|
Rutog County
Rutog County (), (in ) is a county in Ngari Prefecture, Tibet Autonomous Region of the People's Republic of China. The county seat is the new Rutog Town, located some or 700 miles west-northwest of the Tibetan capital, Lhasa. Rutog County shares a border with India. The county has a rich history of folk tales, myths, legends, proverbs and folk songs and has many caves, rock paintings and other relics. The Xinjiang-Tibet Highway runs through the Rutog County for . The modern county established in March 1961 covers . It has a very low population density with a population of just over 10,000. Name 'Rutog' is Tibetan for "mountain shaped like a spear and fork". Geography and climate Rutog County is located in northwestern Tibet, Ngari northwest with a number of territorial borders. It is divided into 12 townships and 30 village committees. The Karakoram Mountains go through the county. The average altitude of with a maximum altitude of . Lakes in Rutog County include Bangda ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
County (People's Republic Of China)
Counties ( zh, t=縣, s=县, hp=Xiàn), formally county-level divisions, are found in the Administrative divisions of China#County level, third level of the administrative hierarchy in Provinces of China, Provinces and Autonomous regions of China, Autonomous regions and the second level in Direct-controlled municipality#People's Republic of China, municipalities and Hainan, a level that is known as "county level" and also contains autonomous county, autonomous counties, county-level city, county-level cities, Banners of Inner Mongolia, banners, Banners of Inner Mongolia#Autonomous banner, autonomous banners and District (China)#City districts, City districts. There are 1,355 counties in Mainland China out of a total of 2,851 county-level divisions. The term ''xian'' is sometimes translated as "district" or "prefecture" when put in the context of History of China, Chinese history. History ''Xian'' have existed since the Warring States period and were set up nationwide by the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lhasa
Lhasa (; Lhasa dialect: ; bo, text=ལྷ་ས, translation=Place of Gods) is the urban center of the prefecture-level Lhasa City and the administrative capital of Tibet Autonomous Region in Southwest China. The inner urban area of Lhasa City is equivalent to the administrative borders of Chengguan District (), which is part of the wider prefectural Lhasa City. Lhasa is the second most populous urban area on the Tibetan Plateau after Xining and, at an altitude of , Lhasa is one of the highest cities in the world. The city has been the religious and administrative capital of Tibet since the mid-17th century. It contains many culturally significant Tibetan Buddhist sites such as the Potala Palace, Jokhang Temple and Norbulingka Palaces. Toponymy Lhasa literally translates to "place of gods" ( , god; , place) in the Tibetan language. Chengguan literally translates to "urban gateway" () in the Chinese language. Ancient Tibetan documents and inscriptions demonstrate th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
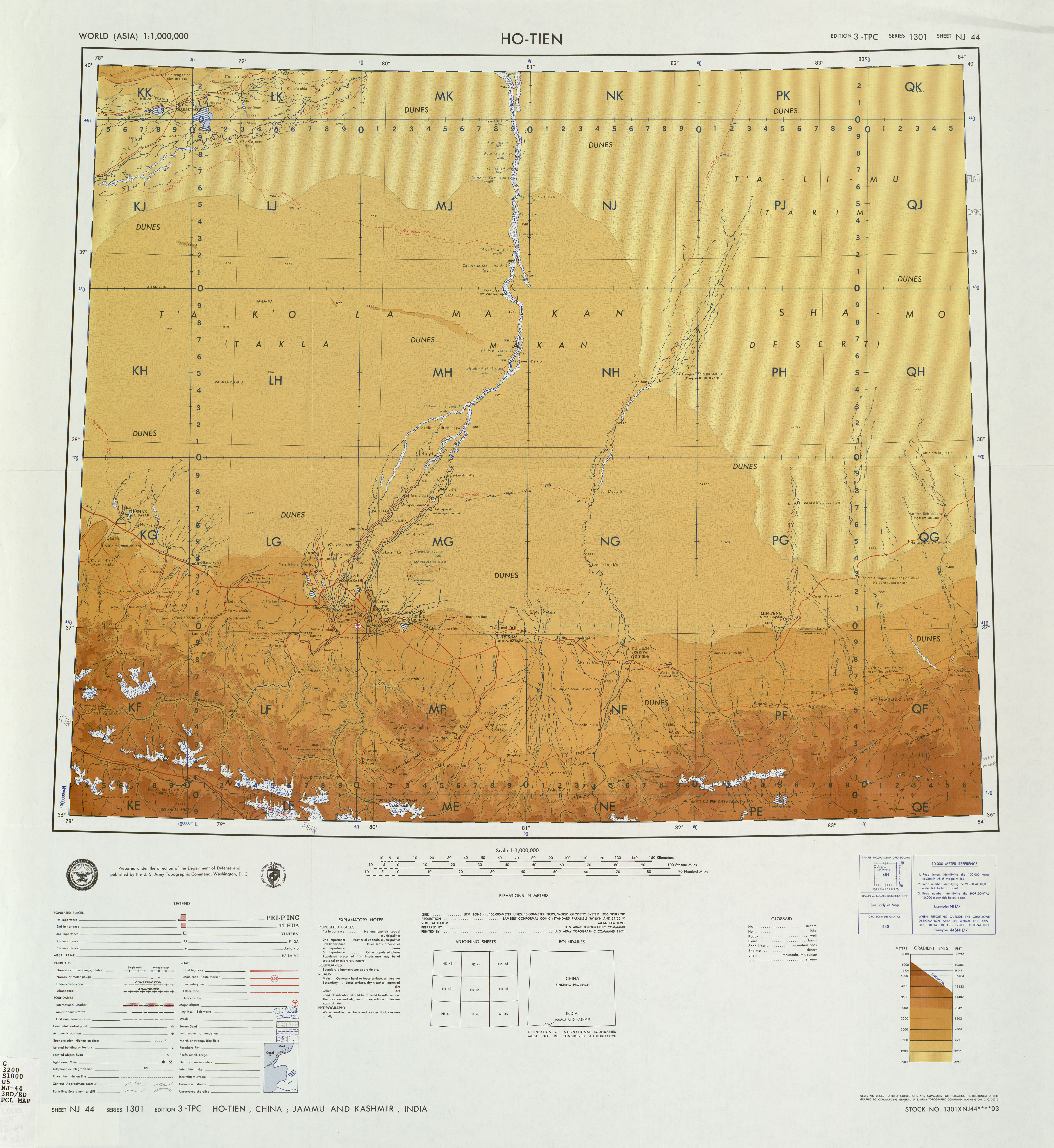
Qira County
Qira County ( Uyghur: ), alternatively Chira or Cele (from Mandarin Chinese), is a county in Hotan Prefecture, Xinjiang Uyghur Autonomous Region, China. Almost all the residents of the county are Uyghurs and live around oases situated between the desolate Taklamakan Desert and Kunlun Mountains. The county is bordered to the north by Aksu Prefecture, to the east by Yutian / Keriya County, to the northwest by Lop County, to the southwest by Hotan County including the China-India disputed Aksai Chin area and to the south by Rutog County, Ngari Prefecture in Tibet. History The sixth century Dandan Oilik oasis town archaeological site where Buddhist shrines and texts were discovered is located in the desert of northern Qira (Chira) County. Qira town (Chira), the town that is the current county seat of Qira County, has been forced to change locations on three occasions due to encroachment by the sands of the Taklamakan Desert. In his 1900-01 expedition in the region, Aurel Stein tra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hotan County
Hotan County (also known as Gosthana, Gaustana, Godana, Godaniya, Khotan, Hetian, Hotien) is a county in the southwest of the Xinjiang Uyghur Autonomous Region and is under the administration of the Hotan Prefecture. Almost all the residents of the county are Uyghurs and live around oases situated between the desolate Taklamakan Desert and Kunlun Mountains. Hotan County is the southernmost county-level division of Xinjiang. The county borders Karakax/Moyu County to the northwest, Hotan City and Lop County to the northeast, Qira County to the east, Pishan County to the west, and (in Aksai Chin) Rutog County, Tibet to the southeast. Hotan County administers most of Aksai Chin, an area disputed between China and India. The Line of Actual Control divides the India-controlled part of Ladakh union territory from the Aksai Chin area administered as part of southwest Hotan County. Name The area of Hotan is originally known as and has been historically referred to as Godana (Godaniya), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Foreign Languages Press
Foreign Languages Press is a publishing house located in China. Based in Beijing, it was founded in 1952 and currently forms part of the China International Publishing Group, which is owned and controlled by the Publicity Department of the Chinese Communist Party. The press publishes books on a wide range of topics in eighteen languages spoken primarily outside China. Much of its output is aimed at the international community – its 1960s editions of works by Marx and Lenin are still widely circulated – but it also publishes some material aimed at foreign language students within China. Beginning in the 1950s many works of classical and modern Chinese literature were translated into English by translators such as Gladys Yang, Yang Xianyi and Sidney Shapiro. As of 2008, the house had published over 30,000 titles in a total of 43 languages. Book series English language titles * Ancient Towns Around Shanghai * China Handbook Series * China Knowledge Series * China Society ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pangong Tso
Pangong Tso or Pangong Lake (; ; hi, text=पैंगोंग झील) is an endorheic lake spanning eastern Ladakh and West Tibet situated at an elevation of . It is long and divided into five sublakes, called ''Pangong Tso'', ''Tso Nyak'', ''Rum Tso'' (twin lakes) and ''Nyak Tso''. Approximately 50% of the length of the overall lake lies within Tibet in China, 40% in Ladakh, India and the remaining 10% is disputed and is a de-facto buffer zone between India and China. The lake is wide at its broadest point. All together it covers almost 700 km2. During winter the lake freezes completely, despite being saline water. It has a land-locked basin separated from the Indus River basin by a small elevated ridge, but is believed to have been part of the latter in prehistoric times. Names Historically, the lake is viewed as being made up five sublakes, which are connected through narrow water channels. The name ''Pangong Tso'' only applied to the westernmost lake that i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wo Erba Lake
Orba Co, also Wo Erba or Wo Erbacuo (; ), is a lake in Rutog County in the Ngari Prefecture in the northwest of the Tibet Autonomous Region of China. It lies at an elevation of , to the southeast of Longmu Lake __NOTOC__ Longmu (; ), also Longmu Co or Longmucuo, is a glacial lake in Rutog County in the Ngari Prefecture in the northwest of the Tibet Autonomous Region The Tibet Autonomous Region or Xizang Autonomous Region, often shortened to Tibet o .... The lake has islands, which are the highest islands in the world. References Ngari Prefecture Lakes of Tibet {{Ngari-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lumajangdong Co
Lumajangdong Co or Lumajiang Dongcuo is a lake in the Ngari Prefecture, Tibet Tibet (; ''Böd''; ) is a region in East Asia, covering much of the Tibetan Plateau and spanning about . It is the traditional homeland of the Tibetan people. Also resident on the plateau are some other ethnic groups such as Monpa, Taman ..., China with an area of 250 km². It is located at 34° 2' 0" and 81° 40' 0". Gormain lies a few miles (5–7 km) to the northwest. 
References ...
|
Longmu Lake
__NOTOC__ Longmu (; ), also Longmu Co or Longmucuo, is a glacial lake in Rutog County in the Ngari Prefecture in the northwest of the Tibet Autonomous Region The Tibet Autonomous Region or Xizang Autonomous Region, often shortened to Tibet or Xizang, is a province-level autonomous region of the People's Republic of China in Southwest China. It was overlayed on the traditional Tibetan regions of � ... of China. It was explored in 1989 in a Sino-French expedition to western Tibet. Climate Map gallery Notes References Ngari Prefecture Lakes of Tibet {{Ngari-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guozha Lake
Kotra Tso (), also known as Guozha Lake (), and Lake Lighten,Michael WardThe Kun Lun Shan: Desert Peaks of Central Asia ''The Alpine Journal'' (1989-90), p. 90. is a glacial lake in Rutog County in the Ngari Prefecture in the northwest of the Tibet Autonomous Region of China. It lies in the western Kunlun Mountains to the northwest of Bangda Lake, not far from the regional border with Xinjiang. Located at an altitude of 5080 metres, it covers an area of 244 square kilometres with a maximum depth of 81.9 metres and his drainage basin contains 62 glaciers. India's claim line in Aksai Chin runs along the water-parting line of the Guozha lake and the Amtogor Lake Aksai Chin Lake or Aksayqin Lake, () is an endorheic lake in the disputed region of Aksai Chin. The plateau is administered by China but also claimed by India. Its Tibetan/Ladakhi name is Amtogor Lake which means "encounter with a round object". ... to the west. However, China has claimed the whole of Aksai Chin in 195 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bangda Lake
Bangda Lake (; ), formerly called Yeshil Kul, is a glacial lake in Ngari Prefecture in the northwest of the Tibet Autonomous Region of China. It lies south of the western Kunlun Mountains, only a few kilometres to the southeast of Guozha Lake (Lake Lighten). Located at an elevation of , the Bangda Lake covers an area of 106 square kilometres with a maximum depth of 21.6 metres and contains 90 glaciers. Yeshil Kul is located along an ancient travel route between Ladakh and Khotan via the Keriya Pass. The route runs along the Longmu Co fault up to Yeshil Kul, and then heads north to the Keriya Pass, after which the valleys of the Iksu, Polu and Keriya rivers are followed. A "Xinjiang–Tibet Highway" was laid by the People's Republic of China between the Polu town and the vicinity of the Bangda Lake during 1950–1951, prior to its annexation of Tibet. Jeep tracks were then made over the relatively flat, hard terrain of the Longmu Co fault, leading to Rudok. A regular j ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Karakoram Mountains
The Karakoram is a mountain range in Kashmir region spanning the borders of Pakistan, China, and India, with the northwest extremity of the range extending to Afghanistan and Tajikistan. Most of the Karakoram mountain range falls under the jurisdiction of Gilgit-Baltistan, which is controlled by Pakistan. Its highest peak (and world's second-highest), K2, is located in Gilgit-Baltistan. It begins in the Wakhan Corridor (Afghanistan) in the west, encompasses the majority of Gilgit-Baltistan, and extends into Ladakh (controlled by India) and Aksai Chin (controlled by China). It is the second-highest mountain range in the world and part of the complex of ranges including the Pamir Mountains, the Hindu Kush and the Himalayan Mountains. The Karakoram has eighteen summits over in height, with four exceeding : K2, the second-highest peak in the world at , Gasherbrum I, Broad Peak and Gasherbrum II. The range is about in length and is the most heavily glaciated part of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |