|
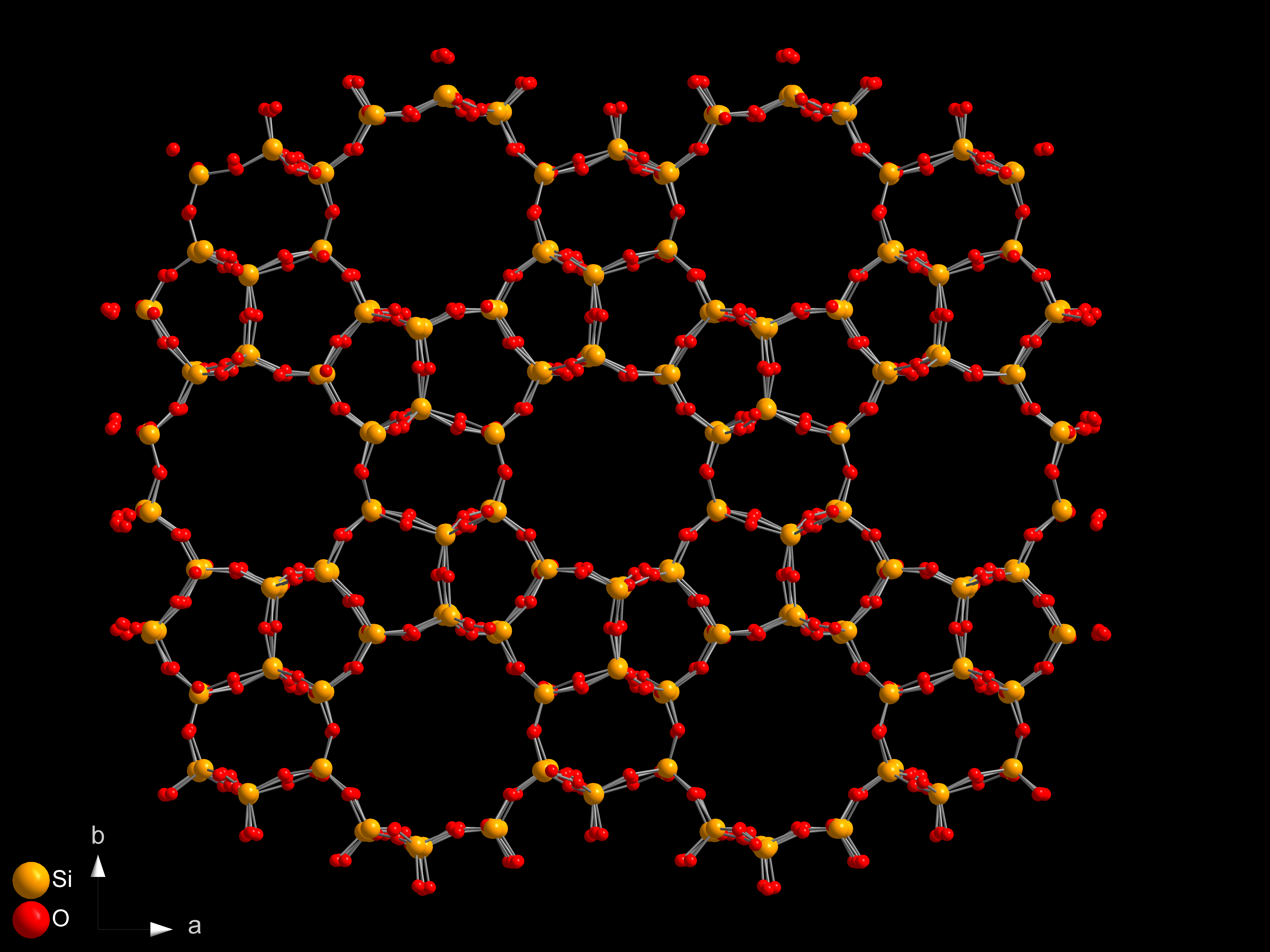
SSZ-13
SSZ-13 (framework type code CHA) is a high-silica aluminosilicate zeolite possessing 0.38 × 0.38 nm micropores.Baerlocher, Ch.; McCusker, L.B..; Olson, D.H. Atlas of Zeolite framework Types, Elsevier, Amsterdam, 6th edn., 2007, see also: http://www.iza-structure.org/databases/. It belongs to the ABC-6 family of zeolites as well as offretite, cancrinite, erionite and other related small-pore zeolites. The framework topology is the same as that of chabazite but SSZ-13 has a high silica composition with Si/Al > 5, which leads to low cation exchange capacity. The typical chemical formula of the unit cell can be described as Q''x''Na''y''Al2.4Si33.6O72•''z''H2O (1.4 < ''x'' <27)(0.7 < ''y'' < 4.3)(1 < ''z'' <7), where Q is ''N'',''N'',''N''-1-trimethyladamantammonium. The material was patented by research Company in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zeolite
Zeolites are microporous, crystalline aluminosilicate materials commonly used as commercial adsorbents and catalysts. They mainly consist of silicon, aluminium, oxygen, and have the general formula ・y where is either a metal ion or H+. These positive ions can be exchanged for others in a contacting electrolyte solution. exchanged zeolites are particularly useful as solid acid catalysts. The term ''zeolite'' was originally coined in 1756 by Swedish mineralogist Axel Fredrik Cronstedt, who observed that rapidly heating a material, believed to have been stilbite, produced large amounts of steam from water that had been adsorbed by the material. Based on this, he called the material ''zeolite'', from the Greek , meaning "to boil" and , meaning "stone". Zeolites occur naturally but are also produced industrially on a large scale. , 253 unique zeolite frameworks have been identified, and over 40 naturally occurring zeolite frameworks are known. Every new zeolite structure th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chabazite-Ca
Chabazite ()The New Oxford Dictionary of English (1998) - p. 300 "chabazite /'kabəzʌɪt/ noun "A colourless, pink or yellow zeolite mineral, typically occurring as rhombohedral crystals.". is a tectosilicate mineral of the zeolite group, closely related to gmelinite, with the chemical formula . Recognized varieties include Chabazite-Ca, Chabazite-K, Chabazite-Na, and Chabazite-Sr, depending on the prominence of the indicated cation. Chabazite crystallizes in the triclinic crystal system with typically rhombohedral shaped crystals that are pseudo-cubic. The crystals are typically twinned, and both contact twinning and penetration twinning may be observed. They may be colorless, white, orange, brown, pink, green, or yellow. The hardness ranges from 3 to 5 and the specific gravity from 2.0 to 2.2. The luster is vitreous. It was named chabasie in 1792 by Bosc d'Antic and later changed to the current spelling. Chabazite occurs most commonly in voids and amygdules in basaltic r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ZSM-5 Oil Company in 1975, it is widely used in the petroleum industry as a heterogeneous catalyst for hydrocarbon isomerization reactions.
ZSM-5, Zeolite Socony Mobil–5 (framework type MFI from ZSM-5 (five)), is an aluminosilicate zeolite belonging to the pentasil family of zeolites. Its chemical formula is NanAlnSi96–nO192·16H2O (0 Structure [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tetraethyl Orthosilicate
Tetraethyl orthosilicate, formally named tetraethoxysilane (TEOS), ethyl silicate is the organic chemical compound with the formula Si(OC2H5)4. TEOS is a colorless liquid. It degrades in water. TEOS is the of orthosilicic acid, Si(OH)4. It is the most prevalent alkoxide of silicon. TEOS is a tetrahedral molecule. Like its many analogues, it is prepared by alcoholysis of silicon tetrachloride: :SiCl4 + 4 EtOH → Si(OEt)4 + 4 HCl where Et is the ethyl group, C2H5, and thus EtOH is ethanol. Applications TEOS is mainly used as a crosslinking agent in silicone polymers and as a precursor to silicon dioxide in the semiconductor industry. TEOS is also used as the silica source for synthesis of some zeolites. Other applications include coatings for carpets and other objects. TEOS is used in the production of aerogel. These applications exploit the reactivity of the Si-OR bonds. TEOS has historically been used as an additive to alcohol based rocket fuels to decrease the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Autoclave
An autoclave is a machine used to carry out industrial and scientific processes requiring elevated temperature and pressure in relation to ambient pressure and/or temperature. Autoclaves are used before surgical procedures to perform sterilization and in the chemical industry to cure coatings and vulcanize rubber and for hydrothermal synthesis. Industrial autoclaves are used in industrial applications, especially in the manufacturing of composites. Many autoclaves are used to sterilize equipment and supplies by subjecting them to pressurized saturated steam at for around 30-60 minutes at a pressure of 15 psi (103 kPa or 1.02 atm) depending on the size of the load and the contents. The autoclave was invented by Charles Chamberland in 1879, although a precursor known as the steam digester was created by Denis Papin in 1679. The name comes from Greek ''auto-'', ultimately meaning self, and Latin ''clavis'' meaning key, thus a self-locking device. Uses Sterilization au ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fumed Silica
Fumed silica ( CAS number 112945-52-5), also known as pyrogenic silica because it is produced in a flame, consists of microscopic droplets of amorphous silica fused into branched, chainlike, three-dimensional secondary particles which then agglomerate into tertiary particles. The resulting powder has an extremely low bulk density and high surface area. Its three-dimensional structure results in viscosity-increasing, thixotropic behavior when used as a thickener or reinforcing filler. Properties Fumed silica has a very strong thickening effect. Primary particle size is 5–50 nm. The particles are non-porous and have a surface area of 50–600 m2/g. The density is 160–190 kg/m3. Production Fumed silica is made from flame pyrolysis of silicon tetrachloride or from quartz sand vaporized in a 3000 °C electric arc. Major global producers are Evonik (who sells it under the name Aerosil), Cabot Corporation (Cab-O-Sil), Wacker Chemie (HDK), Dow Corning ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deionized Water
Purified water is water that has been mechanically filtered or processed to remove impurities and make it suitable for use. Distilled water was, formerly, the most common form of purified water, but, in recent years, water is more frequently purified by other processes including capacitive deionization, reverse osmosis, carbon filtering, microfiltration, ultrafiltration, ultraviolet oxidation, or electrodeionization. Combinations of a number of these processes have come into use to produce ultrapure water of such high purity that its trace contaminants are measured in parts per billion (ppb) or parts per trillion (ppt). Purified water has many uses, largely in the production of medications, in science and engineering laboratories and industries, and is produced in a range of purities. It is also used in the commercial beverage industry as the primary ingredient of any given trademarked bottling formula, in order to maintain product consistency. It can be produced on-site for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NaOH
Sodium hydroxide, also known as lye and caustic soda, is an inorganic compound with the formula NaOH. It is a white solid ionic compound consisting of sodium cations and hydroxide anions . Sodium hydroxide is a highly caustic base and alkali that decomposes proteins at ordinary ambient temperatures and may cause severe chemical burns. It is highly soluble in water, and readily absorbs moisture and carbon dioxide from the air. It forms a series of hydrates . The monohydrate crystallizes from water solutions between 12.3 and 61.8 °C. The commercially available "sodium hydroxide" is often this monohydrate, and published data may refer to it instead of the anhydrous compound. As one of the simplest hydroxides, sodium hydroxide is frequently used alongside neutral water and acidic hydrochloric acid to demonstrate the pH scale to chemistry students. Sodium hydroxide is used in many industries: in the manufacture of pulp and paper, textiles, drinking water, soaps and dete ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |