|
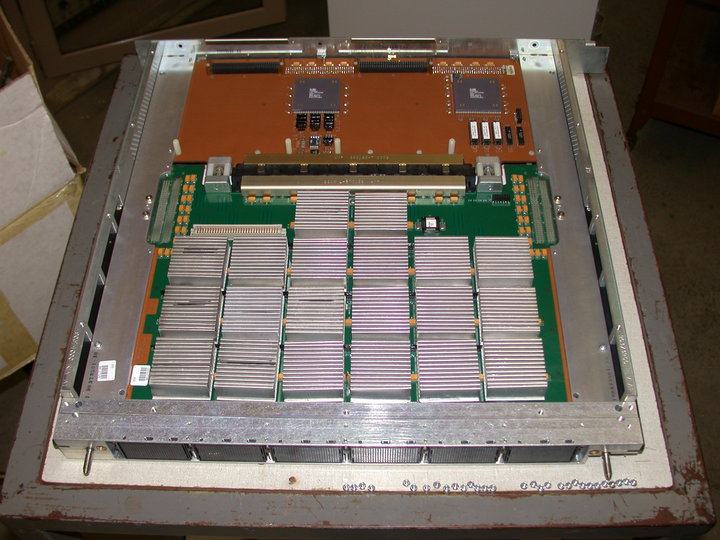
Rigel (microprocessor)
Rigel was a microprocessor chip set developed and fabricated by Digital Equipment Corporation (DEC) that implemented the VAX instruction set architecture (ISA). It was introduced on 11 July 1989 with the introduction of the VAX 6000 Model 400, the first system to feature the chip set. Rigel was also used in the VAX 4000 Model 300 and VAXstation 3100 Model 76. Production Rigel CPUs were rated at 35 to 43 MHz. The Rigel chipset consisted of several devices: *REX520 central processing unit (also known as the DC520 or "P-chip") *DC523 floating-point unit (codenamed ''KIWI'' or "F-chip" during development) *DC592 cache controller (codenamed ''COW'' or "C-chip" during development) *DC521 clock chip In addition, two further devices implemented the VAX vector processor option; these comprised the DC555 Vector Register set chip (''VERSE'') and the DC556 Vector Data Path chip (''FAVOR''). Support chips for Rigel-based systems included the RSSC (Rigel System Support Chip) and ''Ghi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vector Processor
In computing, a vector processor or array processor is a central processing unit (CPU) that implements an instruction set where its instructions are designed to operate efficiently and effectively on large one-dimensional arrays of data called ''vectors''. This is in contrast to scalar processors, whose instructions operate on single data items only, and in contrast to some of those same scalar processors having additional single instruction, multiple data (SIMD) or SWAR Arithmetic Units. Vector processors can greatly improve performance on certain workloads, notably numerical simulation and similar tasks. Vector processing techniques also operate in video-game console hardware and in graphics accelerators. Vector machines appeared in the early 1970s and dominated supercomputer design through the 1970s into the 1990s, notably the various Cray platforms. The rapid fall in the price-to-performance ratio of conventional microprocessor designs led to a decline in vector supercom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MicroVAX
The MicroVAX is a discontinued family of low-cost minicomputers developed and manufactured by Digital Equipment Corporation (DEC). The first model, the MicroVAX I, was introduced in 1983.(announced October 1983) They used processors that implemented the VAX instruction set architecture (ISA) and were succeeded by the VAX 4000. Many members of the MicroVAX family had corresponding VAXstation variants, which primarily differ by the addition of graphics hardware. The MicroVAX family supports Digital's VMS and ULTRIX operating systems. Prior to VMS V5.0, MicroVAX hardware required a dedicated version of VMS named MicroVMS. MicroVAX I The MicroVAX I, code named "''Seahorse''", introduced in October 1984, was one of DEC's first VAX computers to use very-large-scale integration (VLSI) technology. The KA610 CPU module (also known as the KD32) contained two custom chips which implemented the ALU and FPU while TTL chips were used for everything else. Two variants of the floating point ch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Write-back
In computing, a cache ( ) is a hardware or software component that stores data so that future requests for that data can be served faster; the data stored in a cache might be the result of an earlier computation or a copy of data stored elsewhere. A ''cache hit'' occurs when the requested data can be found in a cache, while a ''cache miss'' occurs when it cannot. Cache hits are served by reading data from the cache, which is faster than recomputing a result or reading from a slower data store; thus, the more requests that can be served from the cache, the faster the system performs. To be cost-effective and to enable efficient use of data, caches must be relatively small. Nevertheless, caches have proven themselves in many areas of computing, because typical computer applications access data with a high degree of locality of reference. Such access patterns exhibit temporal locality, where data is requested that has been recently requested already, and spatial locality, where d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aluminium Interconnect
In integrated circuits (ICs), interconnects are structures that connect two or more circuit elements (such as transistors) together electrically. The design and layout of interconnects on an IC is vital to its proper function, performance, power efficiency, reliability, and fabrication yield. The material interconnects are made from depends on many factors. Chemical and mechanical compatibility with the semiconductor substrate and the dielectric between the levels of interconnect is necessary, otherwise barrier layers are needed. Suitability for fabrication is also required; some chemistries and processes prevent the integration of materials and unit processes into a larger technology (recipe) for IC fabrication. In fabrication, interconnects are formed during the back-end-of-line after the fabrication of the transistors on the substrate. Interconnects are classified as ''local'' or ''global'' interconnects depending on the signal propagation distance it is able to support. The wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CMOS
Complementary metal–oxide–semiconductor (CMOS, pronounced "sea-moss", ) is a type of metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistor (MOSFET) fabrication process that uses complementary and symmetrical pairs of p-type and n-type MOSFETs for logic functions. CMOS technology is used for constructing integrated circuit (IC) chips, including microprocessors, microcontrollers, memory chips (including CMOS BIOS), and other digital logic circuits. CMOS technology is also used for analog circuits such as image sensors (CMOS sensors), data converters, RF circuits (RF CMOS), and highly integrated transceivers for many types of communication. The CMOS process was originally conceived by Frank Wanlass at Fairchild Semiconductor and presented by Wanlass and Chih-Tang Sah at the International Solid-State Circuits Conference in 1963. Wanlass later filed US patent 3,356,858 for CMOS circuitry and it was granted in 1967. commercialized the technology with the trademark "COS-MO ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Static Random Access Memory
Static random-access memory (static RAM or SRAM) is a type of random-access memory (RAM) that uses latching circuitry (flip-flop) to store each bit. SRAM is volatile memory; data is lost when power is removed. The term ''static'' differentiates SRAM from DRAM (''dynamic'' random-access memory) — SRAM will hold its data permanently in the presence of power, while data in DRAM decays in seconds and thus must be periodically refreshed. SRAM is faster than DRAM but it is more expensive in terms of silicon area and cost; it is typically used for the cache and internal registers of a CPU while DRAM is used for a computer's main memory. History Semiconductor bipolar SRAM was invented in 1963 by Robert Norman at Fairchild Semiconductor. MOS SRAM was invented in 1964 by John Schmidt at Fairchild Semiconductor. It was a 64-bit MOS p-channel SRAM. The SRAM was the main driver behind any new CMOS-based technology fabrication process since 1959 when CMOS was invented. In 1965 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
VAX 8000
The VAX 8000 is a discontinued family of superminicomputers developed and manufactured by Digital Equipment Corporation (DEC) using processors implementing the VAX instruction set architecture (ISA). The 8000 series was introduced in October 1984 with the 8600, taking over the high-end of the VAX lineup. Originally known as the 11/790, it offers performance roughly double that of the earlier 11/780. It was succeeded by the 8650 (formerly the 11/795) in December 1985. January 1986 saw the introduction of the 8200 and 8300 families in the mid-range. The 8800 replaced the 8600s at the high end in 1987, with the 8700 and 8500 being lower-performance versions of these systems. DEC also offered various clusters of these machines with a variety of model numbers. As with other VAX systems, they were sold with either the VMS or Ultrix operating systems. It was intended that the 8800 was to have been replaced by the VAX 9000 on the high end, but the VAX 6000, originally a mid-range model ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Floating-point Unit
In computing, floating-point arithmetic (FP) is arithmetic that represents real numbers approximately, using an integer with a fixed precision, called the significand, scaled by an integer exponent of a fixed base. For example, 12.345 can be represented as a base-ten floating-point number: 12.345 = \underbrace_\text \times \underbrace_\text\!\!\!\!\!\!^ In practice, most floating-point systems use base two, though base ten (decimal floating point) is also common. The term ''floating point'' refers to the fact that the number's radix point can "float" anywhere to the left, right, or between the significant digits of the number. This position is indicated by the exponent, so floating point can be considered a form of scientific notation. A floating-point system can be used to represent, with a fixed number of digits, numbers of very different orders of magnitude — such as the number of meters between galaxies or between protons in an atom. For this reason, floating-poi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Central Processing Unit
A central processing unit (CPU), also called a central processor, main processor or just processor, is the electronic circuitry that executes instructions comprising a computer program. The CPU performs basic arithmetic, logic, controlling, and input/output (I/O) operations specified by the instructions in the program. This contrasts with external components such as main memory and I/O circuitry, and specialized processors such as graphics processing units (GPUs). The form, design, and implementation of CPUs have changed over time, but their fundamental operation remains almost unchanged. Principal components of a CPU include the arithmetic–logic unit (ALU) that performs arithmetic and logic operations, processor registers that supply operands to the ALU and store the results of ALU operations, and a control unit that orchestrates the fetching (from memory), decoding and execution (of instructions) by directing the coordinated operations of the ALU, registers and other co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |