|
STklos
STklos is a Scheme implementation that succeeded STk. It is a bytecode compiler with an ad hoc virtual machine which aims to be fast as well as light. STklos is free software, released under the GNU General Public License. In addition to implementing most of R5RS, and a large part of R7RS, STklos supports: * an object system based on CLOS with multiple inheritance, generic functions, multimethods and a MOP * a module system * easy connection with the GTK toolkit * a low-level macro system that compiles macro expanders into bytecode (syntax-rules is also present as a high-level macro system) * a full Numerical tower implementation, as defined in R7RS * Unicode support * Perl compatible regular expressions via PCRE library * a simple foreign function interface via libffi libffi is a foreign function interface library. It provides a C programming language interface for calling natively compiled functions given information about the target function at run time instead of comp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
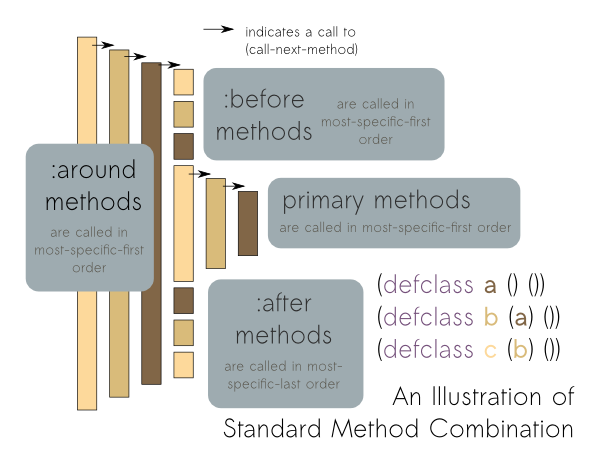
Common Lisp Object System
The Common Lisp Object System (CLOS) is the facility for object-oriented programming in American National Standards Institute, ANSI Common Lisp. CLOS is a powerful dynamic programming language, dynamic object system which differs radically from the OOP facilities found in more static languages such as C++ or Java (programming language), Java. CLOS was inspired by earlier Lisp object systems such as Flavors (computer science), MIT Flavors and CommonLoops, although it is more general than either. Originally proposed as an add-on, CLOS was adopted as part of the ANSI standard for Common Lisp and has been adapted into other Lisp dialects such as EuLisp or Emacs Lisp. Features The basic building blocks of CLOS are method (computer programming), methods, Class (computer programming), classes, instances of those classes, and generic functions. CLOS provides macros to define those: defclass, defmethod, and defgeneric. Instances are created with the method make-instance. Classes can hav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cross-platform
Within computing, cross-platform software (also called multi-platform software, platform-agnostic software, or platform-independent software) is computer software that is designed to work in several Computing platform, computing platforms. Some cross-platform software requires a separate build for each platform, but some can be directly run on any platform without special preparation, being written in an interpreted language or compiled to portable bytecode for which the Interpreter (computing), interpreters or run-time packages are common or standard components of all supported platforms. For example, a cross-platform application software, application may run on Linux, macOS and Microsoft Windows. Cross-platform software may run on many platforms, or as few as two. Some frameworks for cross-platform development are Codename One, ArkUI-X, Kivy (framework), Kivy, Qt (software), Qt, GTK, Flutter (software), Flutter, NativeScript, Xamarin, Apache Cordova, Ionic (mobile app framework ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unicode
Unicode or ''The Unicode Standard'' or TUS is a character encoding standard maintained by the Unicode Consortium designed to support the use of text in all of the world's writing systems that can be digitized. Version 16.0 defines 154,998 Character (computing), characters and 168 script (Unicode), scripts used in various ordinary, literary, academic, and technical contexts. Unicode has largely supplanted the previous environment of a myriad of incompatible character sets used within different locales and on different computer architectures. The entire repertoire of these sets, plus many additional characters, were merged into the single Unicode set. Unicode is used to encode the vast majority of text on the Internet, including most web pages, and relevant Unicode support has become a common consideration in contemporary software development. Unicode is ultimately capable of encoding more than 1.1 million characters. The Unicode character repertoire is synchronized with Univers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SLIB
SLIB is computer software, a library for the programming language Scheme, written by Aubrey Jaffer. It uses only standard Scheme syntax and thus works on many different Scheme implementations, such as Bigloo, Chez Scheme, Extension Language Kit 3.0, Gambit 3.0, GNU Guile, JScheme JScheme is an implementation of the Scheme programming language, created by Kenneth R. Anderson, Timothy J. Hickey and Peter Norvig, which is almost compliant with the R4RS Scheme standard and which has an interface to Java. Distributed under ..., Kawa, Larceny, MacScheme, MIT/GNU Scheme, Pocket Scheme, Racket, RScheme, Scheme 48, SCM, SCM Mac, and scsh. SLIB is used by GnuCash. Other implementations can support SLIB in a unified way through Scheme Requests for Implementation (SRFI) 96. SLIB is a GNU package. References External links * Scheme (programming language) GNU Project software {{prog-lang-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scheme Requests For Implementation
Scheme Requests for Implementation (SRFI) is an effort to coordinate libraries and extensions of standard Scheme programming language, necessitated by Scheme's minimalist design, and particularly the lack of a standard library before Scheme R6RS. Specific SRFI documents are supported by many Scheme implementations. This, in effect, makes SRFI an informal standards process. History At the Scheme Workshop held in Baltimore, Maryland, on September 26, 1998, the attendees considered several proposals for standardized feature sets to include in Scheme implementations. Alan Bawden proposed that there be a repository for library proposals. Shriram Krishnamurthi volunteered to host the library, and Dave Mason and Mike Sperber joined him as initial editors and coordinators of the library process. The term ''Request for Implementation'', a play on the Internet ''Request for Comments A Request for Comments (RFC) is a publication in a series from the principal technical development an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
POSIX Threads
In computing, POSIX Threads, commonly known as pthreads, is an execution model that exists independently from a programming language, as well as a parallel execution model. It allows a program to control multiple different flows of work that overlap in time. Each flow of work is referred to as a '' thread'', and creation and control over these flows is achieved by making calls to the POSIX Threads API. POSIX Threads is an API defined by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) standard ''POSIX.1c, Threads extensions (IEEE Std 1003.1c-1995)''. Implementations of the API are available on many Unix-like POSIX-conformant operating systems such as FreeBSD, NetBSD, OpenBSD, Linux, macOS, Android, Solaris, Redox, and AUTOSAR Adaptive, typically bundled as a library libpthread. DR-DOS and Microsoft Windows implementations also exist: within the SFU/SUA subsystem which provides a native implementation of a number of POSIX APIs, and also within third-party packages su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Libffi
libffi is a foreign function interface library. It provides a C programming language interface for calling natively compiled functions given information about the target function at run time instead of compile time. It also implements the opposite functionality: libffi can produce a pointer to a function that can accept and decode any combination of arguments defined at run time. libffi is most often used as a bridging technology between compiled and interpreted language implementations. libffi may also be used to implement plug-ins, where the plug-in's function signatures are not known at the time of creating the host application. Notable users include Python, Haskell, Dalvik, F-Script, PyPy, PyObjC, RubyCocoa, JRuby, Rubinius, MacRuby, gcj, GNU Smalltalk, IcedTea, Cycript, Pawn, Java Native Access, Common Lisp (via CFFI), Racket, Embeddable Common Lisp and Mozilla. On Mac OS X, libffi is commonly used with BridgeSupport, which provides programming language neut ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Foreign Function Interface
A foreign function interface (FFI) is a mechanism by which a program written in one programming language can call routines or make use of services written or compiled in another one. An FFI is often used in contexts where calls are made into a binary dynamic-link library. Naming The term comes from the specification for Common Lisp, which explicitly refers to the programming language feature enabling for inter-language calls as such; the term is also often used officially by the interpreter and compiler documentation for Haskell, Rust, PHP, Python, and LuaJIT ( Lua). Other languages use other terminology: Ada has ''language bindings'', while Java has '' Java Native Interface'' (JNI) or '' Java Native Access'' (JNA). Foreign function interface has become generic terminology for mechanisms which provide such services. Operation The primary function of a foreign function interface is to mate the semantics and calling conventions of one programming language (the ''host'' lan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PCRE
Perl Compatible Regular Expressions (PCRE) is a library written in C, which implements a regular expression engine, inspired by the capabilities of the Perl programming language. Philip Hazel started writing PCRE in summer 1997. PCRE's syntax is much more powerful and flexible than either of the POSIX regular expression flavors (BRE, ERE) and than that of many other regular-expression libraries. While PCRE originally aimed at feature-equivalence with Perl, the two implementations are not fully equivalent. During the PCRE 7.x and Perl 5.9.x phase, the two projects coordinated development, with features being ported between them in both directions. In 2015, a fork of PCRE was released with a revised programming interface (API). The original software, now called PCRE1 (the 1.xx–8.xx series), has had bugs mended, but no further development. , it is considered obsolete, and the current 8.45 release is likely to be the last. The new PCRE2 code (the 10.xx series) has had a numbe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Numerical Tower
In Scheme, the numerical tower is a set of data types that represent numbers and a logic for their hierarchical organisation. Each type in the tower conceptually "sits on" a more fundamental type, so an integer is a rational number and a number, but the converse is not necessarily true, i.e. not every number is an integer. This asymmetry implies that a language can safely allow implicit coercions of numerical types—without creating semantic problems—in only one direction: coercing an integer to a rational loses no information and will never influence the value returned by a function, but to coerce most reals to an integer would alter any relevant computation (e.g., the real 1/3 does not equal any integer) and is thus impermissible. In Scheme Principally, the numerical tower is designed to codify the set theoretic properties of numbers in an easy-to-implement language facility: every integer is a rational with an implicit denominator of 1, and all reals are complex with an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Programming Language
A programming language is a system of notation for writing computer programs. Programming languages are described in terms of their Syntax (programming languages), syntax (form) and semantics (computer science), semantics (meaning), usually defined by a formal language. Languages usually provide features such as a type system, Variable (computer science), variables, and mechanisms for Exception handling (programming), error handling. An Programming language implementation, implementation of a programming language is required in order to Execution (computing), execute programs, namely an Interpreter (computing), interpreter or a compiler. An interpreter directly executes the source code, while a compiler produces an executable program. Computer architecture has strongly influenced the design of programming languages, with the most common type (imperative languages—which implement operations in a specified order) developed to perform well on the popular von Neumann architecture. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metaobject Protocol
In computer science, a metaobject is an object that manipulates, creates, describes, or implements objects (including itself). The object that the metaobject pertains to is called the base object. Some information that a metaobject might define includes the base object's type, interface, class, methods, attributes, parse tree, etc. Metaobjects are examples of the computer science concept of reflection, where a system has access (usually at run time) to its own internal structure. Reflection enables a system to essentially rewrite itself on the fly, to alter its own implementation as it executes. Metaobject protocol A metaobject protocol (MOP) provides the vocabulary (protocol) to access and manipulate the structure and behaviour of systems of objects. Typical functions of a metaobject protocol include: *Create or delete a new class *Create a new property or method *Cause a class to inherit from a different class ("change the class structure") *Generate or change the code defining ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |