|
Rocketdyne XRS-2200
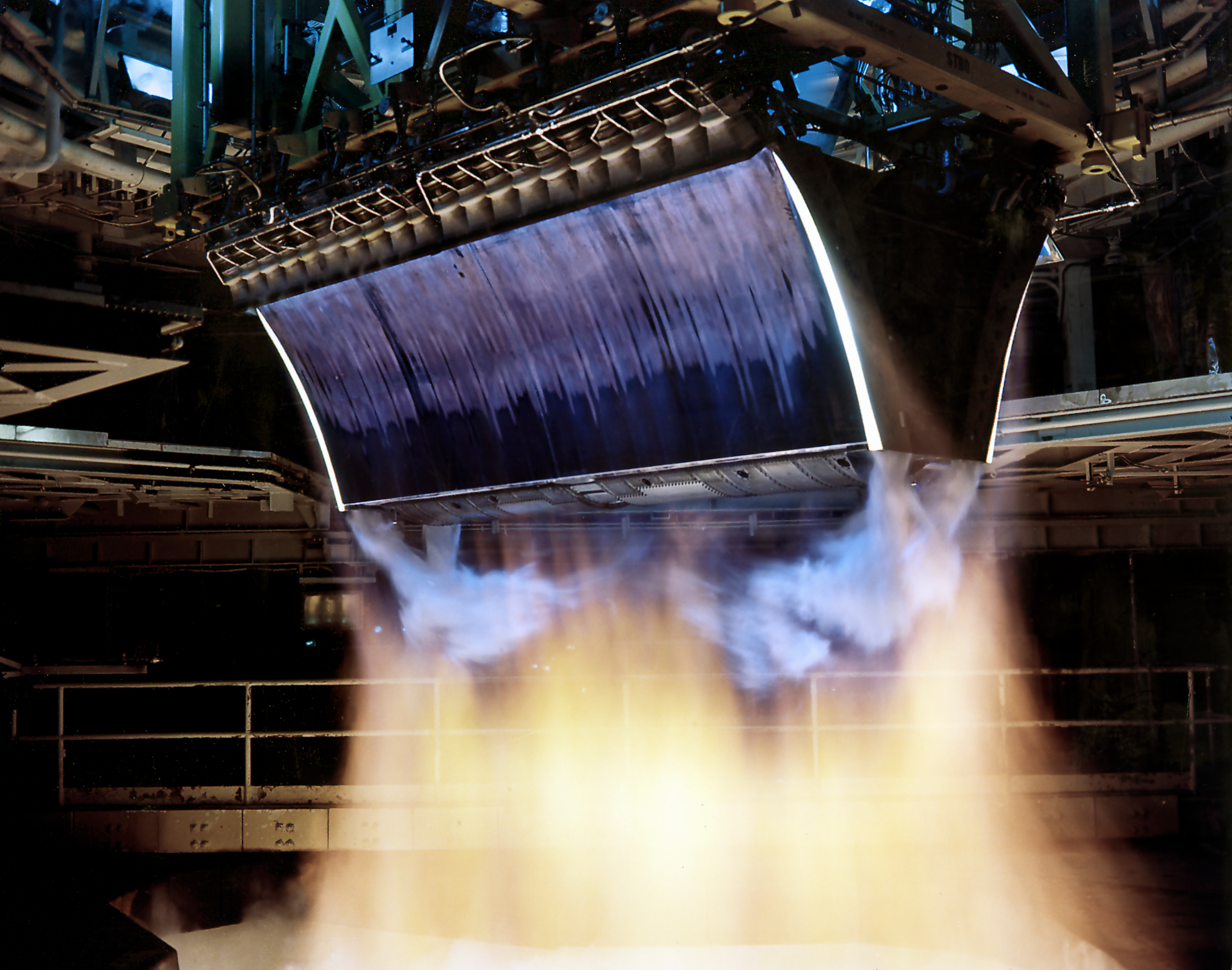
The Rocketdyne XRS-2200 was an experimental linear aerospike engine developed in the mid-1990s for the Lockheed Martin X-33 program. The design was based on the J-2S, the upgraded version of the Apollo era J-2 engine developed in the 1960s. The XRS-2200 used the J-2's combustion cycle and propellant choice. Rocketdyne intended to develop the subscale XRS-2200 into the RS-2200 for use on the VentureStar VentureStar was a single-stage-to-orbit reusable launch system proposed by Lockheed Martin and funded by the U.S. government. The goal was to replace the Space Shuttle by developing a re-usable spaceplane that could launch satellites into orbit a .... While the X-33 program was cancelled, two XRS-2200 engines were produced and tested. References {{Reflist Rocketdyne engines Rocketdyne Rocket engines ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rocketdyne
Rocketdyne was an American rocket engine design and production company headquartered in Canoga Park, California, Canoga Park, in the western San Fernando Valley of suburban Los Angeles, California, Los Angeles, in southern California. The Rocketdyne Division was founded by North American Aviation (NAA) in 1955, and was later part of Rockwell International (1967–1996) and Boeing (1996–2005). In 2005, the Rocketdyne Division was sold to United Technologies Corporation, becoming Pratt & Whitney Rocketdyne as part of Pratt & Whitney. In 2013, Pratt & Whitney Rocketdyne was sold to GenCorp, which merged it with Aerojet to form Aerojet Rocketdyne.Marjorie Censer(18 Dec 2022) L3Harris moves to acquire Aerojet Rocketdynefor $4.7 billion, after Lockheed Martin ended its attempt for Rocketdyne in Feb 2022 History After World War II, North American Aviation (NAA) was contracted by the Defense Department to study the German V-2, V-2 missile and adapt its engine to Society of Automotiv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
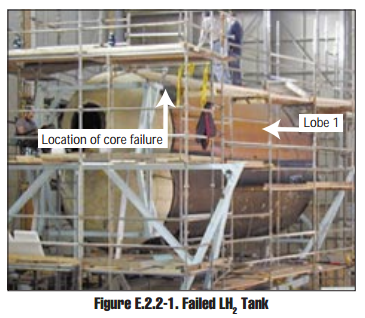
Lockheed Martin X-33
The Lockheed Martin X-33 was a proposed uncrewed, sub-scale technology demonstrator suborbital spaceplane that was developed for a period in the 1990s. The X-33 was a technology demonstrator for the VentureStar orbital spaceplane, which was planned to be a next-generation, commercially operated reusable launch vehicle. The X-33 would flight-test a range of technologies that NASA believed it needed for single-stage-to-orbit reusable launch vehicles (SSTO RLVs), such as metallic thermal protection systems, composite cryogenic fuel tanks for liquid hydrogen, the aerospike engine, autonomous (uncrewed) flight control, rapid flight turn-around times through streamlined operations, and its lifting body aerodynamics. Failures of its 21-meter wingspan and multi-lobed, composite-material fuel tank during pressure testing ultimately led to the withdrawal of federal support for the program in early 2001. Lockheed Martin has conducted unrelated testing, and has had a single success after a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rocketdyne J-2
The J-2 is a liquid-fuel cryogenic rocket engine used on NASA's Saturn IB and Saturn V launch vehicles. Built in the U.S. by Rocketdyne, the J-2 burned cryogenic liquid hydrogen (LH2) and liquid oxygen (LOX) propellants, with each engine producing of thrust in vacuum. The engine's preliminary design dates back to recommendations of the 1959 Silverstein Committee. Rocketdyne won approval to develop the J-2 in June 1960 and the first flight, AS-201, occurred on 26 February 1966. The J-2 underwent several minor upgrades over its operational history to improve the engine's performance, with two major upgrade programs, the de Laval nozzle-type J-2S and aerospike-type J-2T, which were cancelled after the conclusion of the Apollo program. The engine produced a specific impulse (''I''sp) of in a vacuum (or at sea level) and had a mass of approximately . Five J-2 engines were used on the Saturn V's S-II second stage, and one J-2 was used on the S-IVB upper stage used on both the Satu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gas-generator Cycle
The gas-generator cycle is a power cycle of a pumped liquid bipropellant rocket engine. Part of the unburned propellant is burned in a gas generator (or preburner) and the resulting hot gas is used to power the propellant pumps before being exhausted overboard, and lost. Because of this loss, this type of engine is termed open cycle. Usage Gas-generator combustion engines include the following: * Vulcain, HM7B *Merlin *RS-68 *RS-27A *J-2X * F-1 *RD-107 * CE-20 * Rocket launch systems that use gas-generator combustion engines: *Ariane 5 *Falcon 9, Falcon Heavy *Delta IV *Saturn V *Soyuz * Geosynchronous Satellite Launch Vehicle III *Long March 3B, Long March 2F *Rocket Lab Neutron *Miura 5 See also * Combustion tap-off cycle * Expander cycle * Pressure-fed engine * Rocket engine A rocket engine uses stored rocket propellants as the reaction mass for forming a high-speed propulsive jet of fluid, usually high-temperature gas. Rocket engines are reaction engines, producin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aerospike Engine
The aerospike engine is a type of rocket engine that maintains its aerodynamic efficiency across a wide range of altitudes. It belongs to the class of altitude compensating nozzle engines. Aerospike engines have been studied for several years and are the baseline engines for many single-stage-to-orbit (SSTO) designs and were also a strong contender for the Space Shuttle main engine. However, no such engine is in commercial production, although some large-scale aerospikes are in testing phases. The terminology in the literature surrounding this subject is somewhat confusing—the term ''aerospike'' was originally used for a truncated plug nozzle#In rockets, plug nozzle with a very rough conical taper and some gas injection, forming an "air spike" to help make up for the absence of the plug tail. However, frequently, a full-length plug nozzle is now called an aerospike. Principles The purpose of any engine bell is to direct the exhaust of a rocket engine in one direction, generati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NASA Headquarters
NASA Headquarters, officially known as Mary W. Jackson NASA Headquarters or NASA HQ and formerly named Two Independence Square, is a low-rise office building in the two-building Independence Square complex at 300 E Street SW in Washington, D.C. The building houses NASA leadership who provide overall guidance and direction to the US government executive branch agency NASA, under the leadership of the NASA administrator. Ten field centers and a variety of installations around the country conduct the day-to-day work. NASA Headquarters is organized into four Mission Directorates: Aeronautics, Exploration Systems, Science, and Space Operations. The James E. Webb Memorial Auditorium, named for NASA's second administrator James E. Webb, hosts agency news conferences and NASA Social events. A lending library, the history office, archives, production facilities for NASA TV, and a NASA gift shop are also housed in the building. The building, which opened in 1992, was designed by Kohn Ped ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Institute Of Aeronautics And Astronautics
The American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics (AIAA) is a professional society for the field of aerospace engineering. The AIAA is the U.S. representative on the International Astronautical Federation and the International Council of the Aeronautical Sciences. In 2015, it had more than 30,000 members among aerospace professionals worldwide (a majority are American and/or live in the United States). History The AIAA was founded in 1963 from the merger of two earlier societies: the American Rocket Society (ARS), founded in 1930 as the American Interplanetary Society (AIS), and the Institute of the Aerospace Sciences (IAS), founded in 1932 as the Institute of the Aeronautical Sciences. Paul Johnston was the first executive director of the organization. Jim Harford took his seat after 18 months. The newly-formed structure gathered 47 technical committees and one broad technical publication, the ''AIAA Journal''. The ''AIAA Student Journal'' was also launched in 1963. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Encyclopedia Astronautica
The ''Encyclopedia Astronautica'' is a reference web site on space travel. A comprehensive catalog of vehicles, technology, astronauts, and flights, it includes information from most countries that have had an active rocket research program, from Robert Goddard to the NASA Space Shuttle and the Soviet Buran programme. Founded in 1994 and maintained for most of its existence by space enthusiast and author Mark Wade. He has been collecting such information for most of his life. Between 1996 and 2000 the site was hosted by ''Friends and Partners in Space''. The site is no longer updated or maintained and is now considered as partially unreliable. Although it contains a great deal of information, not all of it is correct. Reception and accolades The American Astronautical Society gave the site the Ordway Award for Sustained Excellence in Spaceflight History which "recognizes exceptional, sustained efforts to inform and educate on spaceflight and its history through one or more med ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RS-2200
The Rocketdyne RS-2200 was an experimental linear aerospike rocket engine developed by Rocketdyne for Lockheed Martin's VentureStar VentureStar was a single-stage-to-orbit reusable launch system proposed by Lockheed Martin and funded by the U.S. government. The goal was to replace the Space Shuttle by developing a re-usable spaceplane that could launch satellites into orbit a ... program. The program was ultimately cancelled in 2001 before any RS-2200 engines were assembled. XRS-2200 The XRS-2200 was a subscale testbed engine that was intended to be developed into the full-scale RS-2200. This engine, unlike its full-scale counterpart, made it to the test stand and accumulated approximately 1,600 seconds of hot-fire testing. References {{Include-NASA Rocketdyne engines Rocket engines of the United States Rocketdyne Rocket engines ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
VentureStar
VentureStar was a single-stage-to-orbit reusable launch system proposed by Lockheed Martin and funded by the U.S. government. The goal was to replace the Space Shuttle by developing a re-usable spaceplane that could launch satellites into orbit at a fraction of the cost. While the requirement was for an uncrewed launcher, it was expected to carry passengers as cargo. The VentureStar would have had a wingspan of , a length of , and would have weighed roughly 1000 t (2.2 million lb). VentureStar was intended to be a commercial single-stage-to-orbit vehicle that would be launched vertically, but return to Earth as an airplane. Flights would have been leased to NASA as needed. After failures with the X-33 subscale technology demonstrator test vehicle, funding was cancelled in 2001. VentureStar was essentially a bigger version of the X-33 but was not produced. The X-33 had ongoing problems meeting performance requirements for the carbonfibre hydrogen fuel tank. There were a number of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agency of the US federal government responsible for the civil space program, aeronautics research, and space research. NASA was established in 1958, succeeding the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA), to give the U.S. space development effort a distinctly civilian orientation, emphasizing peaceful applications in space science. NASA has since led most American space exploration, including Project Mercury, Project Gemini, the 1968-1972 Apollo Moon landing missions, the Skylab space station, and the Space Shuttle. NASA supports the International Space Station and oversees the development of the Orion spacecraft and the Space Launch System for the crewed lunar Artemis program, Commercial Crew spacecraft, and the planned Lunar Gateway space station. The agency is also responsible for the Launch Services Program, which provides oversight of launch operations and countdown management f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rocketdyne Engines
Rocketdyne was an American rocket engine design and production company headquartered in Canoga Park, in the western San Fernando Valley of suburban Los Angeles, in southern California. The Rocketdyne Division was founded by North American Aviation (NAA) in 1955, and was later part of Rockwell International (1967–1996) and Boeing (1996–2005). In 2005, the Rocketdyne Division was sold to United Technologies Corporation, becoming Pratt & Whitney Rocketdyne as part of Pratt & Whitney. In 2013, Pratt & Whitney Rocketdyne was sold to GenCorp, which merged it with Aerojet to form Aerojet Rocketdyne.Marjorie Censer(18 Dec 2022) L3Harris moves to acquire Aerojet Rocketdynefor $4.7 billion, after Lockheed Martin ended its attempt for Rocketdyne in Feb 2022 History After World War II, North American Aviation (NAA) was contracted by the Defense Department to study the German V-2 missile and adapt its engine to Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE) measurements and U.S. construction de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |