|
SLC31A1
High affinity copper uptake protein 1 (CTR1) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''SLC31A1'' gene. Copper is an element essential for life, but excessive copper can be toxic or even lethal to the cell. Therefore, cells have developed sophisticated ways to maintain a critical copper balance, with the intake, export, and intracellular compartmentalization or buffering of copper strictly regulated. The 2 related genes ATP7A and ATP7B, responsible for the human diseases Menkes syndrome and Wilson disease Wilson's disease is a genetic disorder in which excess copper builds up in the body. Symptoms are typically related to the brain and liver. Liver-related symptoms include vomiting, weakness, fluid build up in the abdomen, swelling of the legs, ..., respectively, are involved in copper export. In ''S. cerevisiae'', the copper uptake genes CTR1, CTR2, and CTR3 have been identified, and in human the CTR1 and CTR2 (MIM 603088) genes have been identified. Clinical sign ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wilson's Disease
Wilson's disease is a genetic disorder in which excess copper builds up in the body. Symptoms are typically related to the brain and liver. Liver-related symptoms include vomiting, weakness, fluid build up in the abdomen, swelling of the legs, yellowish skin and itchiness. Brain-related symptoms include tremors, muscle stiffness, trouble in speaking, personality changes, anxiety, and psychosis. Wilson's disease is caused by a mutation in the Wilson disease protein (''ATP7B'') gene. This protein transports excess copper into bile, where it is excreted in waste products. The condition is autosomal recessive; for a person to be affected, they must inherit a mutated copy of the gene from both parents. Diagnosis may be difficult and often involves a combination of blood tests, urine tests and a liver biopsy. Genetic testing may be used to screen family members of those affected. Wilson's disease is typically treated with dietary changes and medication. Dietary changes involve e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, responding to stimuli, providing structure to cells and organisms, and transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific 3D structure that determines its activity. A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called peptides. The individual amino acid residues are bonded together by peptide bonds and adjacent amino acid residues. The sequence of amino acid residue ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "...Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity and the molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protein-coding genes and noncoding genes. During gene expression, the DNA is first copied into RNA. The RNA can be directly functional or be the intermediate template for a protein that performs a function. The transmission of genes to an organism's offspring is the basis of the inheritance of phenotypic traits. These genes make up different DNA sequences called genotypes. Genotypes along with environmental and developmental factors determine what the phenotypes will be. Most biological traits are under the influence of polygenes (many different genes) as well as gen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
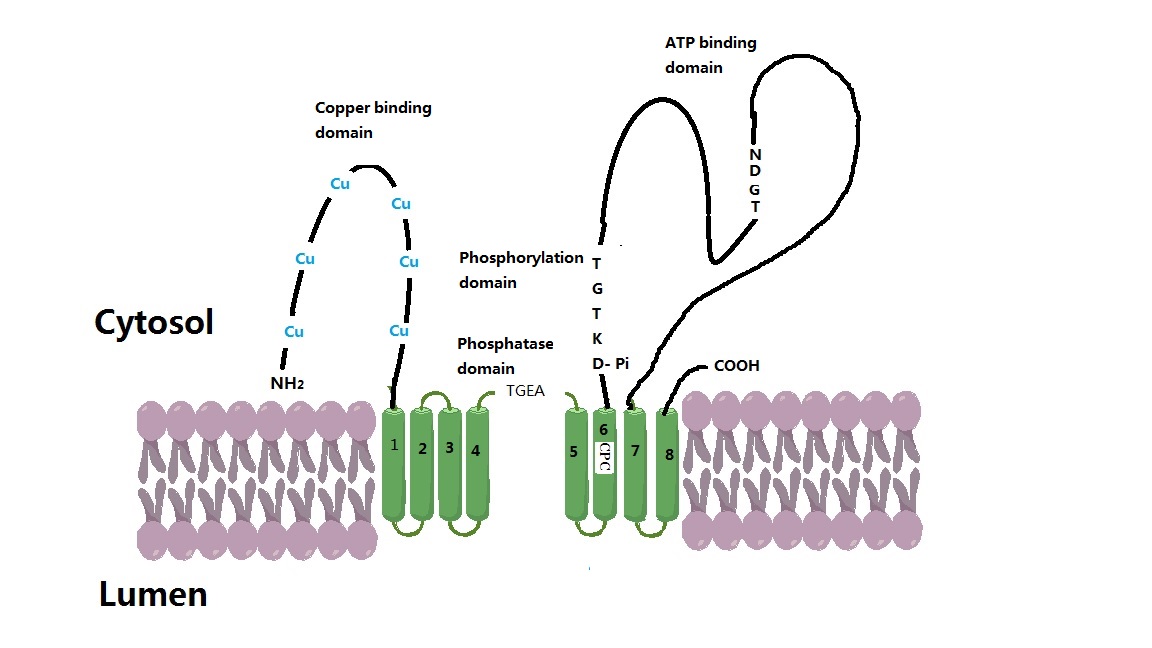
ATP7A
ATP7A, also known as Menkes' protein (MNK), is a copper-transporting P-type ATPase which uses the energy arising from ATP hydrolysis to transport Cu(I) across cell membranes. The ATP7A protein is a transmembrane protein and is expressed in the intestine and all tissues except liver. In the intestine, ATP7A regulates Cu(I) absorption in the human body by transporting Cu(I) from the small intestine into the blood. In other tissues, ATP7A shuttles between the Golgi apparatus and the cell membrane to maintain proper Cu(I) concentrations (since there is no free Cu(I) in the cell, Cu(I) ions are all tightly bound) in the cell and provides certain enzymes with Cu(I) (e.g. peptidyl-α-monooxygenase, tyrosinase, and lysyl oxidase). The X-linked, inherited, lethal genetic disorder of the ''ATP7A'' gene causes Menkes disease, a copper deficiency resulting in early childhood death. Gene The ''ATP7A'' gene is located on the long (q) arm of the X chromosome at band Xq21.1. The encoded ATP7A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wilson Disease Protein
Wilson disease protein (WND), also known as ATP7B protein, is a copper-transporting P-type ATPase which is encoded by the ''ATP7B'' gene. The ATP7B protein is located in the trans-Golgi network of the liver and brain and balances the copper level in the body by excreting excess copper into bile and plasma. Genetic disorder of the ATP7B gene may cause Wilson's disease, a disease in which copper accumulates in tissues, leading to neurological or psychiatric issues and liver diseases. Gene Wilson disease protein is associated with ''ATP7B'' gene, approximately 80 Kb, located on human chromosome 13 and consists of 21 exons. The mRNA transcribed by ''ATP7B'' gene has a size of 7.5 Kb, and which encodes a protein of 1465 amino acids. The gene is a member of the P-type cation transport ATPase family and encodes a protein with several membrane-spanning domains, an ATPase consensus sequence, a hinge domain, a phosphorylation site, and at least two putative copper-binding sites. This ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
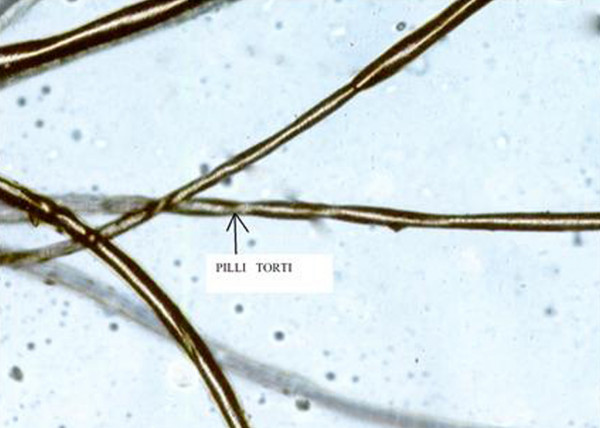
Menkes Syndrome
Menkes disease (MNK), also known as Menkes syndrome, is an X-linked recessive disorder caused by mutations in genes coding for the copper-transport protein ATP7A, leading to copper deficiency. Characteristic findings include kinky hair, growth failure, and nervous system deterioration. Like all X-linked recessive conditions, Menkes disease is more common in males than in females. The disorder was first described by John Hans Menkes in 1962. Onset occurs during infancy, with incidence of about 1 in 100,000 to 250,000 newborns; affected infants often do not live past the age of three years, though there are rare cases in which less severe symptoms emerge later in childhood. Signs and symptoms Affected infants may be born prematurely. Signs and symptoms appear during infancy, typically after a two- to three-month period of normal or slightly slowed development that is followed by a loss of early developmental skills and subsequent developmental delay. Patients exhibit hypoto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Central Nervous System
The central nervous system (CNS) is the part of the nervous system consisting primarily of the brain and spinal cord. The CNS is so named because the brain integrates the received information and coordinates and influences the activity of all parts of the bodies of bilaterally symmetric and triploblastic animals—that is, all multicellular animals except sponges and diploblasts. It is a structure composed of nervous tissue positioned along the rostral (nose end) to caudal (tail end) axis of the body and may have an enlarged section at the rostral end which is a brain. Only arthropods, cephalopods and vertebrates have a true brain (precursor structures exist in onychophorans, gastropods and lancelets). The rest of this article exclusively discusses the vertebrate central nervous system, which is radically distinct from all other animals. Overview In vertebrates, the brain and spinal cord are both enclosed in the meninges. The meninges provide a barrier to chemicals dissolv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |