|
SSIM
The structural similarity index measure (SSIM) is a method for predicting the perceived quality of digital television and cinematic pictures, as well as other kinds of digital images and videos. It is also used for measuring the similarity between two images. The SSIM index is a full reference metric; in other words, the measurement or prediction of image quality is based on an initial uncompressed or distortion-free image as reference. SSIM is a perception-based model that considers image degradation as perceived change in structural information, while also incorporating important perceptual phenomena, including both luminance masking and contrast masking terms. This distinguishes from other techniques such as mean squared error (MSE) or peak signal-to-noise ratio (PSNR) that instead estimate absolute errors. Structural information is the idea that the pixels have strong inter-dependencies especially when they are spatially close. These dependencies carry important informati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Video Quality
Video quality is a characteristic of a video passed through a video transmission or processing system that describes perceived video degradation (typically compared to the original video). Video processing systems may introduce some amount of distortion or artifacts in the video signal that negatively impact the user's perception of the system. For many stakeholders in video production and distribution, ensuring video quality is an important task. Video quality evaluation is performed to describe the quality of a set of video sequences under study. Video quality can be evaluated objectively (by mathematical models) or subjectively (by asking users for their rating). Also, the quality of a system can be determined offline (i.e., in a laboratory setting for developing new codecs or services) or in-service (to monitor and ensure a certain level of quality). From analog to digital video Since the world's first video sequence was recorded and transmitted, many video processing systems ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peak Signal-to-noise Ratio
Peak signal-to-noise ratio (PSNR) is an engineering term for the ratio between the maximum possible power of a signal and the power of corrupting noise that affects the fidelity of its representation. Because many signals have a very wide dynamic range, PSNR is usually expressed as a logarithmic quantity using the decibel scale. PSNR is commonly used to quantify reconstruction quality for images and video subject to lossy compression. Definition PSNR is most easily defined via the mean squared error (''MSE''). Given a noise-free ''m''×''n'' monochrome image ''I'' and its noisy approximation ''K'', ''MSE'' is defined as : \mathit = \frac\sum_^\sum_^ (i,j) - K(i,j)2. The PSNR (in dB) is defined as : \begin \mathit &= 10 \cdot \log_ \left( \frac \right) \\ &= 20 \cdot \log_ \left( \frac \right) \\ &= 20 \cdot \log_(\mathit_I) - 10 \cdot \log_ (\mathit). \end Here, ''MAXI'' is the maximum possible pixel value of the image. When the pixels are represented using 8 bits pe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alan Bovik
Alan Conrad Bovik (born June 25, 1958) is an American engineer, vision scientist, and educator. He is a professor at the University of Texas at Austin (UT-Austin), where he holds the Cockrell Family Regents Endowed Chair in the Cockrell School of Engineering and is Director of the Laboratory for Image and Video Engineering (LIVE). He is a faculty member in the UT-Austin Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, the Machine Learning Laboratory, the Institute for Neuroscience, and the Wireless Networking and Communications Group. Bovik received a Primetime Emmy Award in 2015 for his development of perception-based video quality measurement tools that are now standards in television production. He also received a Technology and Engineering Emmy Award in 2021 for the “development of perceptual metrics for video encoding optimization.” Work Al Bovik was educated at the University of Illinois at Urbana–Champaign (PhD 1984). He has made numerous fundamental contribution ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eero Simoncelli
Eero Simoncelli is an American computational neuroscientist and Silver Professor at New York University. He was a Howard Hughes Medical Institute Investigator from 2000 to 2020. In 2020, he became the inaugural director of the Center for Computational Neuroscience at the Flatiron Institute of the Simons Foundation. Education and early career Simoncelli graduated summa cum laude with a bachelor's degree in physics at Harvard University in 1984. He then attended Cambridge University on a Knox Fellowship to study the Mathematical Tripos, after which he joined the graduate program at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology in electrical engineering and computer science. He received his master's degree in 1988 and his PhD in 1993. He then joined the faculty at the University of Pennsylvania as an assistant professor, and in 1996 he moved to New York University. Awards and professional recognition In 2009, he became an IEEE Fellow. He received an Engineering Emmy Award in 2015 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
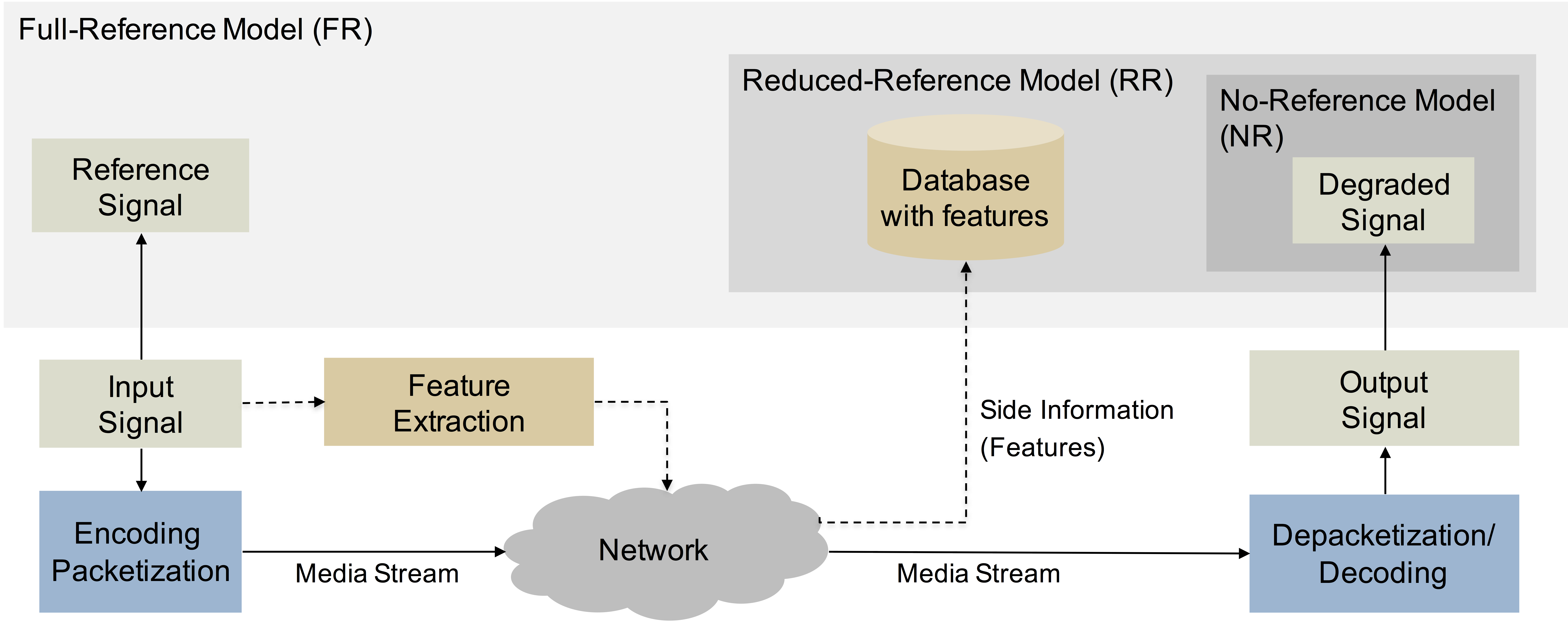
Image Quality
Image quality can refer to the level of accuracy with which different imaging systems capture, process, store, compress, transmit and display the signals that form an image. Another definition refers to image quality as "the weighted combination of all of the visually significant attributes of an image". The difference between the two definitions is that one focuses on the characteristics of signal processing in different imaging systems and the latter on the perceptual assessments that make an image pleasant for human viewers. Image quality should not be mistaken with image fidelity. Image fidelity refers to the ability of a process to render a given copy in a perceptually similar way to the original (without distortion or information loss), i.e., through a digitization or conversion process from analog media to digital image. The process of determining the level of accuracy is called Image Quality Assessment (IQA). Image quality assessment is part of the quality of experience ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Primetime Engineering Emmy Award
The Primetime Engineering Emmy Awards, or Engineering Emmys, are one of two sets of Emmy Awards that are presented for outstanding achievement in engineering development in the television industry. The Primetime Engineering Emmys are presented by the Academy of Television Arts & Sciences (ATAS), while the separate Technology and Engineering Emmy Awards are given by its sister organization, the National Academy of Television Arts and Sciences (NATAS). The Primetime Engineering Emmy is presented to an individual, company or organization for engineering developments so significant an improvement on existing methods or so innovative in nature that they materially affect the transmission, recording or reception of television. The award is determined by a jury of highly qualified, experienced engineers in the television industry. In addition, since 2003 the ATAS also bestows in most years the Philo T. Farnsworth Award, which is a Primetime Engineering Emmy Award given to honor companie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RGB Color Model
The RGB color model is an additive color, additive color model in which the red, green, and blue primary colors of light are added together in various ways to reproduce a broad array of colors. The name of the model comes from the initials of the three additive primary colors, red, green, and blue. The main purpose of the RGB color model is for the sensing, representation, and display of images in electronic systems, such as televisions and computers, though it has also been used in conventional photography and Light-emitting diode#RGB systems, colored lighting. Before the electronic age, the RGB color model already had a solid theory behind it, based in Trichromacy, human perception of colors. RGB is a ''device-dependent'' color model: different devices detect or reproduce a given RGB value differently, since the color elements (such as phosphors or dyes) and their response to the individual red, green, and blue levels vary from manufacturer to manufacturer, or even in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Distance Function
In mathematics, a metric space is a set together with a notion of ''distance'' between its elements, usually called points. The distance is measured by a function called a metric or distance function. Metric spaces are a general setting for studying many of the concepts of mathematical analysis and geometry. The most familiar example of a metric space is 3-dimensional Euclidean space with its usual notion of distance. Other well-known examples are a sphere equipped with the angular distance and the hyperbolic plane. A metric may correspond to a metaphorical, rather than physical, notion of distance: for example, the set of 100-character Unicode strings can be equipped with the Hamming distance, which measures the number of characters that need to be changed to get from one string to another. Since they are very general, metric spaces are a tool used in many different branches of mathematics. Many types of mathematical objects have a natural notion of distance and th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quasiconvex
In mathematics, a quasiconvex function is a real-valued function defined on an interval or on a convex subset of a real vector space such that the inverse image of any set of the form (-\infty,a) is a convex set. For a function of a single variable, along any stretch of the curve the highest point is one of the endpoints. The negative of a quasiconvex function is said to be quasiconcave. Quasiconvexity is a more general property than convexity in that all convex functions are also quasiconvex, but not all quasiconvex functions are convex. ''Univariate'' unimodal functions are quasiconvex or quasiconcave, however this is not necessarily the case for functions with multiple arguments. For example, the 2-dimensional Rosenbrock function is unimodal but not quasiconvex and functions with star-convex sublevel sets can be unimodal without being quasiconvex. Definition and properties A function f:S \to \mathbb defined on a convex subset S of a real vector space is quasiconvex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Luma (video)
In video, luma (Y') represents the brightness in an image (the "black-and-white" or achromatic portion of the image). Luma is typically paired with chrominance. Luma represents the grey, achromatic image, while the chroma components represent the color information. Converting RGB color model, R′G′B′ sources (such as the output of a three-CCD camera) into luma and chroma allows for chroma subsampling: because human vision has finer spatial sensitivity to luminance ("black and white") differences than chromatic differences, video systems can store and transmit chromatic information at lower resolution, optimizing perceived detail at a particular bandwidth. Luma versus relative luminance Luma is the weighted sum of gamma-compressed R′G′B′ components of a color video—the ''prime symbols'' ′ denote Gamma correction, gamma compression. The word was proposed to prevent confusion between luma as implemented in video engineering and relative luminance as used in color s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radial Basis Function Interpolation
Radial basis function (RBF) interpolation is an advanced method in approximation theory for constructing Order of accuracy, high-order accurate interpolation, interpolants of unstructured data, possibly in high-dimensional spaces. The interpolant takes the form of a weighted sum of radial basis functions. RBF interpolation is a Meshfree method, mesh-free method, meaning the nodes (points in the domain) need not lie on a structured grid, and does not require the formation of a Types of mesh, mesh. It is often spectrally accurate and stable for large numbers of nodes even in high dimensions. Many interpolation methods can be used as the theoretical foundation of algorithms for approximating linear operators, and RBF interpolation is no exception. RBF interpolation has been used to approximate differential operators, integral operators, and Differential geometry of surfaces, surface differential operators. Examples Let f(x) = \exp(x \cos(3 \pi x)) and let x_k = \frac, k=0, 1, \dots, 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
YCbCr
YCbCr, Y′CbCr, also written as YCBCR or Y′CBCR, is a family of color spaces used as a part of the color image pipeline in digital video and digital photography, photography systems. Like YPbPr, YPBPR, it is based on RGB primaries; the two are generally equivalent, but YCBCR is intended for digital video, while YPBPR is designed for use in Analogue electronics, analog systems. Y′ is the Luma (video), luma component, and CB and CR are the B-Y, blue-difference and R-Y, red-difference chrominance, chroma components. Luma Y′ (with Prime (symbol), prime) is distinguished from relative luminance, luminance Y, meaning that light intensity is nonlinearly encoded based on gamma corrected RGB primaries. Y′CbCr color spaces are defined by a mathematical coordinate transformation from an associated RGB primaries and white point. If the underlying RGB color spaces, RGB color space is absolute, the Y′CbCr color space is an absolute color space as well; conversely, if the RGB spa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |