|
SL-CoV-WIV1
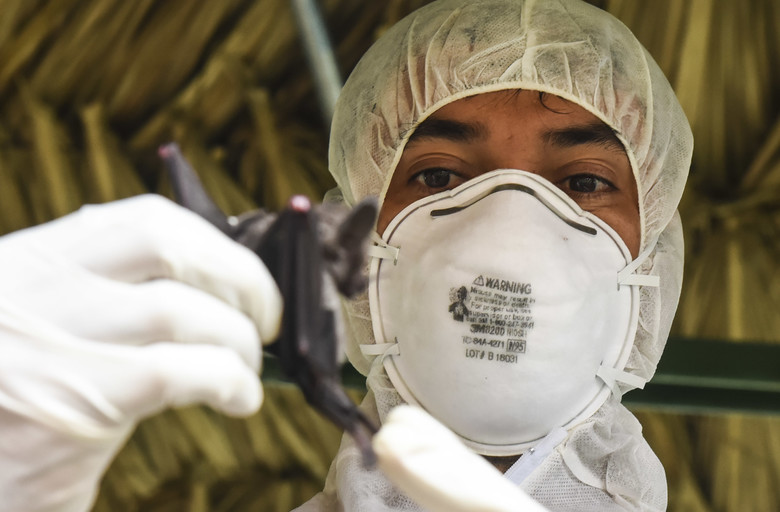
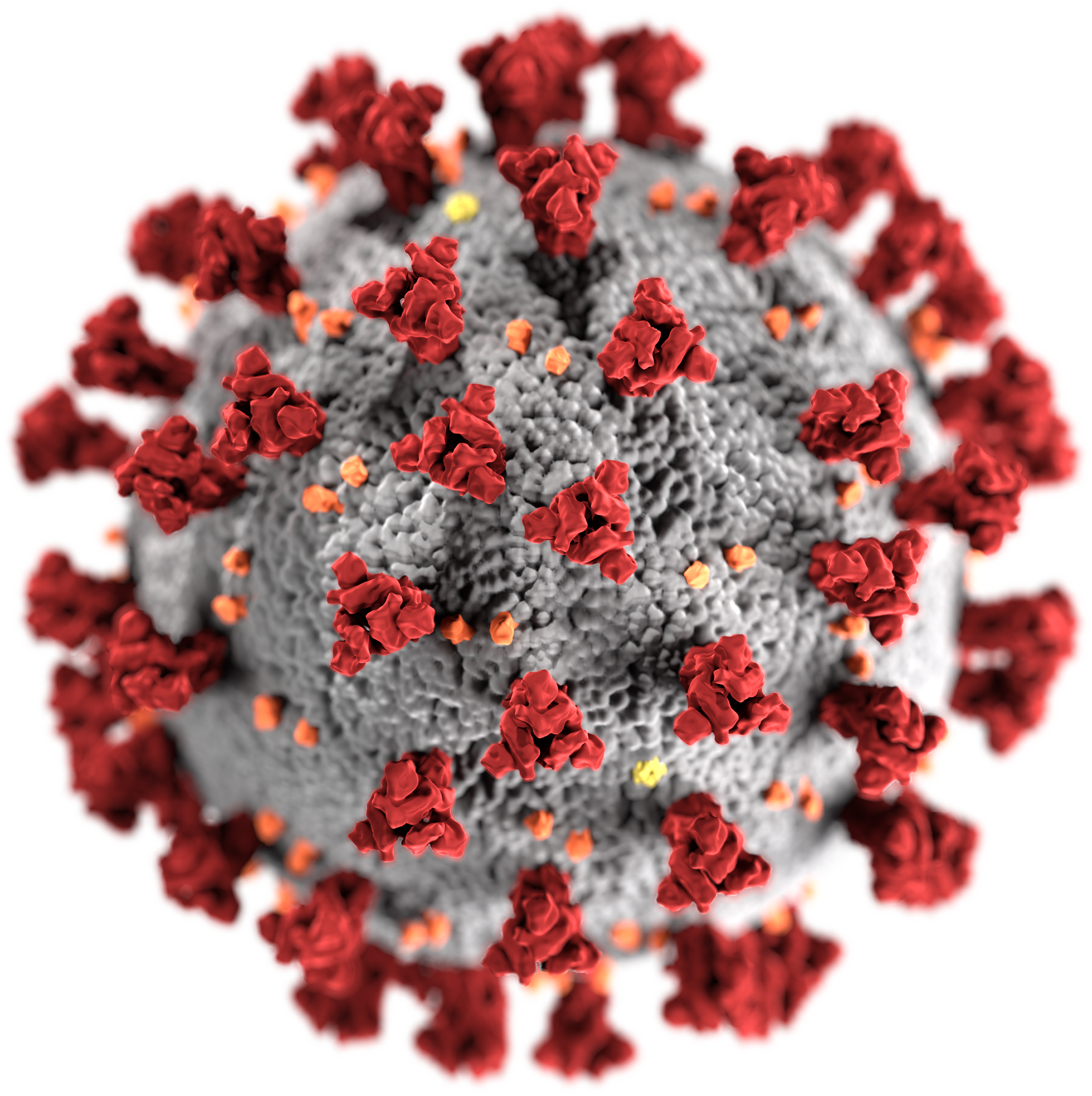
Bat SARS-like coronavirus WIV1 (Bat SL-CoV-WIV1), also sometimes called SARS-like coronavirus WIV1, is a strain of ''severe acute respiratory syndrome–related coronavirus'' (SARSr-CoV) isolated from Chinese rufous horseshoe bats in 2013 ('' Rhinolophus sinicus''). Like all coronaviruses, virions consist of single-stranded positive-sense RNA enclosed within an envelope. Zoonosis The discovery confirms that bats are the natural reservoir of SARS-CoV. Phylogenetic analysis shows the possibility of direct transmission of SARS from bats to humans without the intermediary Chinese civets, as previously believed.Vineet D. Menachery ''et al.'', SARS-like WIV1-CoV poised for human emergence, 2016. Phylogenetic See also * Bat as food * Bat coronavirus RaTG13 *Bat virome *SARS-CoV-2 Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS‑CoV‑2) is a strain of coronavirus that causes COVID-19 (coronavirus disease 2019), the respiratory illness responsible for the ongoing C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome–related Coronavirus
''Severe acute respiratory syndrome–related coronavirus'' (SARSr-CoV or SARS-CoV)The terms ''SARSr-CoV'' and ''SARS-CoV'' are sometimes used interchangeably, especially prior to the discovery of SARS-CoV-2. This may cause confusion when some publications refer to SARS-CoV-1 as ''SARS-CoV''. is a species of virus consisting of many known strains phylogenetically related to severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 1 (SARS-CoV-1) that have been shown to possess the capability to infect humans, bats, and certain other mammals. These enveloped, positive-sense single-stranded RNA viruses enter host cells by binding to the angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) receptor. The SARSr-CoV species is a member of the genus ''Betacoronavirus'' and of the subgenus ''Sarbecovirus'' (SARS Betacoronavirus). Two strains of the virus have caused outbreaks of severe respiratory diseases in humans: severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 1 (SARS-CoV or SARS-CoV-1), which caused the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SARS-related Coronavirus
''Severe acute respiratory syndrome–related coronavirus'' (SARSr-CoV or SARS-CoV)The terms ''SARSr-CoV'' and ''SARS-CoV'' are sometimes used interchangeably, especially prior to the discovery of SARS-CoV-2. This may cause confusion when some publications refer to SARS-CoV-1 as ''SARS-CoV''. is a species of virus consisting of many known strains phylogenetically related to severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 1 (SARS-CoV-1) that have been shown to possess the capability to infect humans, bats, and certain other mammals. These enveloped, positive-sense single-stranded RNA viruses enter host cells by binding to the angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) receptor. The SARSr-CoV species is a member of the genus ''Betacoronavirus'' and of the subgenus ''Sarbecovirus'' (SARS Betacoronavirus). Two strains of the virus have caused outbreaks of severe respiratory diseases in humans: severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 1 (SARS-CoV or SARS-CoV-1), which caused the 20 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhinolophus Sinicus
The Chinese rufous horseshoe bat (''Rhinolophus sinicus'') is a species of bat in the family Rhinolophidae. It is found in Bhutan, China, India, Nepal, and Vietnam. The species is most easily confused with '' R. affinis'', from which it is best distinguished by its straight-sided lancet and the relatively short second phalanx of the third digit (< 66% of the length of the ; Csorba ''et al''. 2003). Subspecies ''Rhinolophus sinicus'' is divided into the following two subspecies: * ''R. s. septentrionalis'' * ''R. s. sinicus''Description The Chinese rufous horseshoe bat has a forearm length of . It has an ear length of and a tail length of . Overall, it is considered a medium-sized horseshoe bat. It is similar in appearance to the |
Positive-sense
In molecular biology and genetics, the sense of a nucleic acid molecule, particularly of a strand of DNA or RNA, refers to the nature of the roles of the strand and its complement in specifying a sequence of amino acids. Depending on the context, sense may have slightly different meanings. For example, negative-sense strand of DNA is equivalent to the template strand, whereas the positive-sense strand is the non-template strand whose nucleotide sequence is equivalent to the sequence of the mRNA transcript. DNA sense Because of the complementary nature of base-pairing between nucleic acid polymers, a double-stranded DNA molecule will be composed of two strands with sequences that are reverse complements of each other. To help molecular biologists specifically identify each strand individually, the two strands are usually differentiated as the "sense" strand and the "antisense" strand. An individual strand of DNA is referred to as positive-sense (also positive (+) or simply sense ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Viral Envelope
A viral envelope is the outermost layer of many types of viruses. It protects the genetic material in their life cycle when traveling between host cells. Not all viruses have envelopes. Numerous human pathogenic viruses in circulation are encased in lipid bilayers, and they infect their target cells by causing the viral envelope and cell membrane to fuse. Although there are effective vaccines against some of these viruses, there is no preventative or curative medicine for the majority of them. In most cases, the known vaccines operate by inducing antibodies that prevent the pathogen from entering cells. This happens in the case of enveloped viruses when the antibodies bind to the viral envelope proteins. The membrane fusion event that triggers viral entrance is caused by the viral fusion protein. Many enveloped viruses only have one protein visible on the surface of the particle, which is required for both mediating adhesion to the cell surface and for the subsequent membrane fusi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phylogenetic
In biology, phylogenetics (; from Greek φυλή/ φῦλον [] "tribe, clan, race", and wikt:γενετικός, γενετικός [] "origin, source, birth") is the study of the evolutionary history and relationships among or within groups of organisms. These relationships are determined by Computational phylogenetics, phylogenetic inference methods that focus on observed heritable traits, such as DNA sequences, protein amino acid sequences, or morphology. The result of such an analysis is a phylogenetic tree—a diagram containing a hypothesis of relationships that reflects the evolutionary history of a group of organisms. The tips of a phylogenetic tree can be living taxa or fossils, and represent the "end" or the present time in an evolutionary lineage. A phylogenetic diagram can be rooted or unrooted. A rooted tree diagram indicates the hypothetical common ancestor of the tree. An unrooted tree diagram (a network) makes no assumption about the ancestral line, and does ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome
Severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) is a viral respiratory disease of zoonotic origin caused by the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus (SARS-CoV or SARS-CoV-1), the first identified strain of the SARS coronavirus species, ''severe acute respiratory syndrome–related coronavirus'' (SARSr-CoV). The first known cases occurred in November 2002, and the syndrome caused the 2002–2004 SARS outbreak. In the 2010s, Chinese scientists traced the virus through the intermediary of Asian palm civets to cave-dwelling horseshoe bats in Xiyang Yi Ethnic Township, Yunnan.The locality was referred to be "a cave in Kunming" in earlier sources because the Xiyang Yi Ethnic Township is administratively part of Kunming, though 70 km apart. Xiyang was identified on * For an earlier interview of the researchers about the locality of the caves, see: SARS was a relatively rare disease; at the end of the epidemic in June 2003, the incidence was 8,469 cases with a case fatality rat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Civet
A civet () is a small, lean, mostly nocturnal mammal native to tropical Asia and Africa, especially the tropical forests. The term civet applies to over a dozen different species, mostly from the family Viverridae. Most of the species diversity is found in southeast Asia. The best-known species is the African civet, ''Civettictis civetta'', which historically has been the main species from which a musky scent used in perfumery, also referred to as " civet", was obtained. Naming The common name is used for a variety of carnivoran mammal species, mostly of the family Viverridae. The African palm civet (''Nandinia binotata'') is genetically distinct and belongs in its own monotypic family, Nandiniidae. Civets are also called "toddycats" in English, "Mara Patti" in Malayalam, "musang" in Malay and Indonesian, and ''urulǣvā'' () in Sinhalese. There can be confusion among speakers of Malay because the indigenous word "musang" has been mistakenly applied to foxes by print ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bat As Food
Bats are eaten by people in parts of some Asian, African, Pacific Rim countries and cultures, including China, Vietnam, Seychelles, the Philippines, Indonesia, Palau, Thailand, and Guam. Half the megabat (fruit bat) species are hunted for food but only eight percent of the insectivorous bat species are. In Guam, Mariana fruit bats (''Pteropus mariannus'') are considered a delicacy. History Bats have likely been consumed as a food source since prehistoric times in the Asia-Pacific region. Chronostratigraphy, Chronostratigraphic analysis of archaeological sites indicate that bats could have been exploited as a food source since 74,000 years ago by ''Homo floresiensis''. On tropical islands, hunting large fruit bats was a worthwhile expenditure for prehistoric hominins. These megabats could be easily captured in caves in large numbers, and processing effort was also minimal. Bats have been hunted by Aboriginal Australians for thousands of years, extending into modern times. Popular ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RaTG13
Bat coronavirus RaTG13 is a SARS-like betacoronavirus that infects the horseshoe bat '' Rhinolophus affinis''. It was discovered in 2013 in bat droppings from a mining cave near the town of Tongguan in Mojiang county in Yunnan, China. In February 2020, it was identified as the closest known (at the time) relative of SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19, sharing 96.1% nucleotide similarity. However, in 2022, scientists found three closer matches in bats found 530 km south, in Feuang, Laos, designated as BANAL-52 (96.8% similarity), BANAL-103 and BANAL-236. History In spring 2012, three miners cleaning bat feces in an abandoned copper mine near the town of Tongguan in Mojiang Hani Autonomous County developed fatal pneumonia. Out of concerns that the miner's cases could represent a novel disease, serum samples collected from the miners were sent to the Wuhan Institute of Virology and tested by Shi Zhengli and her group for Ebola virus, Nipah virus, and bat SARSr-CoV Rp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bat Virome
The bat virome is the virome, group of viruses associated with bats. Bats host a diverse array of viruses, including all seven types described by the Baltimore classification, Baltimore classification system: (I) double-stranded DNA viruses; (II) sDNA virus, single-stranded DNA viruses; (III) dsRNA virus, double-stranded RNA viruses; (IV) positive-sense ssRNA virus, positive-sense single-stranded RNA viruses; (V) negative-sense ssRNA virus, negative-sense single-stranded RNA viruses; (VI) ssRNA-RT virus, positive-sense single-stranded RNA viruses that replicate through a DNA intermediate; and (VII) dsDNA-RT virus, double-stranded DNA viruses that replicate through a single-stranded RNA intermediate. The greatest share of bat-associated viruses identified as of 2020 are of type IV, in the family ''Coronaviridae''. Bats harbor several viruses that are zoonotic, or capable of infecting humans, and some bat-borne viruses are considered important Emergent virus, emerging viruses. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS‑CoV‑2) is a strain of coronavirus that causes COVID-19 (coronavirus disease 2019), the respiratory illness responsible for the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic. The virus previously had a provisional name, 2019 novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV), and has also been called the human coronavirus 2019 (HCoV-19 or hCoV-19). First identified in the city of Wuhan, Hubei, China, the World Health Organization declared the outbreak a public health emergency of international concern on January 30, 2020, and a pandemic on March 11, 2020. SARS‑CoV‑2 is a positive-sense single-stranded RNA virus that is contagious in humans. SARS‑CoV‑2 is a virus of the species ''severe acute respiratory syndrome–related coronavirus'' (SARSr-CoV), related to the SARS-CoV-1 virus that caused the 2002–2004 SARS outbreak. Despite its close relation to SARS-CoV-1, its closest known relatives, with which it forms a sister group, are the derived SAR ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |