|
Saint Quiteria
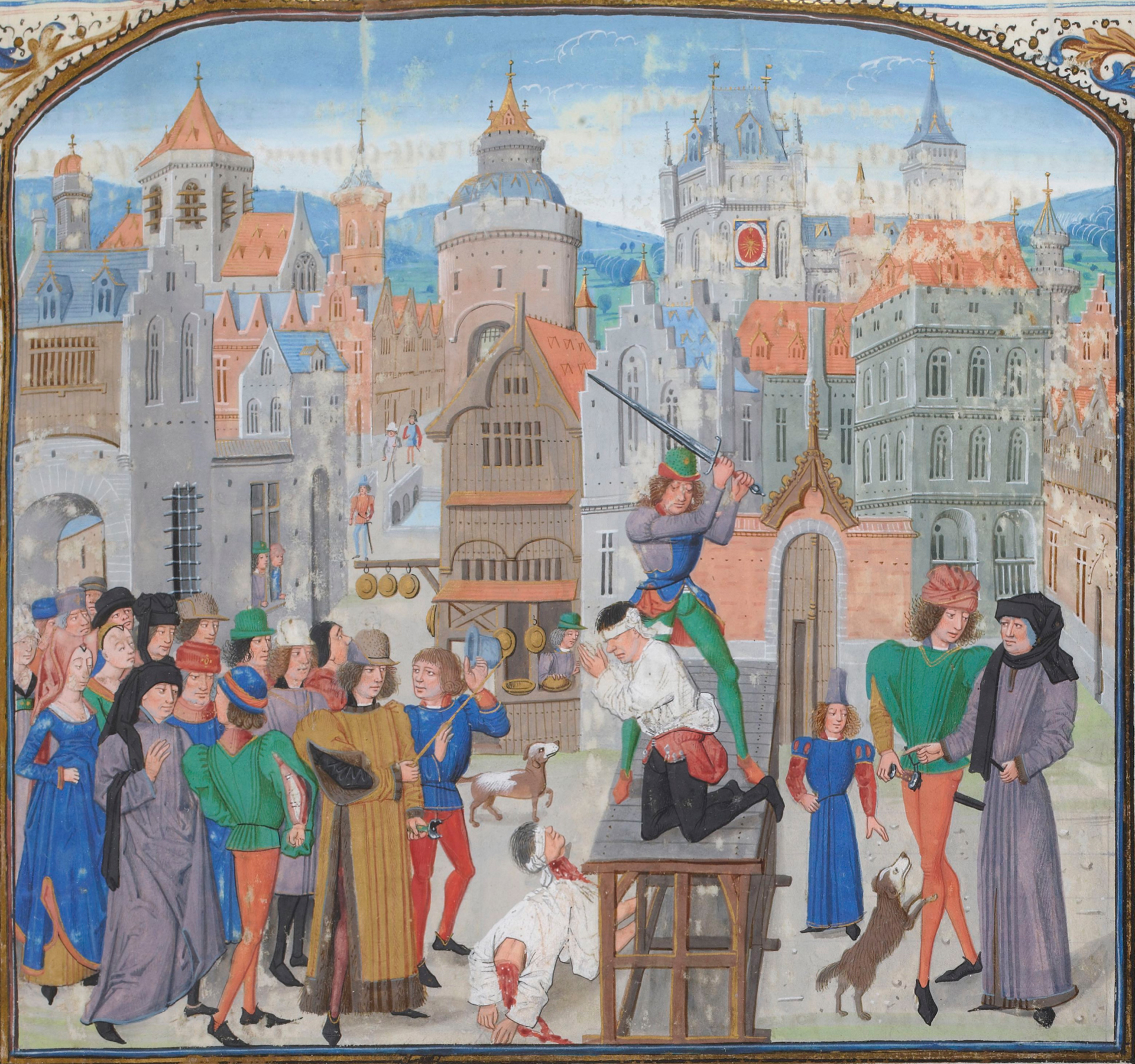
Quiteria ( es, Quiteria; ca, Quitèria; oc, Quiteira; french: Quitterie; pt, Quitéria) was a second-century virgin martyr and saint about whom nothing is certain except her name and her cult. She appears in the ''Roman Martyrology'', but not in any other ancient calendars (such as the ''Martyrologium Hieronymianum''). Name ''Quiteria'' may be derived from ''Kythere'' (or ''Kyteria'', ''Kuteria''), a title applied to the Phoenician goddess Astarte which meant "the red one", or from (the possibly related name) ''Cytherea'', an epithet of the Greek goddess Aphrodite because she was born on the island of Kythira. Legend She is said to have been born in Bracara (now Braga, Portugal) to Lucius Catilius Serves, Roman governor of Gallaecia and Lusitania, and Calcia, his wife. Her father wanted her to marry and renounce Christianity. Quiteria fled and her father's men found her at Aire-sur-l'Adour, in Gascony. She was beheaded on the spot. Her sister, Liberata, also suffered the s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saint
In religious belief, a saint is a person who is recognized as having an exceptional degree of Q-D-Š, holiness, likeness, or closeness to God. However, the use of the term ''saint'' depends on the context and Christian denomination, denomination. In Catholic Church, Catholic, Eastern Orthodox Church, Eastern Orthodox, Anglican Communion, Anglican, Oriental Orthodox, and Lutheranism, Lutheran doctrine, all of their faithful deceased in Heaven are considered to be saints, but some are considered worthy of greater honor or emulation. Official ecclesiastical recognition, and consequently a public cult of veneration, is conferred on some denominational saints through the process of canonization in the Catholic Church or glorification in the Eastern Orthodox Church after their approval. While the English word ''saint'' originated in Christianity, History of religion, historians of religion tend to use the appellation "in a more general way to refer to the state of special holiness t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Astarte
Astarte (; , ) is the Hellenized form of the Ancient Near Eastern goddess Ashtart or Athtart (Northwest Semitic), a deity closely related to Ishtar (East Semitic), who was worshipped from the Bronze Age through classical antiquity. The name is particularly associated with her worship in the ancient Levant among the Canaanites and Phoenicians, though she was originally associated with Amorite cities like Ugarit and Emar, as well as Mari and Ebla. She was also celebrated in Egypt, especially during the reign of the Ramessides, following the importation of foreign cults there. Phoenicians introduced her cult in their colonies on the Iberian Peninsula. Name Astarte was a goddess of both the Canaanite and the Phoenician pantheon, derived from an earlier Syrian deity. She is recorded in Akkadian as (), the feminine form of Ishtar.K. van der Toorn, Bob Becking, Pieter Willem van der Horst, Dictionary of Deities and Demons in the Bible', p. 109-10. The name appears in Ugaritic as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ( la, Imperium Romanum ; grc-gre, Βασιλεία τῶν Ῥωμαίων, Basileía tôn Rhōmaíōn) was the post-Republican period of ancient Rome. As a polity, it included large territorial holdings around the Mediterranean Sea in Europe, North Africa, and Western Asia, and was ruled by emperors. From the accession of Caesar Augustus as the first Roman emperor to the military anarchy of the 3rd century, it was a Principate with Italia as the metropole of its provinces and the city of Rome as its sole capital. The Empire was later ruled by multiple emperors who shared control over the Western Roman Empire and the Eastern Roman Empire. The city of Rome remained the nominal capital of both parts until AD 476 when the imperial insignia were sent to Constantinople following the capture of the Western capital of Ravenna by the Germanic barbarians. The adoption of Christianity as the state church of the Roman Empire in AD 380 and the fall of the Western ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guerrilla War
Guerrilla warfare is a form of irregular warfare in which small groups of combatants, such as paramilitary personnel, armed civilians, or irregulars, use military tactics including ambushes, sabotage, raids, petty warfare, hit-and-run tactics, and mobility, to fight a larger and less-mobile traditional military. Although the term "guerrilla warfare" was coined in the context of the Peninsular War in the 19th century, the tactical methods of guerrilla warfare have long been in use. In the 6th century BC, Sun Tzu proposed the use of guerrilla-style tactics in ''The Art of War''. The 3rd century BC Roman general Quintus Fabius Maximus Verrucosus is also credited with inventing many of the tactics of guerrilla warfare through what is today called the Fabian strategy. Guerrilla warfare has been used by various factions throughout history and is particularly associated with revolutionary movements and popular resistance against invading or occupying armies. Guerrilla tactics focus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Gods
The Roman deities most widely known today are those the Romans identified with Greek counterparts (see ''interpretatio graeca''), integrating Greek myths, iconography, and sometimes religious practices into Roman culture, including Latin literature, Roman art, and religious life as it was experienced throughout the Empire. Many of the Romans' own gods remain obscure, known only by name and sometimes function, through inscriptions and texts that are often fragmentary. This is particularly true of those gods belonging to the archaic religion of the Romans dating back to the era of kings, the so-called "religion of Numa", which was perpetuated or revived over the centuries. Some archaic deities have Italic or Etruscan counterparts, as identified both by ancient sources and by modern scholars. Throughout the Empire, the deities of peoples in the provinces were given new theological interpretations in light of functions or attributes they shared with Roman deities. An extensive al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Rome
In modern historiography, ancient Rome refers to Roman civilisation from the founding of the city of Rome in the 8th century BC to the collapse of the Western Roman Empire in the 5th century AD. It encompasses the Roman Kingdom (753–509 BC), Roman Republic (509–27 BC) and Roman Empire (27 BC–476 AD) until the fall of the western empire. Ancient Rome began as an Italic settlement, traditionally dated to 753 BC, beside the River Tiber in the Italian Peninsula. The settlement grew into the city and polity of Rome, and came to control its neighbours through a combination of treaties and military strength. It eventually dominated the Italian Peninsula, assimilated the Greek culture of southern Italy ( Magna Grecia) and the Etruscan culture and acquired an Empire that took in much of Europe and the lands and peoples surrounding the Mediterranean Sea. It was among the largest empires in the ancient world, with an estimated 50 to 90 million inhabitants, roughly 20% of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
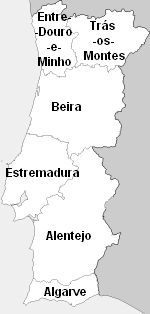
Entre Douro E Minho
Entre Douro e Minho () is one of the historical provinces of Portugal which encompassed the country's northern Atlantic seaboard between the Douro and Minho rivers. Contemporaries often referred to the province as simply "Minho". It was one of six provinces Portugal was commonly divided into from the early modern period until 1936, although these provinces were not recognized as official units of government. Geography The coastline of Entre Minho e Douro is level and unbroken except by the estuaries of the main rivers; inland, the elevation gradually increases towards the north and east, where several mountain ranges mark the frontier. Of these, the most important are the Serra da Peneda (), between the rivers Minho and Lima; the Serra do Gerez (), on the Galician border; the Serra da Cabreira (), immediately to the south; and the Serra do Marão (), in the extreme south-east. As its name implies, the province is bounded by two rivers, the Douro on the south, and the Minho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marina Of Aguas Santas
Saint Marina of Aguas Santas (Marina of Ourense) (c.120–135 AD) is a virgin martyr from Aguas Santas, in the province of Ourense. The story of her life as it has been preserved is a mixture of fact and legends. Legend The traditional account of the life of Santa Marina points to the town of Xinzo de Limia as the place of her birth. At that time, the region of La Limia was a highly Romanized town (Forum Limicorum), through which the Vía Nova, which linked the towns of Bracara (Braga, Portugal) and Asturica (Astorga), passed. Her father, called Theudio or Teódulo, was a person of some importance; her mother, whose name is unknown, died in childbirth. Following the recommendations of the doctors, her father sought someone to be his daughter's nurse. He chose a woman named "Aya" from a farm in Pinnitus. The community was attended by the priest Teotimo. Educated by her nurse, within that community, she chose the Christian life and received baptism in the new faith, which cause ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Santa Quitéria (Vida E Martyrio Da Gloriosa Santa Quitéria, 1651) , Brazil
{{disambiguation, geo ...
Santa Quitéria may refer to: Places *Santa Quitéria, Ceará, a municipality in Brazil *Santa Quitéria do Maranhão, a municipality in Maranhão, Brazil * Santa Quitéria River, Brazil * Santa Quiteria Bridge, in the Province of Castellón, Spain *Santa Quitéria, Funchal Other *Saint Quiteria, 5th-century virgin martyr *Santa Quitéria Futebol Clube Santa Quitéria Futebol Clube, commonly known as Santa Quitéria, is a Brazilian football club based in Santa Quitéria do Maranhão, Maranhão state. They competed in the Copa do Brasil once. History The club was founded on March 16, 2003. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Decapitation
Decapitation or beheading is the total separation of the head from the body. Such an injury is invariably fatal to humans and most other animals, since it deprives the brain of oxygenated blood, while all other organs are deprived of the involuntary functions that are needed for the body to function. The term ''beheading'' refers to the act of deliberately decapitating a person, either as a means of murder or as an execution; it may be performed with an axe, sword, knife, machete or by mechanical means such as a guillotine or chainsaw. An executioner who carries out executions by beheading is sometimes called a headsman. Accidental decapitation can be the result of an explosion, a car or industrial accident, improperly administered execution by hanging or other violent injury. Suicide by decapitation is rare but not unknown. The national laws of Saudi Arabia, Yemen, and Qatar permit beheading; however, in practice, Saudi Arabia is the only country that continues to behead i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gascony
Gascony (; french: Gascogne ; oc, Gasconha ; eu, Gaskoinia) was a province of the southwestern Kingdom of France that succeeded the Duchy of Gascony (602–1453). From the 17th century until the French Revolution (1789–1799), it was part of the combined Province of Guyenne and Gascony. The region is vaguely defined, and the distinction between Guyenne and Gascony is unclear; by some they are seen to overlap, while others consider Gascony a part of Guyenne. Most definitions put Gascony east and south of Bordeaux. It is currently divided between the region of Nouvelle-Aquitaine (departments of Landes, Pyrénées-Atlantiques, southwestern Gironde, and southern Lot-et-Garonne) and the region of Occitanie (departments of Gers, Hautes-Pyrénées, southwestern Tarn-et-Garonne, and western Haute-Garonne). Gascony was historically inhabited by Basque-related people who appear to have spoken a language similar to Basque. The name Gascony comes from the same root as the word Basq ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christianity
Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus of Nazareth. It is the world's largest and most widespread religion with roughly 2.38 billion followers representing one-third of the global population. Its adherents, known as Christians, are estimated to make up a majority of the population in 157 countries and territories, and believe that Jesus is the Son of God, whose coming as the messiah was prophesied in the Hebrew Bible (called the Old Testament in Christianity) and chronicled in the New Testament. Christianity began as a Second Temple Judaic sect in the 1st century Hellenistic Judaism in the Roman province of Judea. Jesus' apostles and their followers spread around the Levant, Europe, Anatolia, Mesopotamia, the South Caucasus, Ancient Carthage, Egypt, and Ethiopia, despite significant initial persecution. It soon attracted gentile God-fearers, which led to a departure from Jewish customs, and, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.png)