|
SUMF1
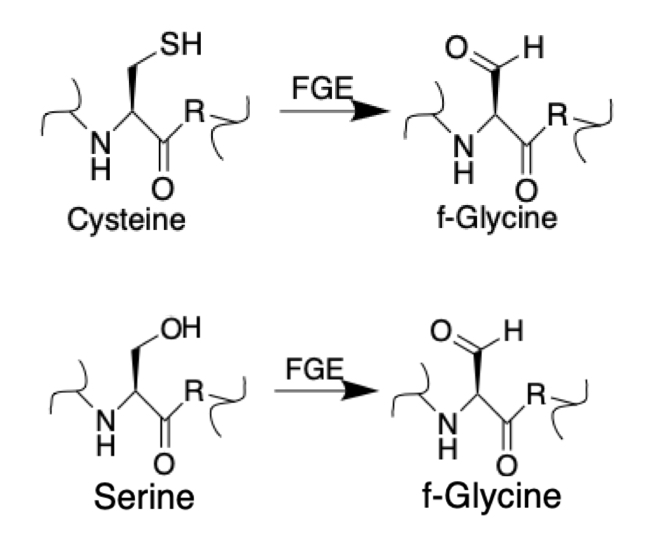
Sulfatase-modifying factor 1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''SUMF1'' gene. Sulfatases catalyze the hydrolysis of sulfate esters such as glycosaminoglycans, sulfolipids, and steroid sulfates. C-alpha-formylglycine (FGly), the catalytic residue in the active site of eukaryotic sulfatases, is posttranslationally generated from a cysteine by SUMF1, the human form of the aerobic Formylglycine-generating enzyme (FGE), in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER). The genetic defect of FGly formation caused by mutations in the SUMF1 gene results in inactive FGE, and subsequently multiple sulfatase deficiency Multiple sulfatase deficiency (MSD), also known as Austin disease, or mucosulfatidosis, is a very rare autosomal recessiveJames, William; Berger, Timothy; Elston, Dirk (2005). ''Andrews' Diseases of the Skin: Clinical Dermatology''. (10th ed.). Sau ... (MSD; MIM 272200), a lysosomal storage disorder (Roeser et al., 2006). upplied by OMIMref name="entrez" /> References Furthe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Formylglycine-generating Enzyme
Formylglycine-generating enzyme (FGE), located at 3p26.1 in humans, is the name for an enzyme present in the endoplasmic reticulum that catalyzes the conversion of cysteine to formylglycine (fGly). There are two main classes of FGE, aerobic and anaerobic. FGE activates sulfatases, which are essential for the degradation of sulfate esters. The catalytic activity of sulfatases is dependent upon a formylglycine (sometimes called oxoalanine) residue in the active site. Aerobic The aerobic enzyme has a structure homologous to the complex alpha/beta topology found in the gene product of human sulfatase-modifying factor 1 (SUMF1). Aerobic FGE converts a cysteine residue in the highly conserved consensus sequence CXPXR to fGly. To do so, FGE “activates” its target by utilizing mononuclear copper. The substrate first binds to copper, increasing reactivity of the substrate-copper complex with oxygen. Activation is then accomplished through oxidation of a cysteine residue in the substr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enzyme
Enzymes () are proteins that act as biological catalysts by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as products. Almost all metabolic processes in the cell need enzyme catalysis in order to occur at rates fast enough to sustain life. Metabolic pathways depend upon enzymes to catalyze individual steps. The study of enzymes is called ''enzymology'' and the field of pseudoenzyme analysis recognizes that during evolution, some enzymes have lost the ability to carry out biological catalysis, which is often reflected in their amino acid sequences and unusual 'pseudocatalytic' properties. Enzymes are known to catalyze more than 5,000 biochemical reaction types. Other biocatalysts are catalytic RNA molecules, called ribozymes. Enzymes' specificity comes from their unique three-dimensional structures. Like all catalysts, enzymes increase the reaction ra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "...Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity and the molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protein-coding genes and noncoding genes. During gene expression, the DNA is first copied into RNA. The RNA can be directly functional or be the intermediate template for a protein that performs a function. The transmission of genes to an organism's offspring is the basis of the inheritance of phenotypic traits. These genes make up different DNA sequences called genotypes. Genotypes along with environmental and developmental factors determine what the phenotypes will be. Most biological traits are under the influence of polygenes (many different genes) as well as gen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sulfate Ester
Organosulfates are a class of organic compounds sharing a common functional group with the structure R-O-SO3−. The SO4 core is a sulfate group and the R group is any organic residue. All organosulfates are formally esters derived from alcohols and sulfuric acid, although many are not prepared in this way. Many sulfate esters are used in detergents, and some are useful reagents. Alkyl sulfates consist of a hydrophobic hydrocarbon chain, a polar sulfate group (containing an anion) and either a cation or amine to neutralize the sulfate group. Examples include: sodium lauryl sulfate (also known as sulfuric acid mono dodecyl ester sodium salt) and related potassium and ammonium salts. Applications Alkyl sulfates are commonly used as an anionic surfactant in liquid soaps and detergents used to clean wool, as surface cleaners, and as active ingredients in laundry detergents, shampoos and conditioners. They can also be found in household products such as toothpaste, antacids, cosmeti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glycosaminoglycan
Glycosaminoglycans (GAGs) or mucopolysaccharides are long, linear polysaccharides consisting of repeating disaccharide units (i.e. two-sugar units). The repeating two-sugar unit consists of a uronic sugar and an amino sugar, except in the case of the sulfated glycosaminoglycan keratan, where, in place of the uronic sugar there is a galactose unit. GAGs are found in vertebrates, invertebrates and bacteria. Because GAGs are highly polar molecules and attract water; the body uses them as lubricants or shock absorbers. Mucopolysaccharidoses are a group of metabolic disorders in which abnormal accumulations of glycosaminoglycans occur due to enzyme deficiencies. Production Glycosaminoglycans vary greatly in molecular mass, disaccharide structure, and sulfation. This is because GAG synthesis is not template driven, as are proteins or nucleic acids, but constantly altered by processing enzymes. GAGs are classified into four groups, based on their core disaccharide structures. Hepa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sulfolipid
Sulfolipids are a class of lipids which possess a sulfur-containing functional group. An abundant sulfolipid is sulfoquinovosyl diacylglycerol, which is composed of a glycoside of sulfoquinovose and diacylglycerol. In plants, sulfoquinovosyl diacylglycerides (SQDG) are important members of the sulfur cycle. Other important sulfolipids include sulfatide and seminolipid, each of which are sulfated glycolipids. Sulfolipids have been implicated in the functions of two of the core components of the photosynthetic electron transport chain and while not necessarily essential, might have a protective function when the photosynthetic apparatus is under stress. Must see * Sulfatide * Galactolipid Galactolipids are a type of glycolipid whose sugar group is galactose. They differ from glycosphingolipids in that they do not have nitrogen in their composition. They are the main part of plant membrane lipids where they substitute phospholipids ... *Phospholipid *Glycolipid References L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Steroid Sulfate
Steroid sulfates are endogenous sulfate esters of steroids. They are formed by steroid sulfotransferases via sulfation of endogenous steroids like cholesterol and steroid hormones. Although steroid sulfates do not bind to steroid hormone receptors and hence are hormonally inert, they can be desulfated by steroid sulfatase and in this way serve as precursors and circulating reservoirs for their active unsulfated counterparts. In addition, some steroid sulfates have biological activity in their own right, for instance acting as neurosteroids and modulating ligand-gated ion channels such as the GABAA and NMDA receptors among other biological targets. List of endogenous steroid sulfates Endogenous steroid sulfates include: * Cholesterol sulfate (formed from cholesterol by SULT2B1b) * Pregnenolone sulfate (formed from pregnenolone by SULT2A1 and SULT2B1a) * sulfate (formed from by SULT2A1 and SULT1E1) * Androstenediol sulfate (formed from androstenediol) * Androsterone sulfate ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |