|
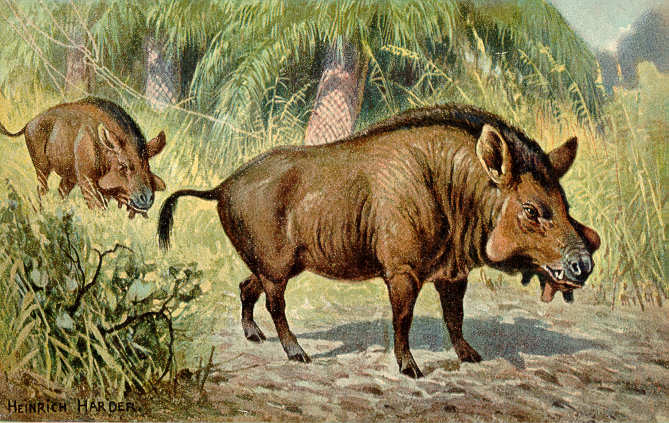
Sanitheriidae
Sanitheriidae were extinct family of suoid artiodactyl ungulates that were once widely distributed in Africa, Europe, and South Asia, existing from the Early Miocene to the Middle Miocene. Unlike pigs and peccaries, the dentition and limb morphology suggests the sanitheres were more carnivorous and cursorial. The dentition in particular is similar to early ruminant Ruminants (suborder Ruminantia) are ungulate, hoofed herbivorous grazing or browsing mammals that are able to acquire nutrients from plant-based food by Enteric fermentation, fermenting it in a specialized stomach prior to digestion, principally ...s. Only two genera are recognized '' Sanitherium'' and '' Diamantohyus''. References Prehistoric mammal families Miocene first appearances Suina {{paleo-eventoedungulate-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Suina
Suina (also known as Suiformes) is a suborder of omnivorous, non-ruminant artiodactyl mammals that includes the domestic pig and peccaries. A member of this clade is known as a suine. Suina includes the family Suidae, termed suids, known in English as pigs or swine, as well as the family Tayassuidae, termed tayassuids or peccaries. Suines are largely native to Africa, South America, and Southeast Asia, with the exception of the wild boar, which is additionally native to Europe and Asia and introduced to North America and Australasia, including widespread use in farming of the domestic pig subspecies. Suines range in size from the 55 cm (22 in) long pygmy hog to the 210 cm (83 in) long giant forest hog, and are primarily found in forest, shrubland, and grassland biomes, though some can be found in deserts, wetlands, or coastal regions. Most species do not have population estimates, though approximately two billion domestic pigs are used in farming, while sever ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Artiodactyl
The even-toed ungulates (Artiodactyla , ) are ungulates—hoofed animals—which bear weight equally on two (an even number) of their five toes: the third and fourth. The other three toes are either present, absent, vestigial, or pointing posteriorly. By contrast, odd-toed ungulates bear weight on an odd number of the five toes. Another difference between the two is that many other even-toed ungulates (with the exception of Suina) digest plant cellulose in one or more stomach chambers rather than in their intestine as the odd-toed ungulates do. Cetaceans (whales, dolphins, and porpoises) evolved from even-toed ungulates, and are therefore often classified under the same taxonomic branch because a species cannot outgrow its evolutionary ancestry; some modern taxonomists combine the two under the name Cetartiodactyla , while others opt to include cetaceans in the already-existing Artiodactyla. The roughly 270 land-based even-toed ungulate species include pigs, peccaries, hippopota ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Suidae
Suidae is a family of artiodactyl mammals which are commonly called pigs, hogs or swine. In addition to numerous fossil species, 18 extant species are currently recognized (or 19 counting domestic pigs and wild boars separately), classified into between four and eight genera. Within this family, the genus ''Sus'' includes the domestic pig, ''Sus scrofa domesticus'' or ''Sus domesticus'', and many species of wild pig from Europe to the Pacific. Other genera include babirusas and warthogs. All suids, or swine, are native to the Old World, ranging from Asia to Europe and Africa. The earliest fossil suids date from the Oligocene epoch in Asia, and their descendants reached Europe during the Miocene. Several fossil species are known and show adaptations to a wide range of different diets, from strict herbivory to possible carrion-eating (in Tetraconodontinae). Physical characteristics Suids belong to the order Artiodactyla, and are generally regarded as the living members of that or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prehistoric Mammal Families
Prehistory, also known as pre-literary history, is the period of human history between the use of the first stone tools by hominins 3.3 million years ago and the beginning of recorded history with the invention of writing systems. The use of symbols, marks, and images appears very early among humans, but the earliest known writing systems appeared 5000 years ago. It took thousands of years for writing systems to be widely adopted, with writing spreading to almost all cultures by the 19th century. The end of prehistory therefore came at very different times in different places, and the term is less often used in discussing societies where prehistory ended relatively recently. In the early Bronze Age, Sumer in Mesopotamia, the Indus Valley Civilisation, and ancient Egypt were the first civilizations to develop their own scripts and to keep historical records, with their neighbors following. Most other civilizations reached the end of prehistory during the following Iron Age. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ruminant
Ruminants (suborder Ruminantia) are ungulate, hoofed herbivorous grazing or browsing mammals that are able to acquire nutrients from plant-based food by Enteric fermentation, fermenting it in a specialized stomach prior to digestion, principally through microbial actions. The process, which takes place in the front part of the digestive system and therefore is called foregut fermentation, typically requires the fermented ingesta (known as cud) to be regurgitated and chewed again. The process of rechewing the cud to further break down plant matter and stimulate digestion is called rumination. The word "ruminant" comes from the Latin ''ruminare'', which means "to chew over again". The roughly 200 species of ruminants include both domestic and wild species. Ruminating mammals include cattle, all domesticated and wild bovines, goats, sheep, giraffes, deer, gazelles, and antelopes.Fowler, M.E. (2010).Medicine and Surgery of Camelids, Ames, Iowa: Wiley-Blackwell. Chapter 1 General Biolo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cursorial
A cursorial organism is one that is adapted specifically to run. An animal can be considered cursorial if it has the ability to run fast (e.g. cheetah) or if it can keep a constant speed for a long distance (high endurance). "Cursorial" is often used to categorize a certain locomotor mode, which is helpful for biologists who examine behaviors of different animals and the way they move in their environment. Cursorial adaptations can be identified by morphological characteristics (e.g. loss of lateral digits as in ungulate species), physiological characteristics, maximum speed, and how often running is used in life. There is much debate over how to define a cursorial animal specifically. The most accepted definitions include that a cursorial organism could be considered adapted to long-distance running at high speeds or has the ability to accelerate quickly over short distances. Among vertebrates, animals under 1 kg of mass are rarely considered cursorial, and cursorial behaviors ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carnivorous
A carnivore , or meat-eater (Latin, ''caro'', genitive ''carnis'', meaning meat or "flesh" and ''vorare'' meaning "to devour"), is an animal or plant whose food and energy requirements derive from animal tissues (mainly muscle, fat and other soft tissues) whether through hunting or scavenging. Nomenclature Mammal order The technical term for mammals in the order Carnivora is ''carnivoran'', and they are so-named because most member species in the group have a carnivorous diet, but the similarity of the name of the order and the name of the diet causes confusion. Many but not all carnivorans are meat eaters; a few, such as the large and small cats (felidae) are ''obligate'' carnivores (see below). Other classes of carnivore are highly variable. The Ursids, for example: While the Arctic polar bear eats meat almost exclusively (more than 90% of its diet is meat), almost all other bear species are omnivorous, and one species, the giant panda, is nearly exclusively herbivorous. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peccary
A peccary (also javelina or skunk pig) is a medium-sized, pig-like hoofed mammal of the family Tayassuidae (New World pigs). They are found throughout Central and South America, Trinidad in the Caribbean, and in the southwestern area of North America. They usually measure between in length, and a full-grown adult usually weighs about . They represent the closest relatives of the family Suidae, which contains pigs and relatives. Together Tayassuidae and Suidae are grouped in the Suina within the Artiodactyla (even toed ungulates). Peccaries are social creatures that live in herds. They eat roots, grubs, and a variety of foods. They can identify each other by their strong odors. A group of peccaries that travel and live together is called a "squadron". A squadron of peccaries averages between six and nine members. Peccaries first appeared in North America during the Miocene, and migrated into South America during the Pliocene-Pleistocene as part of the Great American Interchange ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Early Miocene
The Early Miocene (also known as Lower Miocene) is a sub-epoch of the Miocene Epoch made up of two stages: the Aquitanian and Burdigalian stages. The sub-epoch lasted from 23.03 ± 0.05 Ma to 15.97 ± 0.05 Ma (million years ago). It was preceded by the Oligocene epoch. As the climate started to get cooler, the landscape started to change. New mammals evolved to replace the extinct animals of the Oligocene epoch. The first members of the hyena and weasel family started to evolve to replace the extinct ''Hyaenodon'', entelodonts and bear-dogs. The chalicotheres survived the Oligocene epoch. A new genus of entelodont called ''Daeodon'' evolved in order to adapt to the new habitats and hunt the new prey animals of the Early Miocene epoch; it quickly became the top predator of North America. But it became extinct due to competition from '' Amphicyon'', a newcomer from Eurasia. ''Amphicyon'' bested ''Daeodon'' because the bear-dog Amphicyonidae is an extinct family of terrestr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Middle Miocene
The Middle Miocene is a sub-epoch of the Miocene Epoch made up of two stages: the Langhian and Serravallian stages. The Middle Miocene is preceded by the Early Miocene. The sub-epoch lasted from 15.97 ± 0.05 Ma to 11.608 ± 0.005 Ma (million years ago). During this period, a sharp drop in global temperatures took place. This event is known as the Middle Miocene Climate Transition. For the purpose of establishing European Land Mammal Ages The European Land Mammal Mega Zones (abbreviation: ELMMZ, more commonly known as European land mammal ages or ELMA) are zones in rock layers that have a specific assemblage of fossils (biozones) based on occurrences of fossil assemblages of Europe ... this sub-epoch is equivalent to the Astaracian age. External links GeoWhen Database - Middle Miocene .02 02 * * {{geochronology-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George Gaylord Simpson
George Gaylord Simpson (June 16, 1902 – October 6, 1984) was an American paleontologist. Simpson was perhaps the most influential paleontologist of the twentieth century, and a major participant in the Modern synthesis (20th century), modern synthesis, contributing ''Tempo and Mode in Evolution'' (1944), ''The Meaning of Evolution'' (1949) and ''The Major Features of Evolution'' (1953). He was an expert on extinct mammals and their intercontinental migrations. Simpson was extraordinarily knowledgeable about Mesozoic fossil mammals and fossil mammals of North and South America. He anticipated such concepts as punctuated equilibrium (in ''Tempo and Mode'') and dispelled the myth that the evolution of the horse was a linear process culminating in the modern ''Equus caballus''. He coined the word ''wikt:hypodigm, hypodigm'' in 1940, and published extensively on the Taxonomy (biology), taxonomy of fossil and extant mammals. Simpson was influentially, and incorrectly, opposed to Alf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.png)