|
SHIFTCOR
SHIFTCOR (Shift Correction) is a freely available web server as well as a stand-alone computer program for protein chemical shift re-referencing. Chemical shift referencing is a particularly widespread problem in biomolecular NMR with up to 25% of existing NMR chemical shift assignments being improperly referenced. Some of these referencing problems can lead to systematic errors of between 1.0 and 2.5 ppm (especially in 13C and 15N chemical shifts). Errors of this magnitude can play havoc with any attempt to compare assignments between proteins or to structurally interpret chemical shifts. Identifying which proteins are mis-assigned or improperly referenced can be challenging, as can correcting the errors once they are found. The SHIFTCOR program was designed to assist with identifying and fixing these chemical shift referencing problems. Specifically it compares, identifies, corrects and re-references 1H, 13C and 15N backbone chemical shifts of peptides and proteins by compari ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ShiftX
ShiftX (Shifts from X-ray structures) is a freely available web server for rapidly calculating protein chemical shifts from protein X-ray (or NMR) coordinates. Protein chemical shift prediction (also known as protein chemical shift calculation) is particularly useful in verifying protein chemical shift assignments, adjusting mis-referenced chemical shifts, refining NMR protein structures (via chemical shifts) and assisting with the NMR assignment of unassigned proteins that have either had their structures (or the structures of a homologous protein) determined by X-ray or NMR methods. The ShiftX web server takes atomic coordinates ( PDB s format) of proteins as input and quickly (<1 sec) generates the chemical shifts of both backbone (1H, 13C and 15N) and side chain (1H only) atoms as output (BMRB or Shifty format). The server is optimized to work with [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
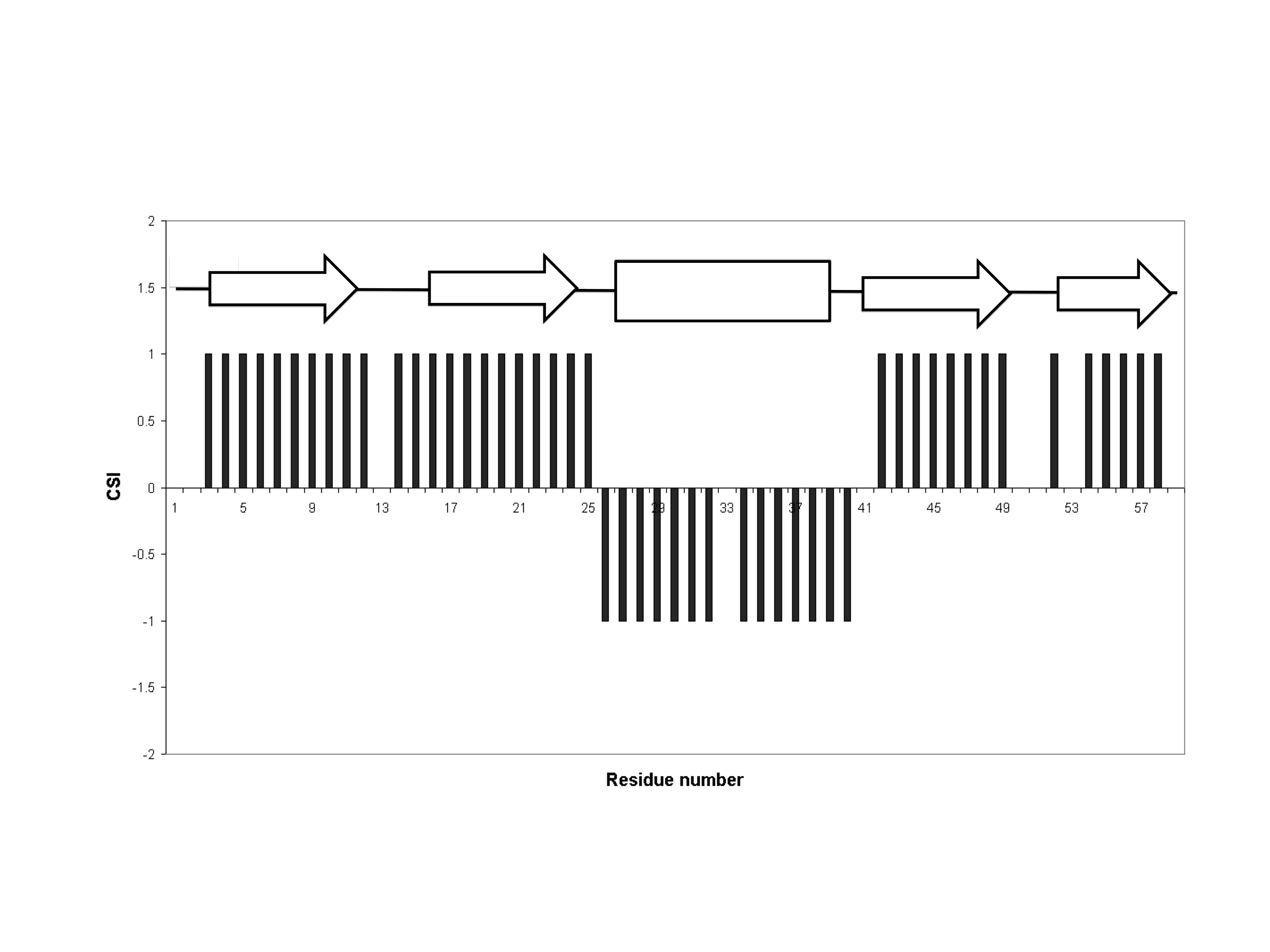
Chemical Shift Index
The chemical shift index or CSI is a widely employed technique in protein nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy that can be used to display and identify the location (i.e. start and end) as well as the type of protein secondary structure (beta strands, helices and random coil regions) found in proteins using only backbone chemical shift data The technique was invented by David S. Wishart in 1992 for analyzing 1Hα chemical shifts and then later extended by him in 1994 to incorporate 13C backbone shifts. The original CSI method makes use of the fact that 1Hα chemical shifts of amino acid residues in helices tends to be shifted upfield (i.e. towards the right side of an NMR spectrum) relative to their random coil values and downfield (i.e. towards the left side of an NMR spectrum) in beta strands. Similar kinds of upfield and downfield trends are also detectable in backbone 13C chemical shifts. Implementation The CSI is a graph-based technique that essentially employs an amino ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biophysics
Biophysics is an interdisciplinary science that applies approaches and methods traditionally used in physics to study biological phenomena. Biophysics covers all scales of biological organization, from molecular to organismic and populations. Biophysical research shares significant overlap with biochemistry, molecular biology, physical chemistry, physiology, nanotechnology, bioengineering, computational biology, biomechanics, developmental biology and systems biology. The term ''biophysics'' was originally introduced by Karl Pearson in 1892. Roland Glaser. Biophysics: An Introduction'. Springer; 23 April 2012. . The term ''biophysics'' is also regularly used in academia to indicate the study of the physical quantities (e.g. electric current, temperature, stress, entropy) in biological systems. Other biological sciences also perform research on the biophysical properties of living organisms including molecular biology, cell biology, chemical biology, and bioche ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein Structure
Protein structure is the three-dimensional arrangement of atoms in an amino acid-chain molecule. Proteins are polymers specifically polypeptides formed from sequences of amino acids, which are the monomers of the polymer. A single amino acid monomer may also be called a ''residue'', which indicates a repeating unit of a polymer. Proteins form by amino acids undergoing condensation reactions, in which the amino acids lose one water molecule per reaction in order to attach to one another with a peptide bond. By convention, a chain under 30 amino acids is often identified as a peptide, rather than a protein. To be able to perform their biological function, proteins fold into one or more specific spatial conformations driven by a number of non-covalent interactions, such as hydrogen bonding, ionic interactions, Van der Waals forces, and hydrophobic packing. To understand the functions of proteins at a molecular level, it is often necessary to determine their three-dimensiona ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein Methods
Protein methods are the techniques used to study proteins. There are experimental methods for studying proteins (e.g., for detecting proteins, for isolating and purifying proteins, and for characterizing the structure and function of proteins, often requiring that the protein first be purified). Computational methods typically use computer programs to analyze proteins. However, many experimental methods (e.g., mass spectrometry) require computational analysis of the raw data. Genetic methods Experimental analysis of proteins typically requires expression and purification of proteins. Expression is achieved by manipulating DNA that encodes the protein(s) of interest. Hence, protein analysis usually requires DNA methods, especially cloning. Some examples of genetic methods include conceptual translation, Site-directed mutagenesis, using a fusion protein, and matching allele with disease states. Some proteins have never been directly sequenced, however by translating codons from known ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Software
Nuclear may refer to: Physics Relating to the nucleus of the atom: *Nuclear engineering *Nuclear physics *Nuclear power *Nuclear reactor *Nuclear weapon *Nuclear medicine *Radiation therapy *Nuclear warfare Mathematics *Nuclear space *Nuclear operator *Nuclear congruence *Nuclear C*-algebra Biology Relating to the nucleus of the cell: * Nuclear DNA Society *Nuclear family, a family consisting of a pair of adults and their children Music * "Nuclear" (band), chilean thrash metal band * "Nuclear" (Ryan Adams song), 2002 *"Nuclear", a song by Mike Oldfield from his ''Man on the Rocks'' album * ''Nu.Clear'' (EP) by South Korean girl group CLC Films * ''Nuclear'' (film), a 2022 documentary by Oliver Stone. See also *Nucleus (other) *Nucleolus *Nucleation *Nucleic acid *Nucular ''Nucular'' is a common, proscribed pronunciation of the word "nuclear". It is a rough phonetic spelling of . The ''Oxford English Dictionary''s entry dates the word's first published appeara ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
A Database Of Uniformly Referenced Protein Chemical Shifts
A, or a, is the first letter and the first vowel letter of the Latin alphabet, used in the modern English alphabet, and others worldwide. Its name in English is '' a'' (pronounced ), plural ''aes''. It is similar in shape to the Ancient Greek letter alpha, from which it derives. The uppercase version consists of the two slanting sides of a triangle, crossed in the middle by a horizontal bar. The lowercase version is often written in one of two forms: the double-storey and single-storey . The latter is commonly used in handwriting and fonts based on it, especially fonts intended to be read by children, and is also found in italic type. In English, '' a'' is the indefinite article, with the alternative form ''an''. Name In English, the name of the letter is the ''long A'' sound, pronounced . Its name in most other languages matches the letter's pronunciation in open syllables. History The earliest known ancestor of A is ''aleph''—the first letter of the Phoenician ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein NMR
Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy of proteins (usually abbreviated protein NMR) is a field of structural biology in which NMR spectroscopy is used to obtain information about the structure and dynamics of proteins, and also nucleic acids, and their complexes. The field was pioneered by Richard R. Ernst and Kurt Wüthrich at the ETH, and by Ad Bax, Marius Clore, Angela Gronenborn at the National Institutes of Health, NIH, and Gerhard Wagner (physicist), Gerhard Wagner at Harvard University, among others. Structure determination by NMR spectroscopy usually consists of several phases, each using a separate set of highly specialized techniques. The sample is prepared, measurements are made, interpretive approaches are applied, and a structure is calculated and validated. NMR involves the quantum-mechanical properties of the central core ("Atomic nucleus, nucleus") of the atom. These properties depend on the local molecular environment, and their measurement provides a map of how t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemical Shift
In nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy, the chemical shift is the resonant frequency of an atomic nucleus relative to a standard in a magnetic field. Often the position and number of chemical shifts are diagnostic of the structure of a molecule. Chemical shifts are also used to describe signals in other forms of spectroscopy such as photoemission spectroscopy. Some atomic nuclei possess a magnetic moment (nuclear spin), which gives rise to different energy levels and resonance frequencies in a magnetic field. The total magnetic field experienced by a nucleus includes local magnetic fields induced by currents of electrons in the molecular orbitals (electrons have a magnetic moment themselves). The electron distribution of the same type of nucleus (e.g. ) usually varies according to the local geometry (binding partners, bond lengths, angles between bonds, and so on), and with it the local magnetic field at each nucleus. This is reflected in the spin energy levels (an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein Secondary Structure
Protein secondary structure is the local spatial conformation of the polypeptide backbone excluding the side chains. The two most common secondary structural elements are alpha helices and beta sheets, though beta turns and omega loops occur as well. Secondary structure elements typically spontaneously form as an intermediate before the protein folds into its three dimensional tertiary structure. Secondary structure is formally defined by the pattern of hydrogen bonds between the amino hydrogen and carboxyl oxygen atoms in the peptide backbone. Secondary structure may alternatively be defined based on the regular pattern of backbone dihedral angles in a particular region of the Ramachandran plot regardless of whether it has the correct hydrogen bonds. The concept of secondary structure was first introduced by Kaj Ulrik Linderstrøm-Lang at Stanford in 1952. Other types of biopolymers such as nucleic acids also possess characteristic secondary structures. Types ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |