|
Saddle (landform)
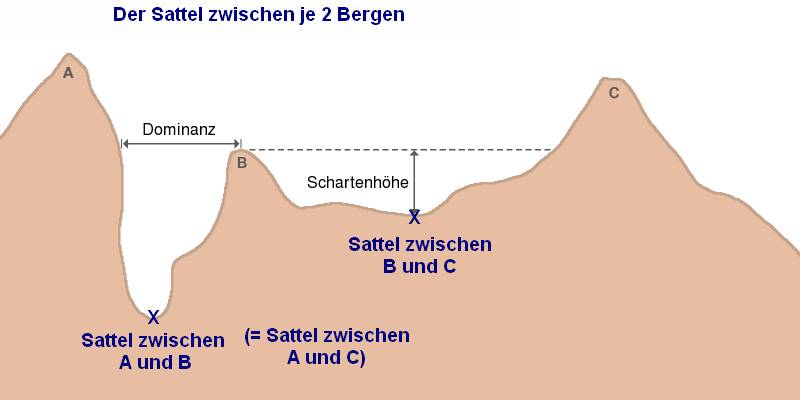
The saddle between two hills or mountains is the region surrounding the saddle point, the lowest point on the line tracing the drainage divide (the col) connecting the peaks. When, and if, the saddle is navigable, even if only on foot, the saddle of a (optimal) mountain pass, pass between the two massifs, is the area generally found around the lowest route on which one could pass between the two summits, which includes that point which is a mathematically when graphed a Maxima and minima, relative high along one axis, and a Maxima and minima, relative low in the perpendicular axis, simultaneously; that point being by definition the col of the saddle. Topography A saddle is the lowest area between two highlands (prominences or peaks) which has two wings which span the divide (the line between the two prominences) by crossing the divide at an angle, and, so is concurrently the local highpoint of the land surface which falls off in the lower direction. That is, the drainage divide ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Key Saddle
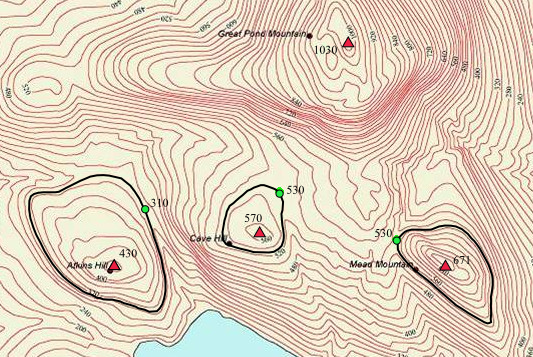
In topography, prominence or relative height (also referred to as autonomous height, and shoulder drop in US English, and drop in British English) measures the height of a mountain or hill's summit relative to the lowest contour line encircling it but containing no higher summit within it. It is a measure of the independence of a summit. The key col ("saddle") around the peak is a unique point on this contour line and the ''parent peak'' (if any) is some higher mountain, selected according to various criteria. Definitions The prominence of a peak is the least drop in height necessary in order to get from the summit to any higher terrain. This can be calculated for a given peak in the following manner: for every path connecting the peak to higher terrain, find the lowest point on the path; the ''key col'' (or ''highest saddle'', or ''linking col'', or ''link'') is defined as the highest of these points, along all connecting paths; the prominence is the difference between the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Landforms
A landform is a land feature on the solid surface of the Earth or other planetary body. They may be natural or may be anthropogenic (caused or influenced by human activity). Landforms together make up a given terrain, and their arrangement in the landscape is known as topography. Landforms include hills, mountains, canyons, and valleys, as well as shoreline features such as bays, peninsulas, and seas, including submerged features such as mid-ocean ridges, volcanoes, and the great oceanic basins. Physical characteristics Landforms are categorized by characteristic physical attributes such as elevation, slope, orientation, structure stratification, rock exposure, and soil type. Gross physical features or landforms include intuitive elements such as berms, cliffs, hills, mounds, peninsulas, ridges, rivers, valleys, volcanoes, and numerous other structural and size-scaled (e.g. ponds vs. lakes, hills vs. mountains) elements including various kinds of inland and oceani ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saddle
A saddle is a supportive structure for a rider of an animal, fastened to an animal's back by a girth. The most common type is equestrian. However, specialized saddles have been created for oxen, camels and other animals. It is not known precisely when riders first began to use some sort of padding or protection, but a blanket attached by some form of surcingle or girth was probably the first "saddle", followed later by more elaborate padded designs. The solid saddle tree was a later invention, and though early stirrup designs predated the invention of the solid tree, the paired stirrup, which attached to the tree, was the last element of the saddle to reach the basic form that is still used today. Present-day saddles come in a wide variety of styles, each designed for a specific equestrianism discipline, and require careful fit to both the rider and the horse. Proper saddle care can extend the useful life of a saddle, often for decades. The saddle was a crucial step in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Surface (mathematics)
In mathematics, a surface is a mathematical model of the common concept of a surface. It is a generalization of a plane, but, unlike a plane, it may be curved; this is analogous to a curve generalizing a straight line. There are several more precise definitions, depending on the context and the mathematical tools that are used for the study. The simplest mathematical surfaces are planes and spheres in the Euclidean 3-space. The exact definition of a surface may depend on the context. Typically, in algebraic geometry, a surface may cross itself (and may have other singularities), while, in topology and differential geometry, it may not. A surface is a topological space of dimension two; this means that a moving point on a surface may move in two directions (it has two degrees of freedom). In other words, around almost every point, there is a '' coordinate patch'' on which a two-dimensional coordinate system is defined. For example, the surface of the Earth resembles ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mathematics
Mathematics is a field of study that discovers and organizes methods, Mathematical theory, theories and theorems that are developed and Mathematical proof, proved for the needs of empirical sciences and mathematics itself. There are many areas of mathematics, which include number theory (the study of numbers), algebra (the study of formulas and related structures), geometry (the study of shapes and spaces that contain them), Mathematical analysis, analysis (the study of continuous changes), and set theory (presently used as a foundation for all mathematics). Mathematics involves the description and manipulation of mathematical object, abstract objects that consist of either abstraction (mathematics), abstractions from nature orin modern mathematicspurely abstract entities that are stipulated to have certain properties, called axioms. Mathematics uses pure reason to proof (mathematics), prove properties of objects, a ''proof'' consisting of a succession of applications of in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anticline
In structural geology, an anticline is a type of Fold (geology), fold that is an arch-like shape and has its oldest Bed (geology), beds at its core, whereas a syncline is the inverse of an anticline. A typical anticline is convex curve, convex up in which the hinge or crest is the location where the curvature is greatest, and the limbs are the sides of the fold that Strike and dip, dip away from the hinge. Anticlines can be recognized and differentiated from antiforms by a sequence of rock layers that become progressively older toward the center of the fold. Therefore, if age relationships between various Stratum, rock strata are unknown, the term antiform should be used. The progressing age of the rock strata towards the core and uplifted center, are the trademark indications for evidence of anticlines on a geological map. These formations occur because anticlinal ridges typically develop above thrust faults during crustal deformations. The uplifted core of the fold cau ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Structural Geology
Structural geology is the study of the three-dimensional distribution of rock units with respect to their deformational histories. The primary goal of structural geology is to use measurements of present-day rock geometries to uncover information about the history of deformation ( strain) in the rocks, and ultimately, to understand the stress field that resulted in the observed strain and geometries. This understanding of the dynamics of the stress field can be linked to important events in the geologic past; a common goal is to understand the structural evolution of a particular area with respect to regionally widespread patterns of rock deformation (e.g., mountain building, rifting) due to plate tectonics. Use and importance The study of geologic structures has been of prime importance in economic geology, both petroleum geology and mining geology. Folded and faulted rock strata commonly form traps that accumulate and concentrate fluids such as petroleum and natural gas. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hill
A hill is a landform that extends above the surrounding terrain. It often has a distinct summit, and is usually applied to peaks which are above elevation compared to the relative landmass, though not as prominent as Mountain, mountains. Hills fall under the category of slope landforms. Terminology The distinction between a hill and a mountain is unclear and largely subjective, but a hill is universally considered to be not as tall, or as Grade (slope), steep as a mountain. Geographers historically regarded mountains as hills greater than above sea level. In contrast, hillwalkers have tended to regard mountains as peaks above sea level. The ''Oxford English Dictionary'' also suggests a limit of and Whittow states "Some authorities regard eminences above as mountains, those below being referred to as hills." Today, a mountain is usually defined in the UK and Ireland as any summit at least high, while the UK government's Countryside and Rights of Way Act 2000 defined mou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Topographic Prominence
In topography, prominence or relative height (also referred to as autonomous height, and shoulder drop in US English, and drop in British English) measures the height of a mountain or hill's summit relative to the lowest contour line encircling it but containing no higher summit within it. It is a measure of the independence of a summit. The key col ("saddle") around the peak is a unique point on this contour line and the ''parent peak'' (if any) is some higher mountain, selected according to various criteria. Definitions The prominence of a peak is the least drop in height necessary in order to get from the summit to any higher terrain. This can be calculated for a given peak in the following manner: for every path connecting the peak to higher terrain, find the lowest point on the path; the ''key col'' (or ''highest saddle (landform), saddle'', or ''linking col'', or ''link'') is defined as the highest of these points, along all connecting paths; the prominence is the differ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxford Dictionary Of English
The ''Oxford Dictionary of English'' (''ODE'') is a single-volume English dictionary published by Oxford University Press, first published in 1998 as ''The New Oxford Dictionary of English'' (''NODE''). The word "New" was dropped from the title with the Second Edition in 2003. The dictionary is not based on the ''Oxford English Dictionary'' (OED) – it is a separate dictionary which strives to represent faithfully the current usage of English words. The Revised Second Edition contains 355,000 words, phrases, and definitions, including biographical references and thousands of encyclopaedic entries. The Third Edition was published in August 2010, with some new words, including ''vuvuzela''. It is currently the largest single-volume English-language dictionary published by Oxford University Press, but is much smaller than the comprehensive ''Oxford English Dictionary'', which is published in multiple volumes. Editorial principles and practices The first editor, Judy Pearsall, wr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |