|
Saccharopolyspora Rectivirgula
''Saccharopolyspora rectivirgula'' is a species of bacteria. It is a Gram-positive rod. It was formerly known as ''Micropolyspora faeni''. Inhalation of the bacteria can cause the disease farmer's lung, a type of hypersensitivity pneumonitis Hypersensitivity pneumonitis (HP) or extrinsic allergic alveolitis (EAA) is a syndrome caused by the repetitive inhalation of antigens from the environment in susceptible or sensitized people. Common antigens include molds, bacteria, bird dropping .... Handling hay bales increases exposure to the bacteria and increases the risk of developing the disease. References External linksType strain of ''Saccharopolyspora rectivirgula'' at Bac''Dive'' - the Bacterial Diversity Metadatabase Pseudonocardineae Bacteria described in 1964 {{Pseudonocardineae-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nikolai Aleksandrovich Krasil'nikov
Nikolai Aleksandrovich Krasilnikov (russian: Никола́й Алекса́ндрович Краси́льников; December 18, 1896 – July 11, 1973) was a Soviet and Russian microbiologist, bacteriologist and Soil science, soil scientist. Tribute * ''Krasilnikovia cinnamomea'' is a List of bacterial genera named after personal names, bacterial genus named after him of the family Micromonosporaceae See also * List of soil scientists References Bibliography * ''Soil Microorganisms and Higher Plants'', 1958 External links eBookSoil Microorganisms and Higher Plants 1896 births 1973 deaths People from Mosalsky Uyezd Corresponding Members of the USSR Academy of Sciences Academic staff of Moscow State University Stalin Prize winners Recipients of the Order of Lenin Recipients of the Order of the Red Banner of Labour Botanists with author abbreviations Russian bacteriologists Russian microbiologists Russian mycologists Russian soil scientists Soviet bacteriologists ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aino Henssen
Aino Marjatta Henssen (12 April 1925, Elberfeld – 29 August 2011, Marburg), was a German lichenologist and systematist. Her father, Gottfried Henssen, was a folklorist and her mother was Finns, Finnish. Education and career Henssen began her studies in Biology in Freiburg, Germany, before continuing in Marburg, Germany. She obtained her doctorate in 1953, which focused on the physiology of ''Spirodela polyrhiza''. In 1963, she became the curator of the ''Botanisches Institut'' at ''University of Marburg, Philipps-Universität'' in Marburg, Germany. Following her habilitation in 1965, she was appointed in 1970 to the position of Associate Professor for thallophyte studies. She retired in 1990. "Short biographies of 104 lichenologists who have played a key role in the development of German lichenology are provided." ("Aino Henssen" on pp. 41–43) Contributions Henssen made many advancements to the taxonomic knowledge of cyanolichens and wrote a textbook on the subject. This book r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Species
In biology, a species is the basic unit of classification and a taxonomic rank of an organism, as well as a unit of biodiversity. A species is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate sexes or mating types can produce fertile offspring, typically by sexual reproduction. Other ways of defining species include their karyotype, DNA sequence, morphology, behaviour or ecological niche. In addition, paleontologists use the concept of the chronospecies since fossil reproduction cannot be examined. The most recent rigorous estimate for the total number of species of eukaryotes is between 8 and 8.7 million. However, only about 14% of these had been described by 2011. All species (except viruses) are given a two-part name, a "binomial". The first part of a binomial is the genus to which the species belongs. The second part is called the specific name or the specific epithet (in botanical nomenclature, also sometimes i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bacteria
Bacteria (; singular: bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one biological cell. They constitute a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria were among the first life forms to appear on Earth, and are present in most of its habitats. Bacteria inhabit soil, water, acidic hot springs, radioactive waste, and the deep biosphere of Earth's crust. Bacteria are vital in many stages of the nutrient cycle by recycling nutrients such as the fixation of nitrogen from the atmosphere. The nutrient cycle includes the decomposition of dead bodies; bacteria are responsible for the putrefaction stage in this process. In the biological communities surrounding hydrothermal vents and cold seeps, extremophile bacteria provide the nutrients needed to sustain life by converting dissolved compounds, such as hydrogen sulphide and methane, to energy. Bacteria also live in symbiotic and parasitic relationsh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gram-positive Bacteria
In bacteriology, gram-positive bacteria are bacteria that give a positive result in the Gram stain test, which is traditionally used to quickly classify bacteria into two broad categories according to their type of cell wall. Gram-positive bacteria take up the crystal violet stain used in the test, and then appear to be purple-coloured when seen through an optical microscope. This is because the thick peptidoglycan layer in the bacterial cell wall retains the stain after it is washed away from the rest of the sample, in the decolorization stage of the test. Conversely, gram-negative bacteria cannot retain the violet stain after the decolorization step; alcohol used in this stage degrades the outer membrane of gram-negative cells, making the cell wall more porous and incapable of retaining the crystal violet stain. Their peptidoglycan layer is much thinner and sandwiched between an inner cell membrane and a bacterial outer membrane, causing them to take up the counterstain (sa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
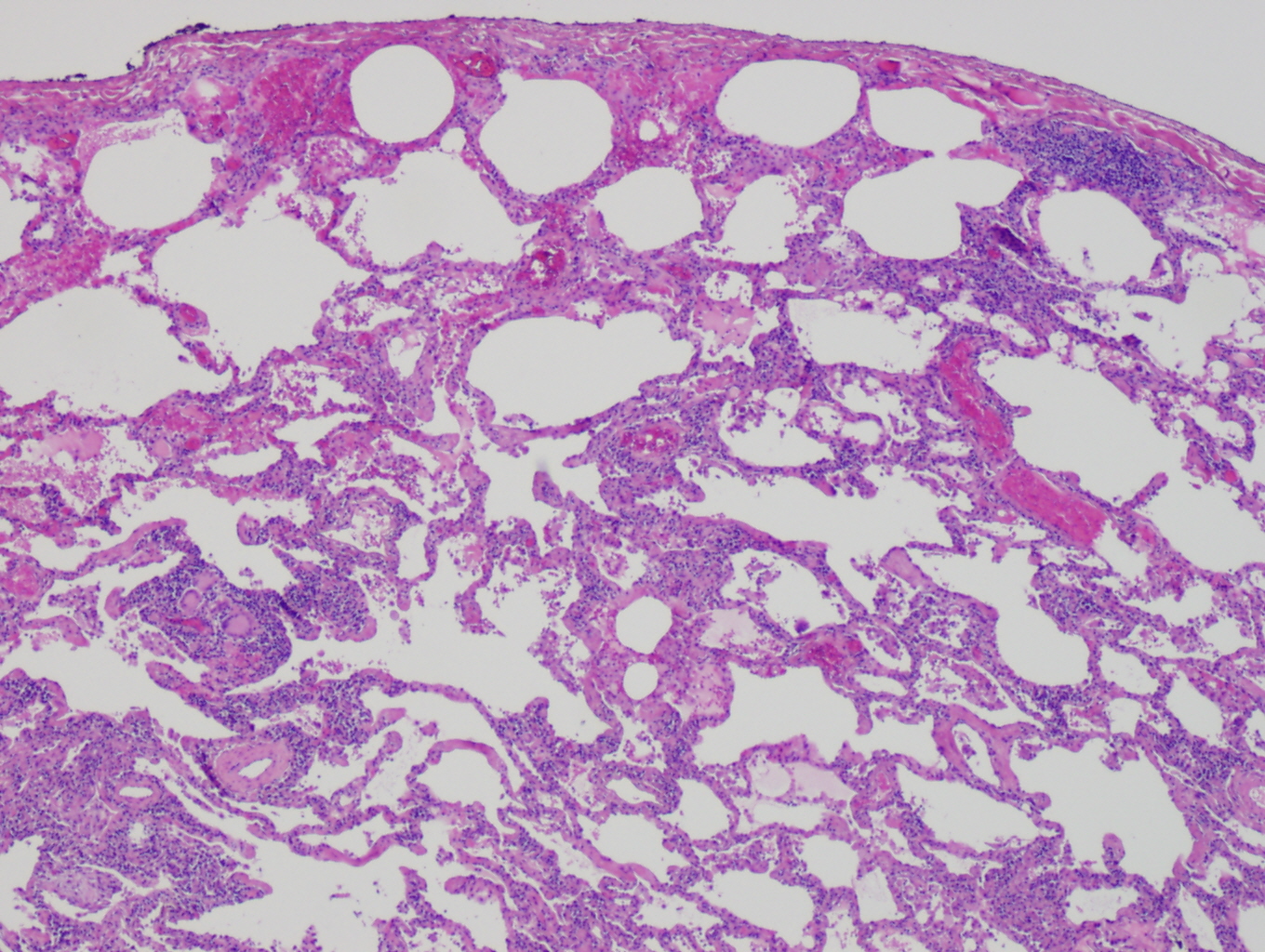
Farmer's Lung
Farmer's lung (not to be confused with silo-filler's disease) is a hypersensitivity pneumonitis induced by the inhalation of biologic dusts coming from hay dust or mold spores or any other agricultural products. It results in a type III hypersensitivity inflammatory response and can progress to become a chronic condition which is considered potentially dangerous. Signs and symptoms * Acute Stage: Appears four to eight hours after exposure. Symptoms such as headache, irritating cough, and shortness of breath upon physical exertion. * Subacute Stage: Symptoms persist without further exposure, and increase in severity. Symptoms include: shortness of breath upon exertion, chronic coughing, physical weakness, occasional fever and sweating, decrease in appetite, aches and pains. * Chronic Stage: Debilitating effects are now considered long-term. Symptoms include: severe shortness of breath, chronic coughing, physical weakness, occasional fever and sweating at night, decrease in ap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis
Hypersensitivity pneumonitis (HP) or extrinsic allergic alveolitis (EAA) is a syndrome caused by the repetitive inhalation of antigens from the environment in susceptible or sensitized people. Common antigens include molds, bacteria, bird droppings, bird feathers, agricultural dusts, bioaerosols and chemicals from paints or plastics. People affected by this type of lung inflammation (pneumonitis) are commonly exposed to the antigens by their occupations, hobbies, the environment and animals. The inhaled antigens produce a hypersensitivity immune reaction causing inflammation of the airspaces (alveoli) and small airways (bronchioles) within the lung. Hypersensitivity pneumonitis may eventually lead to interstitial lung disease. Signs and symptoms Hypersensitivity pneumonitis (HP) can be categorized as acute, subacute, and chronic based on the duration of the illness. Acute In the acute form of HP dose of antigen exposure tends to be very high but only for a short duration. Symptoms ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pseudonocardineae
The Pseudonocardiaceae are a family of bacteria in the order Actinomycetales and the only member of the suborder Pseudonocardineae. Genomics The species within the family Pseudonocardiaceae form a distinct clade in phylogenetic trees based on concatenated protein sequences. Additionally, ''Nakamurella multipartite'', currently part of the order Frankiales, also formed a clade with the Pseudonocardiaceae species in 100% of the bootstrap replications of the phylogenetic trees. A conserved signature indel has been identified which is found in ''N. multipartite'' and all but one of the Pseudonocardiaceae species. This one-amino-acid insertion in UMP kinase serves to both provide a molecular marker for nearly all of the Pseudonocardiaceae and suggests ''N. multipartite'' is closely related to this group. Some evidence also suggests the orders Pseudonocardiales and Corynebacteriales are closely related. Several conserved signature indels have been identified which are found in both ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |