|
Sakkos
The ''sakkos'' (Greek: σάκκος, "sackcloth") is a vestment worn by Orthodox and Greek Catholic bishops instead of the priest's ''phelonion''. The garment is a tunic with wide sleeves, and a distinctive pattern of trim. It reaches below the knees and is fastened up the sides with buttons or tied with ribbons. It is similar in form to the western dalmatic, which is similarly derived from Byzantine dress. The ''sakkos'' was originally worn by the Emperor as an imperial vestment, symbolizing the tunic of disgrace worn by Christ during his trial and mockery. The ''sakkos'' is usually made of a rich brocade fabric and may be intricately embroidered. There is normally a cross in the center of the back, which the bishop kisses before it is placed on him. Buttons or loops are sewn on the back, by which the bishop's ''omophorion'' (either great or small) may be attached. Traditionally, bells are attached to the ''sakkos'', following the biblical directions for the vestments of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phelonion
The phelonion (Greek: , plural, , ''phailónia''; Latin: ''paenula'') is a liturgical vestment worn by a priest of the Byzantine Christian tradition. It is worn over the priest's other vestments and is equivalent to the chasuble of Western Christianity. History Like the chasuble, the phelonion was originally a sort of poncho, a conical round vestment with a hole in the middle for the head, which fell to the feet on all sides. It derived from the Roman civilian ''paenula'', and it was made of wool, silk, or linen. Unlike the chasuble, it was worn at all liturgical functions, not only at the Eucharist. It was in use as early as the sixth century for priests, bishops, and also minor orders, and can be seen in the mosaics in Ravenna and the Euphrasian Basilica in Porec. The phelonion is depicted in the Menologion of Basil II, dating to 1000 AD. It shape evolved, and it was folded above the elbows to free the arms and hands. In its present form (dating from about the fifteenth cen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mitre
The mitre (Commonwealth English) (; Greek: μίτρα, "headband" or "turban") or miter (American English; see spelling differences), is a type of headgear now known as the traditional, ceremonial headdress of bishops and certain abbots in traditional Christianity. Mitres are worn in the Catholic Church, Eastern Orthodox Church, Oriental Orthodox Churches, the Anglican Communion, some Lutheran churches, for important ceremonies, by the Metropolitan of the Malankara Mar Thoma Syrian Church, and also, in the Catholic Church, all cardinals, whether or not bishops, and some Eastern Orthodox archpriests. Etymology μίτρα, ''mítra'' ( Ionic μίτρη, ''mítrē'') is Greek, and means a piece of armour, usually a metal guard worn around the waist and under a cuirass, as mentioned in Homer's Iliad. In later poems, it was used to refer to a headband used by women for their hair; and a sort of formal Babylonian headdress, as mentioned by Herodotus ('' Histories'' 1.195 and 7.90 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dalmatic
The dalmatic is a long, wide-sleeved tunic, which serves as a liturgical vestment in the Catholic, Lutheran, Anglican, United Methodist, and some other churches. When used, it is the proper vestment of a deacon at Mass, Holy Communion or other services such as baptism or marriage held in the context of a Eucharistic service. Although infrequent, it may also be worn by bishops above the alb and below the chasuble, and is then referred to as pontifical dalmatic. Like the chasuble worn by priests and bishops, it is an outer vestment and is supposed to match the liturgical colour of the day. The dalmatic is often made of the same material and decoration as a chasuble, so as to form a matching pair. Traditional Solemn Mass vestment sets include matching chasuble, dalmatic, and tunicle. A dalmatic is also worn by the British monarch during the Coronation service. History In the Roman Empire, the dalmatic was an amply sleeved tunic (from Dalmatia) with wide stripes ''(clavi)'' that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bishop
A bishop is an ordained clergy member who is entrusted with a position of authority and oversight in a religious institution. In Christianity, bishops are normally responsible for the governance of dioceses. The role or office of bishop is called episcopacy. Organizationally, several Christian denominations utilize ecclesiastical structures that call for the position of bishops, while other denominations have dispensed with this office, seeing it as a symbol of power. Bishops have also exercised political authority. Traditionally, bishops claim apostolic succession, a direct historical lineage dating back to the original Twelve Apostles or Saint Paul. The bishops are by doctrine understood as those who possess the full priesthood given by Jesus Christ, and therefore may ordain other clergy, including other bishops. A person ordained as a deacon, priest (i.e. presbyter), and then bishop is understood to hold the fullness of the ministerial priesthood, given responsibility b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Byzantine Dress
Byzantine dress changed considerably over the thousand years of the Empire, but was essentially conservative. Popularly, Byzantine dress remained attached to its classical Greek roots with most changes and different styles being evidenced in the upper strata of Byzantine society always with a touch of the Hellenic environment. The Byzantines liked colour and pattern, and made and exported very richly patterned cloth, especially Byzantine silk, woven and embroidered for the upper classes, and resist-dyed and printed for the lower. A different border or trimming round the edges was very common, and many single stripes down the body or around the upper arm are seen, often denoting class or rank. Taste for the middle and upper classes followed the latest fashions at the Imperial Court. As in the West during the Middle Ages, clothing was very expensive for the poor, who probably wore the same well-worn clothes nearly all the time;Payne, Blanche; Winakor, Geitel; Farrell-Beck Jane: ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vestment
Vestments are liturgical garments and articles associated primarily with the Christian religion, especially by Eastern Churches, Catholics (of all rites), Anglicans, and Lutherans. Many other groups also make use of liturgical garments; this was a point of controversy in the Protestant Reformation and sometimes since, in particular during the ritualist controversies in England in the 19th century. Origins of vestments In the early Christian churches, officers and leaders, like their congregations, wore the normal dress of civil life in the Greco-Roman world, although with an expectation that the clothing should be clean and pure during holy observances. From the 4th century onward, however, modifications began to be made to the form of the garments, and as secular fashions changed from the 6th century the church retained the original forms of their garments, although with separate development and with regional variations. Having separate, consecrated clothing for the cere ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
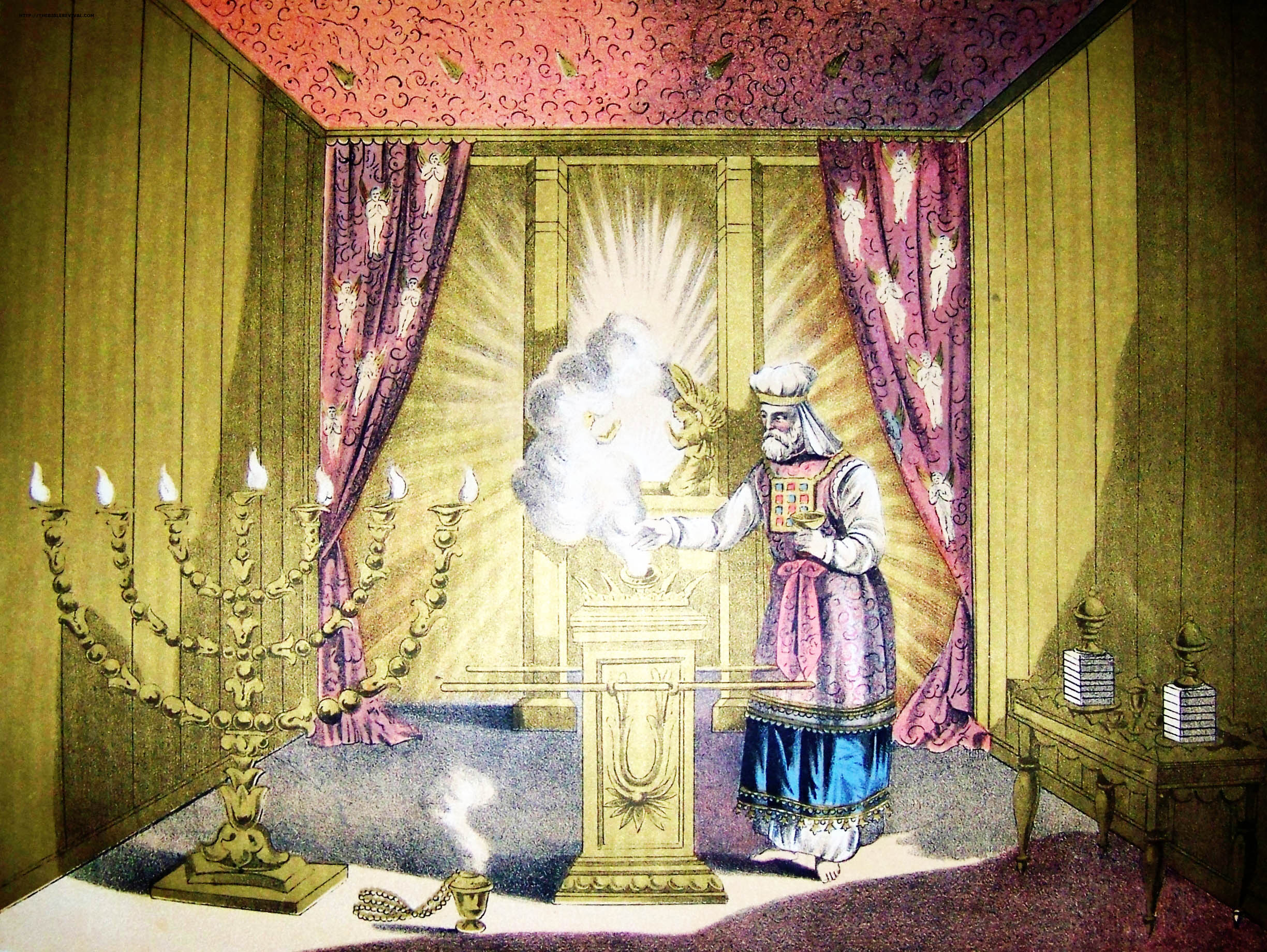
Kohen Gadol
High Priest ( he, כהן גדול, translit=Kohen Gadol or ; ) was the title of the chief religious official of Judaism from the early post-Babylonian captivity, Exilic times until Siege of Jerusalem (70 CE), the destruction of the Second Temple in Jerusalem by the Roman Empire, Romans in 70 CE. Previously, in the Yahwism, Israelite religion, including during the time of the History of ancient Israel and Judah, kingdoms of Israel and Judah, other terms were used to designate the leading priests; however, as long as a king was in place, the supreme ecclesiastical authority lay with him. The official introduction of the term "high priest" went hand-in-hand with a greatly enhanced ritual and political significance bestowed upon the chief priest of the Israelites in the post-Exilic period, especially from 411 BCE onward due to the religious transformations brought about during the time of the Babylonian captivity and due to the lack of a List of Jewish states and dynasties, Jewish kin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Basileus
''Basileus'' ( el, ) is a Greek term and title that has signified various types of monarchs in history. In the English-speaking world it is perhaps most widely understood to mean "monarch", referring to either a "king" or an "emperor" and also by bishops of the Eastern orthodox church and Eastern Catholic Churches. The title was used by sovereigns and other persons of authority in ancient Greece, the Byzantine emperors, and the kings of modern Greece. The feminine forms are ''basileia'' (), ''basilis'' (), ''basilissa'' (), or the archaic '' basilinna'' (), meaning "queen" or "empress". Etymology The etymology of ''basileus'' is uncertain. The Mycenaean form was *''gʷasileus'' ( Linear B: , ''qa-si-re-u''), denoting some sort of court official or local chieftain, but not an actual king. Its hypothetical earlier Proto-Greek form would be *''gʷatileus''. Some linguists assume that it is a non-Greek word that was adopted by Bronze Age Greeks from a pre-existing linguistic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theodore Balsamon
Theodore Balsamon ( el, Θεόδωρος Βαλσαμῶν) was a canonist of the Eastern Orthodox Church and 12th-century Eastern Orthodox Patriarch of Antioch. Biography Born in the second half of the 12th century at Constantinople; died there, after 1195 (Petit). He was ordained a deacon, appointed ''nomophylax'', and from 1178 to 1183, under Patriarch Theodosius I, he had charge of all ecclesiastical trials or cases submitted to the Patriarchate. In 1193 he became the Patriarch of Antioch, though he remained resident in Constantinople. Balsamon's best work is his "Scholia" (Greek: Σχόλια) (c. 1170), a commentary on the Nomocanon of Photios, the standard work on Eastern Orthodox ecclesiastical and imperial laws and decrees, commissioned by the Emperor Manuel I and the Patriarch Michael III.J.M. Hussey, ''the Orthodox Church in the Byzantine Empire'' (Oxford, 1986), p. 307. In his "Scholia", Balsamon insists on existing laws, and dwells on the relation between canons and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Patriarch Of Antioch
Patriarch of Antioch is a traditional title held by the bishop of Antioch (modern-day Antakya, Turkey). As the traditional "overseer" (ἐπίσκοπος, ''episkopos'', from which the word ''bishop'' is derived) of the first gentile Christian community, the position has been of prime importance in Pauline Christianity from its earliest period. This diocese is one of the few for which the names of its bishops from the apostolic beginnings have been preserved. Today five churches use the title of patriarch of Antioch: one Oriental Orthodox (the Syriac Orthodox Church); three Eastern Catholic (the Maronite, Syriac Catholic, and Melkite Greek Catholic Churches); and one Eastern Orthodox (the Greek Orthodox Church of Antioch). According to the pre-congregation church tradition, this ancient patriarchate was founded by the Apostle Saint Peter. The patriarchal succession was disputed at the time of the Meletian schism in 362 and again after the Council of Chalcedon in 451, when ther ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Omophorion
In the Eastern Orthodox and Eastern Catholic liturgical tradition, the ''omophorion'' ( grc-gre, ὠμοφόριον, meaning " omethingborne on the shoulders"; Slavonic: омофоръ, ''omofor'') is the distinguishing vestment of a bishop and the symbol of his spiritual and ecclesiastical authority. Originally woven of wool, it is a band of brocade decorated with four crosses and an eight-pointed star; it is worn about the neck and shoulders. By symbolizing the lost sheep that is found and carried on the 's shoulders, it signifies the bishop's |