|
Samuel Wyatt
Samuel Wyatt (8 September 1737, Weeford, Staffs. – London, 8 February 1807) was an English architect and engineer. A member of the Wyatt family, which included several notable 18th- and 19th-century English architects, his work was primarily in a neoclassical style. Career In his twenties, Wyatt was master carpenter and later Robert Adam's clerk of works at Kedleston Hall in Derbyshire, which was a landmark in English neoclassical architecture. He later worked with his brother James Wyatt on the Pantheon in Oxford Street, London. He designed neoclassical country houses such as Tatton Park in Cheshire, and Trinity House in London and Digswell House in Hertfordshire. Wyatt's career was diverse. He designed the Albion Mills in London, which was the first in the world to be powered by steam engines, and patented designs for cast iron bridges. He designed model farm buildings, cottages, and several lighthouses, including those at Dungeness, Longships and Flamborough Head. Between ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
England
England is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Wales to its west and Scotland to its north. The Irish Sea lies northwest and the Celtic Sea to the southwest. It is separated from continental Europe by the North Sea to the east and the English Channel to the south. The country covers five-eighths of the island of Great Britain, which lies in the North Atlantic, and includes over 100 smaller islands, such as the Isles of Scilly and the Isle of Wight. The area now called England was first inhabited by modern humans during the Upper Paleolithic period, but takes its name from the Angles, a Germanic tribe deriving its name from the Anglia peninsula, who settled during the 5th and 6th centuries. England became a unified state in the 10th century and has had a significant cultural and legal impact on the wider world since the Age of Discovery, which began during the 15th century. The English language, the Anglican Church, and Engli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Longships Lighthouse
Longships Lighthouse is an active 19th-century lighthouse about off the coast of Land's End in Cornwall, England. It is the second lighthouse to be built on Carn Bras, the highest of the Longships islets which rises above high water level. In 1988 the lighthouse was automated, and the keepers withdrawn. It is now remotely monitored from the Trinity House Operations & Planning Centre in Harwich, Essex. History In the second half of the 18th century, Trinity House was petitioned repeatedly by ship owners for a lighthouse to be built on one of the rocks off Land's End. In 1790 John Smeaton surveyed the area, and recommended either Wolf Rock or the Longships reef as potentially suitable locations. Trinity House sought a leaseholder, who would be responsible for building the tower and maintaining the light in return for the right to levy dues on passing ships. The lease was eventually granted, for a period of fifty years, to a Lieutenant Henry Smith (who had previously been invo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
James Watt
James Watt (; 30 January 1736 (19 January 1736 OS) – 25 August 1819) was a Scottish inventor, mechanical engineer, and chemist who improved on Thomas Newcomen's 1712 Newcomen steam engine with his Watt steam engine in 1776, which was fundamental to the changes brought by the Industrial Revolution in both his native Great Britain and the rest of the world. While working as an instrument maker at the University of Glasgow, Watt became interested in the technology of steam engines. He realised that contemporary engine designs wasted a great deal of energy by repeatedly cooling and reheating the cylinder. Watt introduced a design enhancement, the separate condenser, which avoided this waste of energy and radically improved the power, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness of steam engines. Eventually, he adapted his engine to produce rotary motion, greatly broadening its use beyond pumping water. Watt attempted to commercialise his invention, but experienced great financial di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
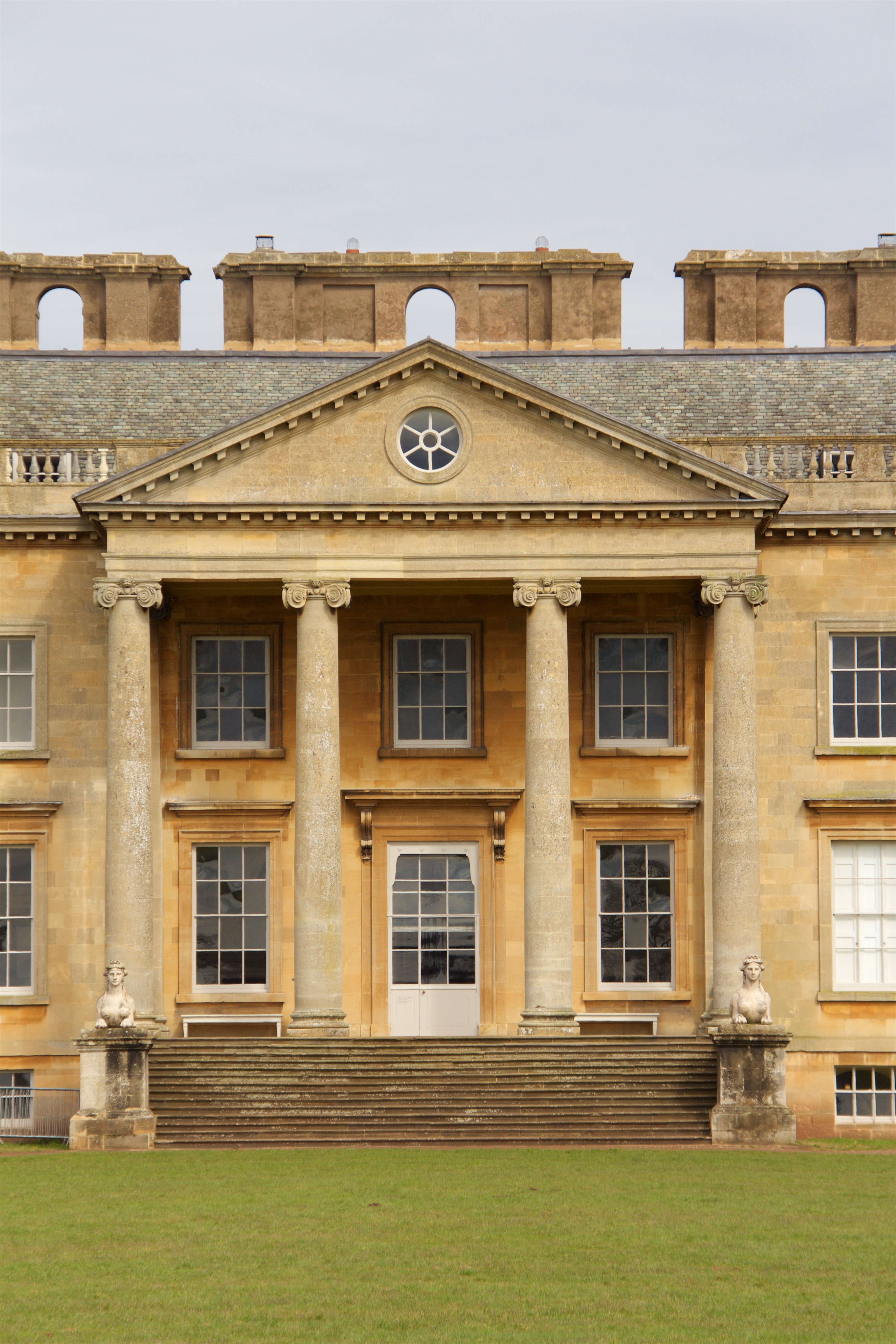
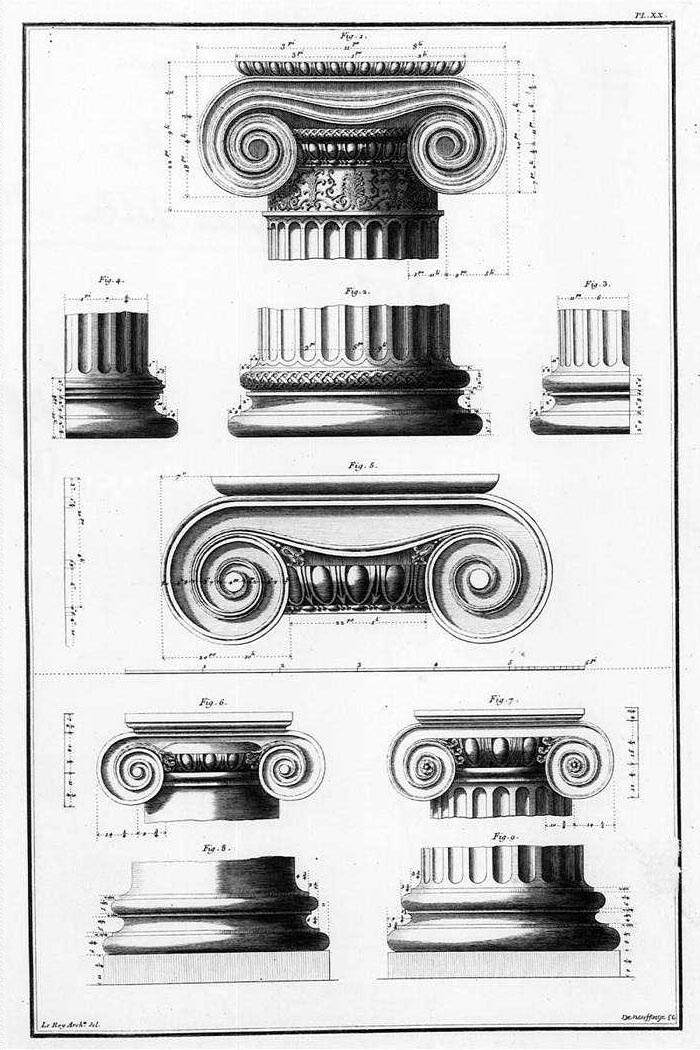
Ionic Column
The Ionic order is one of the three canonic orders of classical architecture, the other two being the Doric and the Corinthian. There are two lesser orders: the Tuscan (a plainer Doric), and the rich variant of Corinthian called the composite order. Of the three classical canonic orders, the Corinthian order has the narrowest columns, followed by the Ionic order, with the Doric order having the widest columns. The Ionic capital is characterized by the use of volutes. The Ionic columns normally stand on a base which separates the shaft of the column from the stylobate or platform while the cap is usually enriched with egg-and-dart. The ancient architect and architectural historian Vitruvius associates the Ionic with feminine proportions (the Doric representing the masculine). Description Capital The major features of the Ionic order are the volutes of its capital, which have been the subject of much theoretical and practical discourse, based on a brief and obscure passage in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Portico
A portico is a porch leading to the entrance of a building, or extended as a colonnade, with a roof structure over a walkway, supported by columns or enclosed by walls. This idea was widely used in ancient Greece and has influenced many cultures, including most Western cultures. Some noteworthy examples of porticos are the East Portico of the United States Capitol, the portico adorning the Pantheon in Rome and the portico of University College London. Porticos are sometimes topped with pediments. Palladio was a pioneer of using temple-fronts for secular buildings. In the UK, the temple-front applied to The Vyne, Hampshire, was the first portico applied to an English country house. A pronaos ( or ) is the inner area of the portico of a Greek or Roman temple, situated between the portico's colonnade or walls and the entrance to the ''cella'', or shrine. Roman temples commonly had an open pronaos, usually with only columns and no walls, and the pronaos could be as long as th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Street, Birmingham
New Street is a street in Birmingham City Centre, central Birmingham, England. It is one of the city's principal thoroughfares and shopping streets linking Victoria Square, Birmingham, Victoria Square to the Bull Ring, Birmingham, Bullring Shopping Centre. It gives its name to Birmingham New Street railway station, New Street railway station, although the station has never had direct access to New Street except via the Grand Central, Birmingham, Grand Central shopping centre through Stephenson Street. History New Street is first mentioned as ''novus vicus'' in the surviving borough rental records of 1296, at which point it was partly built upon with burgage plots, but was also the site of most of the few open fields remaining within the borough, including ''Barlycroft'', ''Stoctonesfeld'' and ''Wodegrene''. It is mentioned again, this time as ''le Newestret'' in the rentals of 1344–45. The street may have been created at the time of the establishment of Birmingham's mark ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theatre Royal, Birmingham
The Theatre Royal, until 1807 the New Street Theatre, or, colloquially, New Theatre, was a 2000-seat theatre located on New Street in Birmingham, England. It was erected in 1774 and demolished in 1956. The theatre was damaged by fire in 1792 (as a result of arson) and again in 1820, after which it was rebuilt. In 1897, W. S. Gilbert's ''The Fortune Hunter'' premiered at the theatre. The theatre was rebuilt again in 1902, designed by Ernest Runtz, reopening in 1904 with 2200 seats. This building lasted until 1956 when it was closed and demolished. The Woolworth Building was then constructed on the site, seen today as the location of a branch of Boots and Bella Italia. Two large coade stone medallions, from the front of the theatre, depicting David Garrick (on the viewer's left) and William Shakespeare, survive and are now displayed in the Library of Birmingham A library is a collection of materials, books or media that are accessible for use and not just for display pu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Birmingham
Birmingham ( ) is a city and metropolitan borough in the metropolitan county of West Midlands in England. It is the second-largest city in the United Kingdom with a population of 1.145 million in the city proper, 2.92 million in the West Midlands metropolitan county, and approximately 4.3 million in the wider metropolitan area. It is the largest UK metropolitan area outside of London. Birmingham is known as the second city of the United Kingdom. Located in the West Midlands region of England, approximately from London, Birmingham is considered to be the social, cultural, financial and commercial centre of the Midlands. Distinctively, Birmingham only has small rivers flowing through it, mainly the River Tame and its tributaries River Rea and River Cole – one of the closest main rivers is the Severn, approximately west of the city centre. Historically a market town in Warwickshire in the medieval period, Birmingham grew during the 18th century during the Midla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Handsworth, West Midlands
Handsworth () is a suburb and an inner-city area of Birmingham in the West Midlands. Historically in Staffordshire, Handsworth lies just outside Birmingham City Centre and near the town of Smethwick. History The name ''Handsworth'' originates from its Saxon owner Hondes and the Old English word ''weorthing'', meaning farm or estate. It was recorded in the Domesday Survey of 1086, as a holding of William Fitz-Ansculf, the Lord of Dudley, although at that time it would only have been a very small village surrounded by farmland and extensive woodland. Historically in the county of Staffordshire, it remained a small village from the 13th century to the 18th century. Accommodation was built for factory workers, the village quickly grew, and in 1851, more than 6,000 people were living in the township. In that year, work began to build St James' Church. Later St Michael's Church was built as a daughter church to St James'. In the census of 1881, the town was recorded as havin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soho House
Soho House is a museum run by Birmingham Museums Trust, celebrating Matthew Boulton's life, his partnership with James Watt, his membership of the Lunar Society of Birmingham and his contribution to the Midlands Enlightenment and the Industrial Revolution. It is a Grade II* listed 18th-century house in Handsworth, part of Birmingham since 1911, but historically in the county of Staffordshire. It was the home of entrepreneur Matthew Boulton from 1766 until his death in 1809, and a regular meeting-place of the Lunar Society. History Matthew Boulton, one of the 18th century's most significant entrepreneurs, acquired the lease of the five-year-old Soho Mill in 1761 and developed it into Soho Manufactory. He expanded the cottage next to it into Soho House, changing it several times. It is faced with sheets of painted slate to give the appearance of large stone blocks. Boulton moved into Soho House when the Manufactory was completed. The Soho Manufactory was demolished in 186 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Matthew Boulton
Matthew Boulton (; 3 September 172817 August 1809) was an English manufacturer and business partner of Scottish engineer James Watt. In the final quarter of the 18th century, the partnership installed hundreds of Boulton & Watt steam engines, which were a great advance on the state of the art, making possible the mechanisation of factories and mills. Boulton applied modern techniques to the minting of coins, striking millions of pieces for Britain and other countries, and supplying the Royal Mint with up-to-date equipment. Born in Birmingham, he was the son of a Birmingham manufacturer of small metal products who died when Boulton was 31. By then Boulton had managed the business for several years, and thereafter expanded it considerably, consolidating operations at the Soho Manufactory, built by him near Birmingham. At Soho, he adopted the latest techniques, branching into silver plate, ormolu and other decorative arts. He became associated with James Watt when Watt's bus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kinmel Hall
Kinmel Hall is a large country mansion within Kimnel Park near the village of St. George, close to the coastal town of Abergele, in Conwy county borough, Wales. The hall, the third building on the site, was completed in the mid 19th century for the family of a Welsh mining magnate. In 1929, the property ceased being a private residence; it has since been used as a boys' school, health spa, girls' school, wartime hospital, conference centre and hotel (on two occasions). Since 2001 Kimnel Hall has remained empty after plans by several owners to renovate the building were not undertaken. In 2015 the UK's Victorian Society put it in its top ten at-risk Victorian and Edwardian buildings. In 2021 a campaign started to save Kinmel Hall from dereliction. The hall is a Grade I listed building and its gardens and parkland are designated on the Cadw/ICOMOS Register of Parks and Gardens of Special Historic Interest in Wales. History Early hall The original Kinmel Hall was owned by t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |








.jpg)

