|
Ronchi Test
In optical testing a Ronchi test is a method of determining the surface shape (figure) of a mirror used in telescopes and other optical devices. Description In 1923 Italian physicist Vasco Ronchi published a description of the eponymous Ronchi test, which is a variation of the Foucault knife-edge test and which uses simple equipment to test the quality of optics, especially concave mirrors.Masud Mansuripur (July 1997) "The Ronchi test," ''Optics & Photonics News'', vol. 8, pages 42-46. Available on-line at: http://www.mmresearch.com/articles/article1/index.htm . A "Ronchi tester" consists of: *A light source *A Diffuser (optics), diffuser *A Ronchi grating A Ronchi grating consists of alternate dark and clear stripes. One design is a small frame with several evenly spaced fine wires attached. Light is emitted through the Ronchi grating (or a single slit), reflected by the mirror being tested, then passes through the Ronchi grating again and is observed by the person doing th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Optics
Optics is the branch of physics that studies the behaviour and properties of light, including its interactions with matter and the construction of instruments that use or detect it. Optics usually describes the behaviour of visible, ultraviolet, and infrared light. Because light is an electromagnetic wave, other forms of electromagnetic radiation such as X-rays, microwaves, and radio waves exhibit similar properties. Most optical phenomena can be accounted for by using the classical electromagnetic description of light. Complete electromagnetic descriptions of light are, however, often difficult to apply in practice. Practical optics is usually done using simplified models. The most common of these, geometric optics, treats light as a collection of rays that travel in straight lines and bend when they pass through or reflect from surfaces. Physical optics is a more comprehensive model of light, which includes wave effects such as diffraction and interference that cannot be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Figuring
Figuring is the process of final polishing of an optical surface to remove imperfections or modify the surface curvature to achieve the shape required for a given application. Types An example of figuring is that used in reflecting telescope primary mirrors in a process of converting the smooth spherical mirror produced by earlier stages into the aspherical or parabolic shapes needed to form the correct image. It is done by applying different polishing stroke lengths with different sized and shaped tools. Manual figuring is a very laborious process, since the heat produced by polishing has to be allowed to dissipate before the shape of the mirror can be measured again, and the places for later polishing selected. Testing of the figure is usually done by a Foucault knife-edge test or Ronchi test in amateur telescope making and with very sophisticated null testers on research telescope optics. For large mirrors, ion figuring is often used, in which a beam of neutral atoms is u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Optical Telescope
An optical telescope is a telescope that gathers and focuses light mainly from the visible part of the electromagnetic spectrum, to create a magnified image for direct visual inspection, to make a photograph, or to collect data through electronic image sensors. There are three primary types of optical telescope: * Refracting telescopes, which use lenses and less commonly also prisms (dioptrics) * Reflecting telescopes, which use mirrors (catoptrics) * Catadioptric telescopes, which combine lenses and mirrors An optical telescope's ability to resolve small details is directly related to the diameter (or aperture) of its objective (the primary lens or mirror that collects and focuses the light), and its light-gathering power is related to the area of the objective. The larger the objective, the more light the telescope collects and the finer detail it resolves. People use optical telescopes (including monoculars and binoculars) for outdoor activities such as observational as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Italian People
, flag = , flag_caption = The national flag of Italy , population = , regions = Italy 55,551,000 , region1 = Brazil , pop1 = 25–33 million , ref1 = , region2 = Argentina , pop2 = 20–25 million , ref2 = , region3 = United States , pop3 = 17-20 million , ref3 = , region4 = France , pop4 = 1-5 million , ref4 = , region5 = Venezuela , pop5 = 1-5 million , ref5 = , region6 = Paraguay , pop6 = 2.5 million , region7 = Colombia , pop7 = 2 million , ref7 = , region8 = Canada , pop8 = 1.5 million , ref8 = , region9 = Australia , pop9 = 1.0 million , ref9 = , region10 = Uruguay , pop10 = 1.0 million , r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Physicist
A physicist is a scientist who specializes in the field of physics, which encompasses the interactions of matter and energy at all length and time scales in the physical universe. Physicists generally are interested in the root or ultimate causes of phenomena, and usually frame their understanding in mathematical terms. Physicists work across a wide range of research fields, spanning all length scales: from sub-atomic and particle physics, through biological physics, to cosmological length scales encompassing the universe as a whole. The field generally includes two types of physicists: experimental physicists who specialize in the observation of natural phenomena and the development and analysis of experiments, and theoretical physicists who specialize in mathematical modeling of physical systems to rationalize, explain and predict natural phenomena. Physicists can apply their knowledge towards solving practical problems or to developing new technologies (also known as applie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vasco Ronchi
Vasco Ronchi (; December 19, 1897 – October 31, 1988) was an Italian people, Italian physicist known for his work in optics. He was born on 19 December 1897 in Florence, Italy. Along with Enrico Fermi, he was a student of Luigi Puccianti. He studied at the Faculty of Physics of the University of Pisa from 1915 to 1919. In 1922 Ronchi published work describing testing methods for optics using simple equipment. The Ronchi test is widely used in amateur telescope making. The Ronchi ruling also bears his name. He served numerous terms as the President of the 'Union Internationale d'Histoire des Sciences' within the UNESCO. Ronchi authored 900 papers and 30 books. External links Ronchi, Vasco (1897-1988) 1897 births 1988 deaths 20th-century Italian physicists {{Italy-physicist-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eponymous
An eponym is a person, a place, or a thing after whom or which someone or something is, or is believed to be, named. The adjectives which are derived from the word eponym include ''eponymous'' and ''eponymic''. Usage of the word The term ''eponym'' functions in multiple related ways, all based on an explicit relationship between two named things. A person, place, or thing named after a particular person share an eponymous relationship. In this way, Elizabeth I of England is the eponym of the Elizabethan era. When Henry Ford is referred to as "the ''eponymous'' founder of the Ford Motor Company", his surname "Ford" serves as the eponym. The term also refers to the title character of a fictional work (such as Rocky Balboa of the ''Rocky'' film series), as well as to ''self-titled'' works named after their creators (such as the album ''The Doors'' by the band the Doors). Walt Disney created the eponymous Walt Disney Company, with his name similarly extended to theme parks such a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
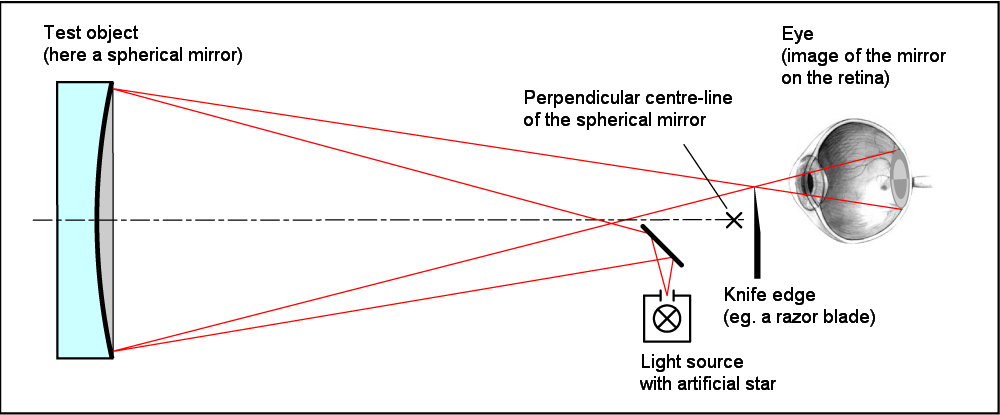
Foucault Knife-edge Test
The Foucault knife-edge test is an optical test to accurately measure the shape of concave curved mirrors. It is commonly used by amateur telescope makers for figuring primary mirrors in reflecting telescopes. It uses a relatively simple, inexpensive apparatus compared to other testing techniques. Overview The Foucault knife-edge test was described in 1858 by French physicist Léon Foucault as a way to measure conic shapes of optical mirrors. It measures mirror surface dimensions by reflecting light into a knife edge at or near the mirror's centre of curvature. In doing so, it only needs a tester which in its most basic 19th century form consists of a light bulb, a piece of tinfoil with a pinhole in it, and a razor blade to create the knife edge. The testing device is adjustable along the X-axis (knife cut direction) across the Y-axis (optical axis), and is usually equipped with measurable adjustment to 0.001 inch (25 µm) or better along lines parallel to the optical axi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Léon Foucault
Jean Bernard Léon Foucault (, ; ; 18 September 1819 – 11 February 1868) was a French physicist best known for his demonstration of the Foucault pendulum, a device demonstrating the effect of Earth's rotation. He also made an early measurement of the speed of light, discovered eddy currents, and is credited with naming the gyroscope. Early years The son of a publisher, Foucault was born in Paris on 18 September 1819. After an education received chiefly at home, he studied medicine, which he abandoned in favour of physics due to a blood phobia. He first directed his attention to the improvement of Louis Daguerre's photographic processes. For three years he was experimental assistant to Alfred Donné (1801–1878) in his course of lectures on microscopic anatomy. With Hippolyte Fizeau he carried out a series of investigations on the intensity of the light of the sun, as compared with that of carbon in the arc lamp, and of lime in the flame of the oxyhydrogen blowpipe; on the int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Concave Mirror
A curved mirror is a mirror with a curved reflecting surface. The surface may be either ''convex'' (bulging outward) or ''concave'' (recessed inward). Most curved mirrors have surfaces that are shaped like part of a sphere, but other shapes are sometimes used in optical devices. The most common non-spherical type are parabolic reflectors, found in optical devices such as reflecting telescopes that need to image distant objects, since spherical mirror systems, like spherical lenses, suffer from spherical aberration. Distorting mirrors are used for entertainment. They have convex and concave regions that produce deliberately distorted images. They also provide highly magnified or highly diminished (smaller) images when the object is placed at certain distances. Convex mirrors A convex mirror or diverging mirror is a curved mirror in which the reflective surface bulges towards the light source. Convex mirrors reflect light outwards, therefore they are not used to focus light. Su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diffuser (optics)
In optics, a diffuser (also called a light diffuser or optical diffuser) is any material that diffuses or scatters light in some manner to transmit soft light. Diffused light can be easily obtained by reflecting light from a white surface, while more compact diffusers may use translucent material, including ground glass, teflon, opal glass, and greyed glass. Types Perfect reflecting diffuser A perfect (reflecting) diffuser (PRD) is a theoretical perfectly white surface with Lambertian reflectance (its brightness appears the same from any angle of view). It does not absorb light, giving back 100% of the light it receives. Reflective diffusers can be easily characterised by scatterometers.{{cite web, url=http://www.zebraoptical.com/roughnessviascatterometry.html, title=Page Title, website=www.zebraoptical.com Diffractive diffuser/homogenizer A diffractive diffuser is a kind of diffractive optical element (DOE) that exploits the principles of diffraction and refraction. It uses d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ronchi Grating
A Ronchi ruling, Ronchi grating, or Ronchi mask, named after the Italian physicist Vasco Ronchi, is a constant-interval bar and space square-wave optical target or mask. The design produces a precisely patterned light source by reflection or illumination, or a stop pattern by transmission, with precise uniformity, spatial frequency, sharp edge definition, and high contrast ratio. Manufacturing Ronchi rulings are typically manufactured through photolithographic deposition of metallic chromium on a substrate, which yields a precise, nearly 100% contrast pattern. For a reflective or illuminated type, dark stripes are printed on a diffusely reflecting or translucent substrate, such as a square of white ceramic material or opal glass. For a transmissive type, opaque stripes are printed on a transparent glass substrate. A transmissive type may be readily modified to act as an illuminated type by stacking a reflective object behind it. Applications A test target in the Ronchi patter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |