced with disagreement between the CME and the other departments, o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gold Plating
Gold plating is a method of depositing a thin layer of gold onto the surface of another metal, most often copper or silver (to make silver-gilt), by chemical or electrochemical plating. This article covers plating methods used in the modern electronics industry; for more traditional methods, often used for much larger objects, see gilding. Types There are several types of gold plating used in the electronics industry: * ''Soft, pure gold plating'' is used in the semiconductor industry. The gold layer is easily soldered and wire bonded. Its Knoop hardness ranges between 60 and 85. The plating baths have to be kept free of contamination. * ''Soft, pure gold'' is deposited from special electrolytes. Entire printed circuit boards can be plated. This technology can be used for depositing layers suitable for wire bonding. * ''Bright hard gold on contacts'', with Knoop hardness between 120–300 and purity of 99.7–99.9% gold. Often contains a small amount of nickel and/or cobalt; ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crampton Locomotive
A Crampton locomotive is a type of steam locomotive designed by Thomas Russell Crampton and built by various firms from 1846. The main British builders were Tulk and Ley and Robert Stephenson and Company. Notable features were a low boiler and large driving wheels. The crux of the Crampton patent was that the single driving axle was placed behind the firebox, so that the driving wheels could be very large. This helped to give this design a low centre of gravity, so that it did not require a very broad-gauge track to travel safely at high speeds. Its wheel arrangement was usually or . Design variations Because the single driving axle was behind the firebox, Crampton locomotives usually had outside cylinders. However, some inside cylinder versions were built using indirect drive, then known as a ''jackshaft''. The inside cylinders drove a crankshaft located in front of the firebox and the crankshaft was connected to the driving wheels by outside rods. Some long-wheelbase s we ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Basel
, french: link=no, Bâlois(e), it, Basilese , neighboring_municipalities= Allschwil (BL), Hégenheim (FR-68), Binningen (BL), Birsfelden (BL), Bottmingen (BL), Huningue (FR-68), Münchenstein (BL), Muttenz (BL), Reinach (BL), Riehen (BS), Saint-Louis (FR-68), Weil am Rhein (DE-BW) , twintowns = Shanghai, Miami Beach , website = www.bs.ch Basel ( , ), also known as Basle ( ),french: Bâle ; it, Basilea ; rm, label= Sutsilvan, Basileia; other rm, Basilea . is a city in northwestern Switzerland on the river Rhine. Basel is Switzerland's third-most-populous city (after Zürich and Geneva) with about 175,000 inhabitants. The official language of Basel is (the Swiss variety of Standard) German, but the main spoken language is the local Basel German dialect. Basel is commonly considered to be the cultural capital of Switzerland and the city is famous for its many museums, including the Kunstmuseum, which is the first collection of art accessibl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Railway Museum
The National Railway Museum is a museum in York forming part of the Science Museum Group. The museum tells the story of rail transport in Britain and its impact on society. It is the home of the national collection of historically significant railway vehicles such as LNER Class A4 4468 Mallard, Mallard, GNR Stirling 4-2-2, Stirling Single, LMS Princess Coronation Class 6229 Duchess of Hamilton, Duchess of Hamilton and a Japanese Shinkansen, bullet train. In addition, the National Railway Museum holds a diverse collection of other objects, from a household recipe book used in George Stephenson's house to film showing a "People mover, never-stop railway" developed for the British Empire Exhibition. It has won many awards, including the European Museum of the Year Award in 2001. the museum is about to embark on a major site development. As part of the York Central redevelopment which will divert Leeman Road, the National Railway Museum will be building a new entrance building to c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shildon Locomotion Museum
Locomotion, previously known as Locomotion the National Railway Museum at Shildon, is a railway museum in Shildon, County Durham, England. The museum was renamed in 2017 when it became part of the Science Museum Group. Overview The museum was opened on 22 October 2004 by Prime Minister and local MP Tony Blair. Built at a cost of £11.3 million, it is based on the former "Timothy Hackworth Victorian Railway Museum". The museum is operated in partnership with Durham County Council and was expected to bring 60,000 visitors a year to the small town. However, during its first six months, the museum attracted 94,000 visits. Locomotion was shortlisted as one of the final five contenders in the Gulbenkian Prize, which is the largest arts prize in the United Kingdom. As part of the 2025 plans for the National Railway Museum, a second building will be built to house more of the wider collection. In addition, parts of the original museum including the coal drops will be restored having ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Hick (MP)
John Hick (2 July 1815 – 2 February 1894) was a wealthy English industrialist, art collector and Conservative Party (UK), Conservative Party politician who sat in the House of Commons of the United Kingdom, House of Commons from 1868 to 1880, he is associated with the improvement of steam-engines for cotton mills and the work of his firm Hick, Hargreaves and Co. universal in countries where fibre was Spinning (textiles), spun or fabrics Power loom, woven. Family Hick was the eldest son of Benjamin Hick (1790–1842), a civil and mechanical engineer responsible for improvements to the steam-engine, and his wife Elizabeth Routledge (1783–1826), daughter of William Routledge of Elvington, City of York, Elvington Yorkshire. Elizabeth's brother and Hick's uncle, Joshua Routledge (1773–1829) also an engineer living in Bolton, designed the ''Engineer's Improved Slide Rule'' and patented improvements to the Steam engine#Rotary steam engines, Rotary steam engine. Education and e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Science Museum (London)
The Science Museum is a major museum on Exhibition Road in South Kensington, London. It was founded in 1857 and is one of the city's major tourist attractions, attracting 3.3 million visitors annually in 2019. Like other publicly funded national museums in the United Kingdom, the Science Museum does not charge visitors for admission, although visitors are requested to make a donation if they are able. Temporary exhibitions may incur an admission fee. It is one of the five museums in the Science Museum Group. Founding and history The museum was founded in 1857 under Bennet Woodcroft from the collection of the Royal Society of Arts and surplus items from the Great Exhibition as part of the South Kensington Museum, together with what is now the Victoria and Albert Museum. It included a collection of machinery which became the ''Museum of Patents'' in 1858, and the ''Patent Office Museum'' in 1863. This collection contained many of the most famous exhibits of what is now t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chorley
Chorley is a town and the administrative centre of the wider Borough of Chorley in Lancashire, England, north of Wigan, south west of Blackburn, north west of Bolton, south of Preston and north west of Manchester. The town's wealth came principally from the cotton industry. In the 1970s, the skyline was dominated by factory chimneys, but most have now been demolished: remnants of the industrial past include Morrisons chimney and other mill buildings, and the streets of terraced houses for mill workers. Chorley is the home of the Chorley cake. History Toponymy The name ''Chorley'' comes from two Anglo-Saxon words, and , probably meaning "the peasants' clearing". (also or ) is a common element of place-name, meaning a clearing in a woodland; refers to a person of status similar to a freeman or a yeoman. Prehistory There was no known occupation in Chorley until the Middle Ages, though archaeological evidence has shown that the area around the town has been inhabited ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |