|
Rumold Mercator
Rumold Mercator (Leuven, 1541 – Duisburg, 31 December 1599) was a cartographer and the son of cartographer Gerardus Mercator. He completed some at the time unfinished projects left after his father's death and added new materials of his own research. Biography Rumold Mercator was the youngest son of cartographer Gerardus Mercator and his first wife Barbara Schellekens. He rose to fame in his father's wake when, in 1587, he published a copy of his father's Ptolemaic map of the world from 1569, revised in its overall graphic design. In 1595, a year after his father's death, Rumold Mercator published a supplement of 34 maps to his father's ''Tabulae Geographicae'' map book. It contains 29 maps, engraved by Gerardus Mercator, of the missing parts of Europe (Iceland, the British Isles and the Northern and Eastern European countries). To complete the map collection quickly, Rumold added his own world map from 1587 and had four maps of the continents from his father's large worl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mercator World Map
__NOTOC__ Mercator (Latin for " merchant") may refer to: People * Marius Mercator (c. 390–451), a Catholic ecclesiastical writer * Arnold Mercator, a 16th-century cartographer * Gerardus Mercator, a 16th-century cartographer ** Mercator 1569 world map ** Mercator projection, a cartographic projection devised by Gerardus Mercator * Rumold Mercator, a 16th-century cartographer * Nicholas Mercator, a 17th-century mathematician ** Mercator series, a representation of the natural logarithm Companies and universities * Mercator (retail), a Slovenian supermarket chain * Mercator-S, a retail company in Serbia, part of Agrokor Group * Mercator School of Management, University of Duisburg-Essen, Germany * Mercator Limited, a shipping company in India * Mercator Corporation, a consulting firm and investment bank formed by James Giffen, involved with Kazakhgate Vehicles * ''Mercator'' (ship), a barquentine museum ship in Oostende, Belgium * P4M Mercator, a reconnaissance ai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
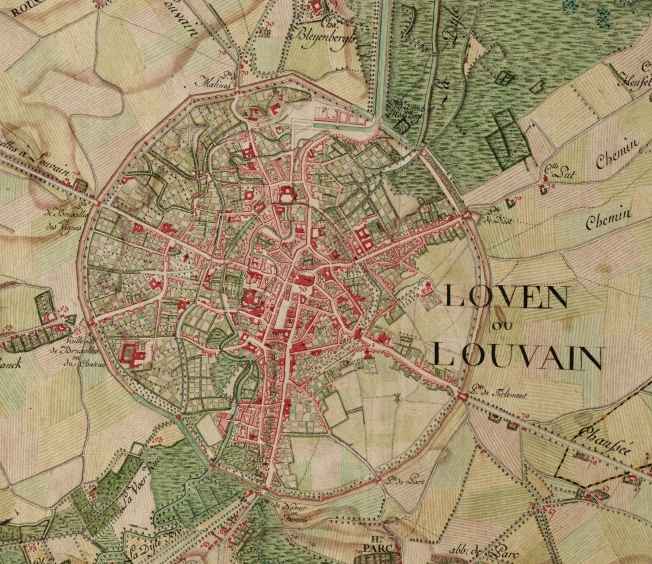
Leuven
Leuven (, ) or Louvain (, , ; german: link=no, Löwen ) is the capital and largest city of the province of Flemish Brabant in the Flemish Region of Belgium. It is located about east of Brussels. The municipality itself comprises the historic city and the former neighbouring municipalities of Heverlee, Kessel-Lo, a part of Korbeek-Lo, Wilsele and Wijgmaal. It is the eighth largest city in Belgium, with more than 100,244 inhabitants. KU Leuven, Belgium's largest university, has its flagship campus in Leuven, which has been a university city since 1425. This makes it the oldest university city in the Low Countries. The city is home of the headquarters of Anheuser-Busch InBev, the world's largest beer brewer and sixth-largest fast-moving consumer goods company. History Middle Ages The earliest mention of Leuven (''Loven'') dates from 891, when a Viking army was defeated by the Frankish king Arnulf of Carinthia (see: Battle of Leuven). According to a legend, the city's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duisburg
Duisburg () is a city in the Ruhr metropolitan area of the western German state of North Rhine-Westphalia. Lying on the confluence of the Rhine and the Ruhr rivers in the center of the Rhine-Ruhr Region, Duisburg is the 5th largest city in North Rhine-Westphalia and the 15th-largest city in Germany. In the Middle Ages, it was a city-state and a member of the Hanseatic League, and later became a major centre of iron, steel, and chemicals industries. For this reason, it was heavily bombed in World War II. Today it boasts the world's largest inland port, with 21 docks and 40 kilometres of wharf. Status Duisburg is a city in Germany's Rhineland, the fifth-largest (after Cologne, Düsseldorf, Dortmund and Essen) of the nation's most populous federal state of North Rhine-Westphalia. Its 500,000 inhabitants make it Germany's 15th-largest city. Located at the confluence of the Rhine river and its tributary the Ruhr river, it lies in the west of the Ruhr urban area, Germa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cartographer
Cartography (; from grc, χάρτης , "papyrus, sheet of paper, map"; and , "write") is the study and practice of making and using maps. Combining science, aesthetics and technique, cartography builds on the premise that reality (or an imagined reality) can be modeled in ways that communicate spatial information effectively. The fundamental objectives of traditional cartography are to: * Set the map's agenda and select traits of the object to be mapped. This is the concern of map editing. Traits may be physical, such as roads or land masses, or may be abstract, such as toponyms or political boundaries. * Represent the terrain of the mapped object on flat media. This is the concern of map projections. * Eliminate characteristics of the mapped object that are not relevant to the map's purpose. This is the concern of generalization. * Reduce the complexity of the characteristics that will be mapped. This is also the concern of generalization. * Orchestrate the elements of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gerardus Mercator
Gerardus Mercator (; 5 March 1512 – 2 December 1594) was a 16th-century geographer, cosmographer and cartographer from the County of Flanders. He is most renowned for creating the 1569 world map based on a new projection which represented sailing courses of constant bearing ( rhumb lines) as straight lines—an innovation that is still employed in nautical charts. Mercator was a highly influential pioneer in the history of cartography. Monmonier, Mark: ''Rhumb Lines and Map Wars: A Social History of the Mercator Projection''. (Chicago: University of Chicago Press, 2004)Van der Krogt, Peter (2015), 'Chapter 6: Gerhard Mercator and his Cosmography: How the 'Atlas' became an Atlas,'; in: Gerhard Holzer, et al. (eds.), ''A World of Innovation: Cartography in the Time of Gerhard Mercator''. (Newcastle upon Tyne: Cambridge Scholars Publishing, 2015), pp. 112–130 Along with Gemma Frisius and Abraham Ortelius, he is generally considered one of the founders of the Netherlandish ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unfinished Work
Unfinished may refer to: *Unfinished creative work, a work which a creator either chose not to finish or was prevented from finishing. Music * Symphony No. 8 (Schubert) "Unfinished" * ''Unfinished'' (album), 2011 album by American singer Jordan Knight * "Unfinished" (Kotoko song), stylized "→unfinished→", 2012 * "Unfinished" (Mandisa song), 2017 * "Unfinished", song by Stone Sour from the 2010 album ''Audio Secrecy'' * "Unfinished", song by Mineral from the 1998 album ''EndSerenading'' Television and film * "Unfinished" (''How I Met Your Mother''), 2010 television show episode * ''Unfinished'' (film), 2018 South Korean film Literature * ''Unfinished'' (book), a 2021 memoir by Priyanka Chopra See also * * Unfinished symphony * Unfinished building An unfinished building is a building (or other architectural structure, as a bridge, a road or a tower) where construction work was abandoned or on-hold at some stage or only exists as a design. It may also refer to bu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ptolemy
Claudius Ptolemy (; grc-gre, Πτολεμαῖος, ; la, Claudius Ptolemaeus; AD) was a mathematician, astronomer, astrologer, geographer, and music theorist, who wrote about a dozen scientific treatises, three of which were of importance to later Byzantine, Islamic, and Western European science. The first is the astronomical treatise now known as the '' Almagest'', although it was originally entitled the ''Mathēmatikē Syntaxis'' or ''Mathematical Treatise'', and later known as ''The Greatest Treatise''. The second is the ''Geography'', which is a thorough discussion on maps and the geographic knowledge of the Greco-Roman world. The third is the astrological treatise in which he attempted to adapt horoscopic astrology to the Aristotelian natural philosophy of his day. This is sometimes known as the ''Apotelesmatika'' (lit. "On the Effects") but more commonly known as the '' Tetrábiblos'', from the Koine Greek meaning "Four Books", or by its Latin equivalent ''Quadripa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arnold Mercator
Arnold or Arnoldus Mercator (Leuven, 31 August 1537 – Duisburg, 6 July 1587) was a Southern Netherlandish cartographer, mathematician and classical philologist. He was the eldest son of cartographer Gerardus Mercator and a brother of Rumold Mercator. Life Leuven Arnold was the eldest child of Gerardus Mercator and Barbara Schellekens from Leuven, who married in 1536. Arnold grew up in Leuven and, as a 7-year-old boy, witnessed the arrest of his father, who was then a professor in Leuven. Gerardus Mercator was suspected of Lutheranism. His father was released after a few months. The family remained impoverished in Leuven for a few more years until 1552. Duisburg In 1552 the Mercator family moved to the imperial city of Duisburg. The Duke of Cleves, the Lutheran William V, was hospitable to humanist scholars. Gerardus Mercator may have been attracted by the Duke's intention to found a university in Duisburg. Arnold learned the trade of cartography and mathematics from his father ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1545 Births
Year 1545 ( MDXLV) was a common year starting on Thursday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar. Events January–June * February 22 – A firman of the Ottoman Empire is issued for the dethronement of Radu Paisie as Prince of Wallachia. * February 27 – Battle of Ancrum Moor: The Scots are victorious over numerically superior English forces. * March 24 – At a diet in Worms, Germany, summoned by Pope Paul III, the German Protestant princes demand a national religious settlement for Germany. Holy Roman Emperor, Charles V refuses. *April 1 – Potosí is founded by the Spanish as a mining town after the discovery of huge silver deposits in this area of modern-day Bolivia. Silver mined from Huayna Potosí Mountain provides most of the wealth on which the Spanish Empire is based until its fall in the early 19th century. * June 13 – Spanish explorer Yñigo Ortiz de Retez sets out to navigate the northern coast of New Guine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1599 Deaths
__NOTOC__ Events January–June * January 8 – The Jesuit educational plan, known as the '' Ratio Studiorum'', is issued. * March 12 – Robert Devereux, 2nd Earl of Essex, is appointed Lord Lieutenant of Ireland, by Queen Elizabeth I of England. * April 23 – The Earl of Essex arrives in Dublin at the head of 16,000 troops, the largest army ever seen in Ireland. * May 16 – The Kalmar Bloodbath takes place in Kalmar, Sweden. * May 29 – Essex takes Cahir Castle, supposedly the strongest in Ireland, after a short siege. * June 20 – The Synod of Diamper is convened. July–December * July – Second Dutch Expedition to Indonesia: A Dutch fleet returns to Amsterdam, carrying 600,000 pounds of pepper and 250,000 pounds of cloves and nutmeg. * July 24 – Swedish King Sigismund III Vasa is dethroned by his uncle Duke Charles, who takes over as regent of the realm until 1604, when he becomes King Charles IX. * August 15 – First Battle of Curlew Pass: Iri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |