|
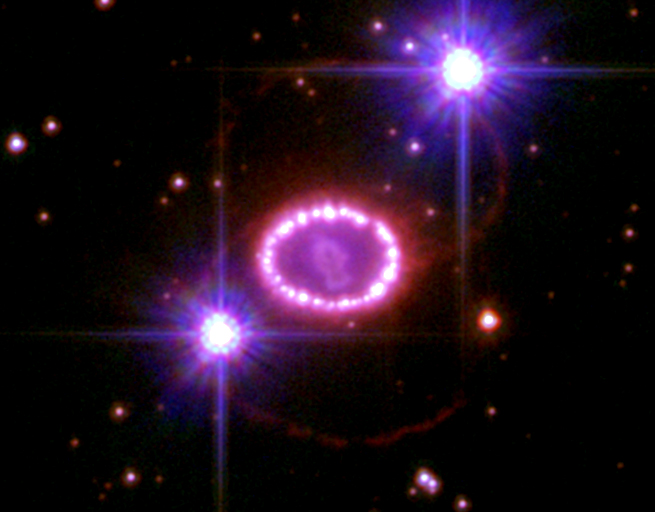
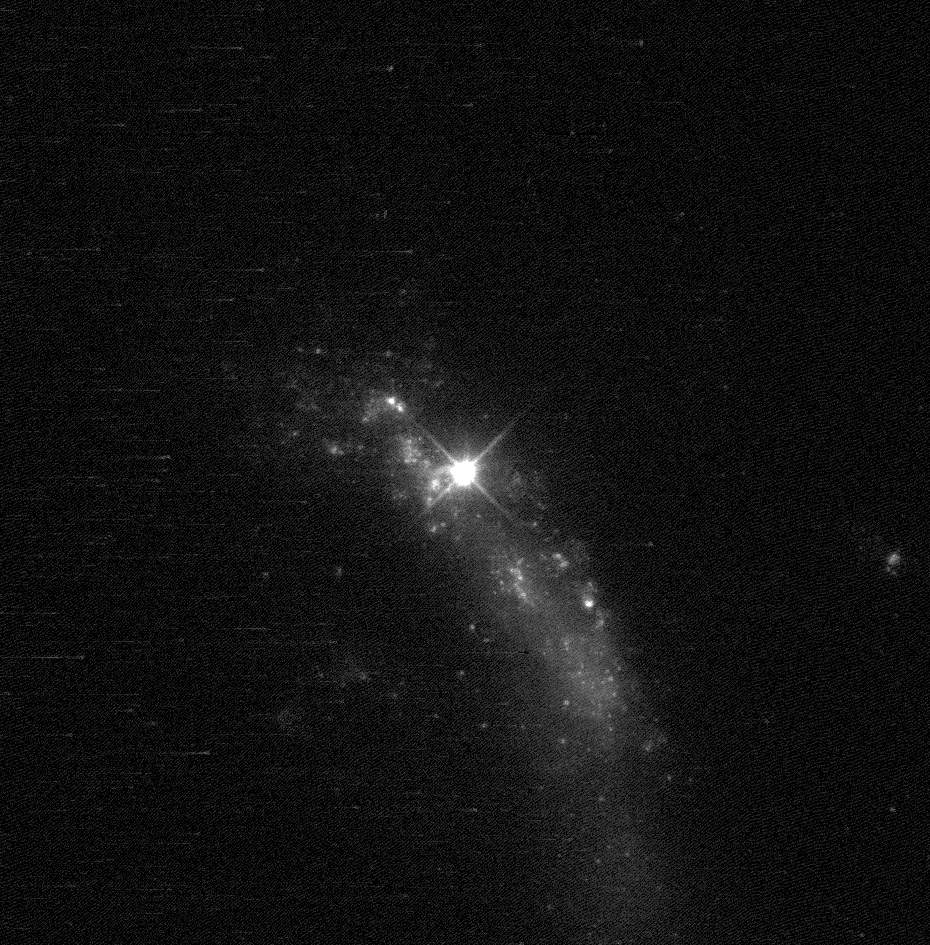
SN 2010jl
SN 2010jl was a luminous Type II supernova, type IIn supernova that was discovered on November 3, 2010, in the irregular galaxy UGC 5189A. It is 48.9 ± 3.4 Parsec, Mpc distant from the Solar System. It showed an infrared excess which lasted for over 1400 days. Discovery 2010jl was discovered during the Puckett Observatory Supernova Search, by Newton & Puckett with a 0.40-m Reflecting telescope, reflector at Portal, Arizona, Portal, Arizona. The discovery was made on Nov. 3.52 Universal Time, UT and was confirmed on Nov. 4.50. Follow-up spectroscopy showed broad emission and narrow-line emission from hydrogen and helium leading to a classification of type IIn. Infrared excess CSM interaction The classification as type IIn showed that the supernova was interacting with the circumstellar medium (CSM). The supernova itself produces the broad emission, the flash-ionized circumstellar medium produces on the other hand the type IIn typical narrow-line emission features. Observat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Type II Supernova
A Type II supernova or SNII (plural: ''supernovae'') results from the rapid collapse and violent explosion of a massive star. A star must have at least eight times, but no more than 40 to 50 times, the mass of the Sun () to undergo this type of explosion. Type II supernovae are distinguished from other types of supernovae by the presence of hydrogen in their spectra. They are usually observed in the spiral arms of galaxies and in H II regions, but not in elliptical galaxies; those are generally composed of older, low-mass stars, with few of the young, very massive stars necessary to cause a supernova. Stars generate energy by the nuclear fusion of elements. Unlike the Sun, massive stars possess the mass needed to fuse elements that have an atomic mass greater than hydrogen and helium, albeit at increasingly higher temperatures and pressures, causing correspondingly shorter stellar life spans. The degeneracy pressure of electrons and the energy generated by th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SN 2010jl Hubble
SN, Sn, sn, .sn, or s.n. may refer to: Businesses and organizations *Brussels Airlines (IATA code: SN) ** Sabena **SN Brussels Airlines (IATA code: SN) *Servant of the People (''Sluha Narodu''), political party in Ukraine * Slovaks Forward (''Slovaci Napred''), a political party in Serbia * Standards Norway, the main standards organization of Norway * (National Party), a Polish political party *Supreme Court of Poland (''Sąd Najwyższy''), the court of last resort for non-administrative matters Places *Senegal (ISO country code SN) *Shaanxi, a province of China (Guobiao abbreviation SN) *South Sulawesi, a province of Indonesia (ISO 3166-2:ID code) *Saxony, a state of Germany *SN postcode area, the UK postcode district containing Swindon and much of North Wiltshire Religion * Samyutta Nikaya or SN, a Buddhist scripture *Sutta Nipata or Sn, a Buddhist scripture Science, technology, and mathematics Computing * .sn, the country-code top level domain of Senegal *sn, the ''surname ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2010jl-like Supernovae
1 (one, unit, unity) is a number, numeral, and glyph. It is the first and smallest positive integer of the infinite sequence of natural numbers. This fundamental property has led to its unique uses in other fields, ranging from science to sports, where it commonly denotes the first, leading, or top thing in a group. 1 is the unit of counting or measurement, a determiner for singular nouns, and a gender-neutral pronoun. Historically, the representation of 1 evolved from ancient Sumerian and Babylonian symbols to the modern Arabic numeral. In mathematics, 1 is the multiplicative identity, meaning that any number multiplied by 1 equals the same number. 1 is by convention not considered a prime number. In digital technology, 1 represents the "on" state in binary code, the foundation of computing. Philosophically, 1 symbolizes the ultimate reality or source of existence in various traditions. In mathematics The number 1 is the first natural number after 0. Each natural number, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbon
Carbon () is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol C and atomic number 6. It is nonmetallic and tetravalence, tetravalent—meaning that its atoms are able to form up to four covalent bonds due to its valence shell exhibiting 4 electrons. It belongs to group 14 of the periodic table. Carbon makes up about 0.025 percent of Earth's crust. Three Isotopes of carbon, isotopes occur naturally, carbon-12, C and carbon-13, C being stable, while carbon-14, C is a radionuclide, decaying with a half-life of 5,700 years. Carbon is one of the timeline of chemical element discoveries#Pre-modern and early modern discoveries, few elements known since antiquity. Carbon is the 15th abundance of elements in Earth's crust, most abundant element in the Earth's crust, and the abundance of the chemical elements, fourth most abundant element in the universe by mass after hydrogen, helium, and oxygen. Carbon's abundance, its unique diversity of organic compounds, and its unusual abi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spitzer Space Telescope
The Spitzer Space Telescope, formerly the Space Infrared Telescope Facility (SIRTF), was an infrared space telescope launched in 2003, that was deactivated when operations ended on 30 January 2020. Spitzer was the third space telescope dedicated to infrared astronomy, following IRAS (1983) and ISO (1995–1998). It was the first spacecraft to use an Earth-trailing orbit, later used by the Kepler planet-finder. The planned mission period was to be 2.5 years with a pre-launch expectation that the mission could extend to five or slightly more years until the onboard liquid helium supply was exhausted. This occurred on 15 May 2009. Without liquid helium to cool the telescope to the very low temperatures needed to operate, most of the instruments were no longer usable. However, the two shortest-wavelength modules of the IRAC camera continued to operate with the same sensitivity as before the helium was exhausted, and continued to be used into early 2020 in the Spitzer Warm Mission ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gemini Observatory
The Gemini Observatory comprises two 8.1-metre (26.6 ft) telescopes, Gemini North and Gemini South, situated in Hawaii and Chile, respectively. These twin telescopes offer extensive coverage of the northern and southern skies and rank among the most advanced optical/infrared astronomy, infrared telescopes available to astronomers. ''(See List of largest optical reflecting telescopes)''. The observatory is owned and operated by the National Science Foundation (NSF) of the United States, the National Research Council Canada, National Research Council of Canada, CONICYT of Chile, MCTI of Brazil, MCTIP of Argentina, and Korea Astronomy and Space Science Institute, Korea Astronomy and Space Science Institute (KASI) of Republic of Korea. The NSF is the primary funding contributor, providing about 70% of the required resources. The Association of Universities for Research in Astronomy (AURA) manages the operations and maintenance of the observatory through a cooperative agreement wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hubble Space Telescope
The Hubble Space Telescope (HST or Hubble) is a space telescope that was launched into low Earth orbit in 1990 and remains in operation. It was not the Orbiting Solar Observatory, first space telescope, but it is one of the largest and most versatile, renowned as a vital research tool and as a public relations boon for astronomy. The Hubble Space Telescope is named after astronomer Edwin Hubble and is one of NASA's Great Observatories program, Great Observatories. The Space Telescope Science Institute (STScI) selects Hubble's targets and processes the resulting data, while the Goddard Space Flight Center (GSFC) controls the spacecraft. Hubble features a mirror, and its five main instruments observe in the ultraviolet, visible spectrum, visible, and near-infrared regions of the electromagnetic spectrum. Hubble's orbit outside the distortion of atmosphere of Earth, Earth's atmosphere allows it to capture extremely high-resolution images with substantially lower background lig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
X-ray
An X-ray (also known in many languages as Röntgen radiation) is a form of high-energy electromagnetic radiation with a wavelength shorter than those of ultraviolet rays and longer than those of gamma rays. Roughly, X-rays have a wavelength ranging from 10 Nanometre, nanometers to 10 Picometre, picometers, corresponding to frequency, frequencies in the range of 30 Hertz, petahertz to 30 Hertz, exahertz ( to ) and photon energies in the range of 100 electronvolt, eV to 100 keV, respectively. X-rays were discovered in 1895 in science, 1895 by the German scientist Wilhelm Röntgen, Wilhelm Conrad Röntgen, who named it ''X-radiation'' to signify an unknown type of radiation.Novelline, Robert (1997). ''Squire's Fundamentals of Radiology''. Harvard University Press. 5th edition. . X-rays can penetrate many solid substances such as construction materials and living tissue, so X-ray radiography is widely used in medical diagnostics (e.g., checking for Bo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Advanced CCD Imaging Spectrometer
The Advanced CCD Imaging Spectrometer (ACIS), formerly the AXAF CCD Imaging Spectrometer, is an instrument built by a team from the Massachusetts Institute of Technology's Center for Space Research and the Pennsylvania State University for the ''Chandra X-ray Observatory''. ACIS is a focal plane instrument that uses an array of charge-coupled devices. It serves as an X-ray integral field spectrograph for ''Chandra''. The instrument is capable of measuring both the position and energy of incoming X-rays. The CCD sensors of ACIS operate at and its filters at . It carries a special heater that allows contamination from ''Chandra'' to be baked off; the spacecraft contains lubricants, and the ACIS design took this into account in order to clean its sensors. Contamination buildup can reduce the instrument's sensitivity. Radiation in space is another potential danger to the sensor. , after 15 years of operation, there was no indication of a limit to the lifetime of ACIS. Another design ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chandra X-ray Observatory
The Chandra X-ray Observatory (CXO), previously known as the Advanced X-ray Astrophysics Facility (AXAF), is a Flagship-class space telescope launched aboard the during STS-93 by NASA on July 23, 1999. Chandra is sensitive to X-ray sources 100 times fainter than any previous X-ray telescope, enabled by the high angular resolution of its mirrors. Since the Earth's atmosphere absorbs the vast majority of X-rays, they are not detectable from Earth-based telescopes; therefore space-based telescopes are required to make these observations. Chandra is an Earth satellite in a 64-hour orbit, and its mission is ongoing . Chandra is one of the Great Observatories, along with the Hubble Space Telescope, Compton Gamma Ray Observatory (1991–2000), and the Spitzer Space Telescope (2003–2020). The telescope is named after the Nobel Prize-winning Indian-American astrophysicist Subrahmanyan Chandrasekhar. Its mission is similar to that of ESA's XMM-Newton spacecraft, also launched in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Helium
Helium (from ) is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol He and atomic number 2. It is a colorless, odorless, non-toxic, inert gas, inert, monatomic gas and the first in the noble gas group in the periodic table. Its boiling point is the lowest among all the Chemical element, elements, and it does not have a melting point at standard pressures. It is the second-lightest and second-most Abundance of the chemical elements, abundant element in the observable universe, after hydrogen. It is present at about 24% of the total elemental mass, which is more than 12 times the mass of all the heavier elements combined. Its abundance is similar to this in both the Sun and Jupiter, because of the very high nuclear binding energy (per nucleon) of helium-4 with respect to the next three elements after helium. This helium-4 binding energy also accounts for why it is a product of both nuclear fusion and radioactive decay. The most common isotope of helium in the universe is helium-4, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
UGC 5189A
UGC may refer to: Organisations * Canadian Geophysical Union, official abbreviation in French (Union géophysique canadienne) * UGC (cinema operator), a European cinema chain, formerly Union Générale Cinématographique * UGC Fox Distribution, a former French-American film production company formed in 1995 * Union Graduate College, Schenectady, New York * United Grain Company, a Russian grain trading company based in Moscow * University Grants Commission (other) * University Grants Committee (other) * UnitedGlobalCom, former name of the cable TV operator Liberty Global * UnderGround Crips, an African American street gang mainly from Los Angeles, California Science and technology * Universal gravitational constant G, in physics * Uppsala General Catalogue, an astronomical catalogue of galaxies * UGC, a codon for cysteine * Unique games conjecture, a conjecture in computational complexity Other * User-generated content, media content made by the general public * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |