|
Sack Of Delhi (1398)
The Sack of Delhi was a battle between Timur, founder of the Timurid Empire and the Delhi Sultanate. It took place on 17 December 1398 and lasted for 3 days and ended with the massacre of over 100,000 citizens as well as the Delhi army. Background Timur gained power in 1370, he swiftly began engaging in wars and conquering many surrounding nations. While he conquered Persia, and Iraq, a civil war broke out in the Delhi Sultanate and by 1398, there were two rulers who called themselves Sultan: Nasir ud-Din Mahmud Shah Tughlaq, the grandson of Firuz Shah Tughlaq who ruled from Delhi, and Nasir ud-Din Nusrat Shah Tughlaq, another relative of Firuz Shah Tughlaq who ruled from Firozabad, which was a few miles from Delhi. Timur who had heard about this quickly turned his eye on Delhi knowing about the rich wealth of India. Timur had begun preparations and mobilization for his next campaign. While Timur had no intention of ruling over India or interest in an Indian empire, he ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Timurid Conquests And Invasions
Timurid conquests and invasions started in the seventh decade of the 14th century with Timur's control over Chagatai Khanate and ended at the start of the 15th century with the death of Timur. Due to the sheer scale of Timur's wars, and the fact that he was generally undefeated in battle, he has been regarded as one of the most successful military commanders of all time. These wars resulted in the supremacy of Timur over Central Asia, Persia, the Caucasus and the Levant, and parts of South Asia and Eastern Europe, and also the formation of the short-lived Timurid Empire. Scholars estimate that his military campaigns caused the deaths of 17 million people, amounting to about 5% of the world population at the time. Timur gained power over the Western Chagatai Khanate (Transoxiana) after defeating Amir Husayn, the regent of the Chagatai Khanate, at the Battle of Balkh but the laws laid down by Genghis Khan prevented him from becoming Khagan in his own right because he was not d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Looting
Looting is the act of stealing, or the taking of goods by force, typically in the midst of a military, political, or other social crisis, such as war, natural disasters (where law and civil enforcement are temporarily ineffective), or rioting. The proceeds of all these activities can be described as booty, loot, plunder, spoils, or pillage. During modern-day armed conflicts, looting is prohibited by international law, and constitutes a war crime.Rule 52. Pillage is prohibited. ''Customary IHL Database'', (ICRC)/ |
Military History Of The Timurid Empire
A military, also known collectively as armed forces, is a heavily armed, highly organized force primarily intended for warfare. It is typically authorized and maintained by a sovereign state, with its members identifiable by their distinct military uniform. It may consist of one or more military branches such as an army, navy, air force, space force, marines, or coast guard. The main task of the military is usually defined as defence of the state and its interests against external armed threats. In broad usage, the terms ''armed forces'' and ''military'' are often treated as synonymous, although in technical usage a distinction is sometimes made in which a country's armed forces may include both its military and other paramilitary forces. There are various forms of irregular military forces, not belonging to a recognized state; though they share many attributes with regular military forces, they are less often referred to as simply ''military''. A nation's military may ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battles Of Pir Muhammad (son Of Jahangir)
A battle is an occurrence of combat in warfare between opposing military units of any number or size. A war usually consists of multiple battles. In general, a battle is a military engagement that is well defined in duration, area, and force commitment. An engagement with only limited commitment between the forces and without decisive results is sometimes called a skirmish. The word "battle" can also be used infrequently to refer to an entire operational campaign, although this usage greatly diverges from its conventional or customary meaning. Generally, the word "battle" is used for such campaigns if referring to a protracted combat encounter in which either one or both of the combatants had the same methods, resources, and strategic objectives throughout the encounter. Some prominent examples of this would be the Battle of the Atlantic, Battle of Britain, and Battle of Stalingrad, all in World War II. Wars and military campaigns are guided by military strategy, wher ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battles Involving The Delhi Sultanate
A battle is an occurrence of combat in warfare between opposing military units of any number or size. A war usually consists of multiple battles. In general, a battle is a military engagement that is well defined in duration, area, and force commitment. An engagement with only limited commitment between the forces and without decisive results is sometimes called a skirmish. The word "battle" can also be used infrequently to refer to an entire operational campaign, although this usage greatly diverges from its conventional or customary meaning. Generally, the word "battle" is used for such campaigns if referring to a protracted combat encounter in which either one or both of the combatants had the same methods, resources, and strategic objectives throughout the encounter. Some prominent examples of this would be the Battle of the Atlantic, Battle of Britain, and Battle of Stalingrad, all in World War II. Wars and military campaigns are guided by military strategy, whereas bat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battles Involving The Timurid Empire
A battle is an occurrence of combat in warfare between opposing military units of any number or size. A war usually consists of multiple battles. In general, a battle is a military engagement that is well defined in duration, area, and force commitment. An engagement with only limited commitment between the forces and without decisive results is sometimes called a skirmish. The word "battle" can also be used infrequently to refer to an entire operational campaign, although this usage greatly diverges from its conventional or customary meaning. Generally, the word "battle" is used for such campaigns if referring to a protracted combat encounter in which either one or both of the combatants had the same methods, resources, and strategic objectives throughout the encounter. Some prominent examples of this would be the Battle of the Atlantic, Battle of Britain, and Battle of Stalingrad, all in World War II. Wars and military campaigns are guided by military strategy, wher ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battles Of Timur
A battle is an occurrence of combat in warfare between opposing military units of any number or size. A war usually consists of multiple battles. In general, a battle is a military engagement that is well defined in duration, area, and force commitment. An engagement with only limited commitment between the forces and without decisive results is sometimes called a skirmish. The word "battle" can also be used infrequently to refer to an entire operational campaign, although this usage greatly diverges from its conventional or customary meaning. Generally, the word "battle" is used for such campaigns if referring to a protracted combat encounter in which either one or both of the combatants had the same methods, resources, and strategic objectives throughout the encounter. Some prominent examples of this would be the Battle of the Atlantic, Battle of Britain, and Battle of Stalingrad, all in World War II. Wars and military campaigns are guided by military strategy, wher ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
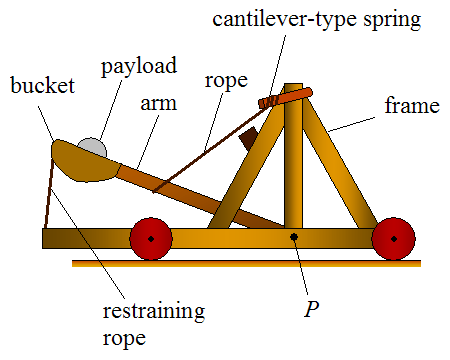
Catapults
A catapult is a ballistic device used to launch a projectile a great distance without the aid of gunpowder or other propellants – particularly various types of ancient and medieval siege engines. A catapult uses the sudden release of stored potential energy to propel its payload. Most convert tension or torsion energy that was more slowly and manually built up within the device before release, via springs, bows, twisted rope, elastic, or any of numerous other materials and mechanisms. In use since ancient times, the catapult has proven to be one of the most persistently effective mechanisms in warfare. In modern times the term can apply to devices ranging from a simple hand-held implement (also called a "slingshot") to a mechanism for launching aircraft from a ship. The earliest catapults date to at least the 7th century BC, with King Uzziah, of Judah, recorded as equipping the walls of Jerusalem with machines that shot "great stones". Catapults are mentioned in Yajurveda ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arrow
An arrow is a fin-stabilized projectile launched by a bow. A typical arrow usually consists of a long, stiff, straight shaft with a weighty (and usually sharp and pointed) arrowhead attached to the front end, multiple fin-like stabilizers called fletchings mounted near the rear, and a slot at the rear end called a nock for engaging the bowstring. A container or bag carrying additional arrows for convenient reloading is called a quiver. The use of bows and arrows by humans predates recorded history and is common to most cultures. A craftsman who makes arrows is a fletcher, and one that makes arrowheads is an arrowsmith.Paterson ''Encyclopaedia of Archery'' p. 56 History The oldest evidence of likely arrowheads, dating to c. 64,000 years ago, were found in Sibudu Cave, current South Africa.Backwell L, d'Errico F, Wadley L.(2008). Middle Stone Age bone tools from the Howiesons Poort layers, Sibudu Cave, South Africa. Journal of Archaeological Science, 35:1566–1580. Backwe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Camels
A camel (from: la, camelus and grc-gre, κάμηλος (''kamēlos'') from Hebrew or Phoenician: גָמָל ''gāmāl''.) is an even-toed ungulate in the genus ''Camelus'' that bears distinctive fatty deposits known as "humps" on its back. Camels have long been domesticated and, as livestock, they provide food (milk and meat) and textiles (fiber and felt from hair). Camels are working animals especially suited to their desert habitat and are a vital means of transport for passengers and cargo. There are three surviving species of camel. The one-humped dromedary makes up 94% of the world's camel population, and the two-humped Bactrian camel makes up 6%. The Wild Bactrian camel is a separate species and is now critically endangered. The word ''camel'' is also used informally in a wider sense, where the more correct term is "camelid", to include all seven species of the family Camelidae: the true camels (the above three species), along with the "New World" camelids: the llama, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ispahsalar
''Ispahsālār'' ( fa, اسپهسالار) or ''sipahsālār'' (; "army commander"), in Arabic rendered as ''isfahsalār'' () or ''iṣbahsalār'' (), was a title used in much of the Islamic world during the 10th–15th centuries, to denote the senior-most military commanders but also as a generic general officer rank. Islamic East and Persia The title derives from Middle Persian ''spāh-sālār'' (),"Kursi-i hazrat Zartosht"''Nirangs'' already attested in Pazend texts of the 9th century. It was the equivalent of the old Sasanian title of ''Spahbed'' (New Persian ''ispahbadh''), which during the Islamic era fell out of general use and became a regnal title among certain local dynasties in Tabaristan and Khurasan. The titles of ''Ispahsalar'' and ''Sipahsalar'' came into prominence in the Islamic world in the later 10th century, with the rise to power of Iranian dynasties during the so-called "Iranian Intermezzo". In its sense of " commander-in-chief", the title was used in paralle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
War Elephant
A war elephant was an elephant that was trained and guided by humans for combat. The war elephant's main use was to charge the enemy, break their ranks and instill terror and fear. Elephantry is a term for specific military units using elephant-mounted troops. Description War elephants played a critical role in several key battles in antiquity, especially in Ancient India. While seeing limited and periodic use in Ancient China, they became a permanent fixture in armies of historical kingdoms in Southeast Asia. During classical antiquity they were also used in ancient Persia and in the Mediterranean world within armies of Macedon, Hellenistic Greek states, the Roman Republic and later Empire, and Carthage in North Africa. In some regions they maintained a firm presence on the battlefield throughout the Middle Ages. However, their use declined with the spread of firearms and other gunpowder weaponry in early modern warfare. After this, war elephants became restricted to non- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |