|
SLIMCAT
TOMCAT/SLIMCAT is an off-line chemical transport model (CTM), which models the time-dependent distribution of chemical species in the troposphere and stratosphere. It can be used to study topics such as ozone depletion and tropospheric pollution, and was one of the models used the IPCC report on Aviation and the Global Atmospher It incorporates a choice of detailed chemistry schemes for the troposphere or stratosphere, and an optional chemical data assimilation scheme. The original model code, called the Toulouse Off-line Model of Chemistry And Transport (TOMCAT), was written by Martyn Chipperfield at Météo France. "Off-line" in this sense describes the fact that although the meteorological data (wind components and other fields) which are used as input to the CTM typically derive from a general circulation model (GCM), the CTM is run as a separate program outside of a GCM; this is as distinct from a chemistry simulation scheme which runs within a GCM, in which the simulated ch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemical Transport Model
A chemical transport model (CTM) is a type of computer numerical model which typically simulates atmospheric chemistry and may give air pollution forecasting Air pollution forecasting is the application of science and technology to predict the composition of the air pollution in the atmosphere for a given location and time. An algorithm prediction of the pollutant concentrations can be translated into .... Chemical transport models and general circulation models While related global climate model, general circulation models (GCMs) focus on simulating overall atmospheric dynamics (e.g. fluid flow, fluid and heat flows), a CTM instead focuses on the stocks and flows of one or more chemical species. Similarly, a CTM must solve only the continuity equation for its species of interest, a GCM must solve all the primitive equations for the atmosphere; but a CTM will be expected to accurately represent the entire biogeochemical cycle, cycle for the species of interest, including Flux# ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ozone Depletion
Ozone depletion consists of two related events observed since the late 1970s: a steady lowering of about four percent in the total amount of ozone in Earth's atmosphere, and a much larger springtime decrease in stratospheric ozone (the ozone layer) around Earth's polar regions. The latter phenomenon is referred to as the ozone hole. There are also springtime polar tropospheric ozone depletion events in addition to these stratospheric events. The main causes of ozone depletion and the ozone hole are manufactured chemicals, especially manufactured halocarbon refrigerants, solvents, propellants, and foam-blowing agents (chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs), HCFCs, halons), referred to as ozone-depleting substances (ODS). These compounds are transported into the stratosphere by turbulent mixing after being emitted from the surface, mixing much faster than the molecules can settle. Once in the stratosphere, they release atoms from the halogen group through photodissociation, which ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Entropy
Entropy is a scientific concept, as well as a measurable physical property, that is most commonly associated with a state of disorder, randomness, or uncertainty. The term and the concept are used in diverse fields, from classical thermodynamics, where it was first recognized, to the microscopic description of nature in statistical physics, and to the principles of information theory. It has found far-ranging applications in chemistry and physics, in biological systems and their relation to life, in cosmology, economics, sociology, weather science, climate change, and information systems including the transmission of information in telecommunication. The thermodynamic concept was referred to by Scottish scientist and engineer William Rankine in 1850 with the names ''thermodynamic function'' and ''heat-potential''. In 1865, German physicist Rudolf Clausius, one of the leading founders of the field of thermodynamics, defined it as the quotient of an infinitesimal amount of hea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Meteorological Society
The Royal Meteorological Society is a long-established institution that promotes academic and public engagement in weather and climate science. Fellows of the Society must possess relevant qualifications, but Associate Fellows can be lay enthusiasts. Its Quarterly Journal is one of the world's leading sources of original research in the atmospheric sciences. The chief executive officer is Liz Bentley. Constitution The Royal Meteorological Society traces its origins back to 3 April 1850 when the British Meteorological Society was formed as "a society the objects of which should be the advancement and extension of meteorological science by determining the laws of climate and of meteorological phenomena in general". Along with nine others, including James Glaisher, John Drew, Edward Joseph Lowe, The Revd Joseph Bancroft Reade, and Samuel Charles Whitbread, Dr John Lee, an astronomer, of Hartwell House, near Aylesbury, Buckinghamshire founded in the library of his house the Bri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radiative Forcing
Radiative forcing (or climate forcing) is the change in energy flux in the atmosphere caused by natural or anthropogenic factors of climate change as measured by watts / metre2. It is a scientific concept used to quantify and compare the external drivers of change to Earth's energy balance. System feedbacks and internal variability are related concepts, encompassing other factors that also influence the direction and magnitude of imbalance. Positive radiative forcing means Earth receives more incoming energy from sunlight than it radiates to space. This net gain of energy will cause warming. Conversely, negative radiative forcing means that Earth loses more energy to space than it receives from the sun, which produces cooling. A planet in radiative equilibrium with its parent star and the rest of space can be characterized by net zero radiative forcing and by a planetary equilibrium temperature. Radiative forcing on Earth is meaningfully evaluated at the tropopause and at the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sulfate
The sulfate or sulphate ion is a polyatomic anion with the empirical formula . Salts, acid derivatives, and peroxides of sulfate are widely used in industry. Sulfates occur widely in everyday life. Sulfates are salts of sulfuric acid and many are prepared from that acid. Spelling "Sulfate" is the spelling recommended by IUPAC, but "sulphate" was traditionally used in British English. Structure The sulfate anion consists of a central sulfur atom surrounded by four equivalent oxygen atoms in a tetrahedral arrangement. The symmetry is the same as that of methane. The sulfur atom is in the +6 oxidation state while the four oxygen atoms are each in the −2 state. The sulfate ion carries an overall charge of −2 and it is the conjugate base of the bisulfate (or hydrogensulfate) ion, , which is in turn the conjugate base of , sulfuric acid. Organic sulfate esters, such as dimethyl sulfate, are covalent compounds and esters of sulfuric acid. The tetrahedral molecular geometry of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Black Carbon
Chemically, black carbon (BC) is a component of fine particulate matter (PM ≤ 2.5 µm in aerodynamic diameter). Black carbon consists of pure carbon in several linked forms. It is formed through the incomplete combustion of fossil fuels, biofuel, and biomass, and is one of the main types of particle in both anthropogenic and naturally occurring soot. Black carbon causes human morbidity and premature mortality. Because of these human health impacts, many countries have worked to reduce their emissions, making it an easy pollutant to abate in anthropogenic sources. In climatology, black carbon is a climate forcing agent contributing to global warming. Black carbon warms the Earth by absorbing sunlight and heating the atmosphere and by reducing albedo when deposited on snow and ice (direct effects) and indirectly by interaction with clouds, with the total forcing of 1.1 W/m2. Black carbon stays in the atmosphere for only several days to weeks, whereas potent greenhouse ga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aerosol
An aerosol is a suspension (chemistry), suspension of fine solid particles or liquid Drop (liquid), droplets in air or another gas. Aerosols can be natural or Human impact on the environment, anthropogenic. Examples of natural aerosols are fog or mist, dust, forest exudates, and geyser steam. Examples of anthropogenic aerosols include particulate air pollutants, mist from the discharge at Hydroelectric dam, hydroelectric dams, Irrigation, irrigation mist, Perfume, perfume from atomizers, smoke, steam from a kettle, Pesticide, sprayed pesticides, and medical treatments for respiratory illnesses. When a person inhales the contents of a vape pen or e-cigarette, they are inhaling an Human impact on the environment, anthropogenic aerosol. The liquid or solid particles in an aerosol have diameters typically less than micrometre, 1 μm (larger particles with a significant settling speed make the mixture a Suspension (chemistry), suspension, but the distinction is not clear-cut) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
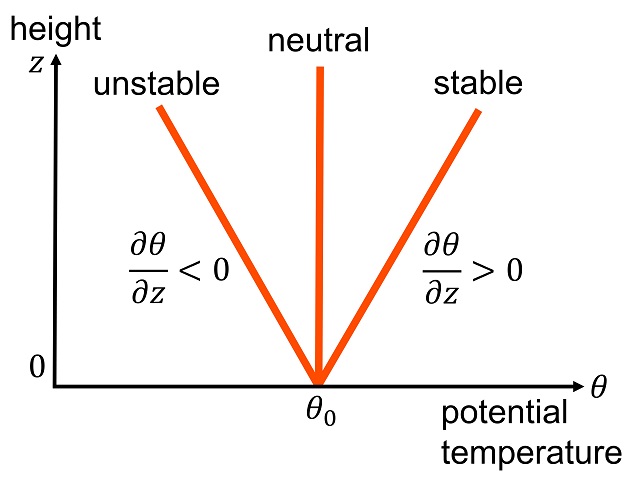
Potential Temperature
The potential temperature of a parcel of fluid at pressure P is the temperature that the parcel would attain if adiabatically brought to a standard reference pressure P_, usually . The potential temperature is denoted \theta and, for a gas well-approximated as ideal, is given by : \theta = T \left(\frac\right)^, where T is the current absolute temperature (in K) of the parcel, R is the gas constant of air, and c_p is the specific heat capacity at a constant pressure. R/c_p = 0.286 for air (meteorology). The reference point for potential temperature in the ocean is usually at the ocean's surface which has a water pressure of 0 dbar. The potential temperature in the ocean doesn't account for the varying heat capacities of seawater, therefore it is not a conservative measure of heat content. Graphical representation of potential temperature will always be less than the actual temperature line in a temperature vs depth graph. Contexts The concept of potential temperature applies ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Troposphere
The troposphere is the first and lowest layer of the atmosphere of the Earth, and contains 75% of the total mass of the planetary atmosphere, 99% of the total mass of water vapour and aerosols, and is where most weather phenomena occur. From the planetary surface of the Earth, the average height of the troposphere is in the tropics; in the middle latitudes; and in the high latitudes of the polar regions in winter; thus the average height of the troposphere is . The term ''troposphere'' derives from the Greek words ''tropos'' (rotating) and '' sphaira'' (sphere) indicating that rotational turbulence mixes the layers of air and so determines the structure and the phenomena of the troposphere. The rotational friction of the troposphere against the planetary surface affects the flow of the air, and so forms the planetary boundary layer (PBL) that varies in height from hundreds of meters up to . The measures of the PBL vary according to the latitude, the landform, and th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |