|
Richard Bulkeley (governor)
Richard Bulkeley (26 December 1717 – 7 December 1800) was an influential administrator in Nova Scotia from 1749 to 1800. Historian Phyllis Blakeley writes that Bulkeley, "assisted 13 governors and lieutenant governors from Cornwallis to Wentworth. In half a century of service he took part in the founding of Halifax, the immigration of New Englanders and loyalists, and the prosperity of the French revolutionary wars." During his lifetime, known for hosting dignitaries and grand parties, he was known as "the Father of the Province." When he died, he was the last surviving settler who arrived with Cornwallis. Career During Father Le Loutre's War he was an Aide-de-camp to three consecutive Governors of Nova Scotia: Cornwallis, Hobson and Lawrence. During the French and Indian War he also served on the Nova Scotia Council (1759-1800). Historian Blakney writes that Bulkeley was "noted for his lavish hospitality, entertaining and many other military men during the Seven Year ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dublin
Dublin (; , or ) is the capital and largest city of Republic of Ireland, Ireland. On a bay at the mouth of the River Liffey, it is in the Provinces of Ireland, province of Leinster, bordered on the south by the Dublin Mountains, a part of the Wicklow Mountains range. At the 2016 census of Ireland, 2016 census it had a population of 1,173,179, while the preliminary results of the 2022 census of Ireland, 2022 census recorded that County Dublin as a whole had a population of 1,450,701, and that the population of the Greater Dublin Area was over 2 million, or roughly 40% of the Republic of Ireland's total population. A settlement was established in the area by the Gaels during or before the 7th century, followed by the Vikings. As the Kings of Dublin, Kingdom of Dublin grew, it became Ireland's principal settlement by the 12th century Anglo-Norman invasion of Ireland. The city expanded rapidly from the 17th century and was briefly the second largest in the British Empire and sixt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Pontack (Halifax)
The Great Pontack (also known as Great Pontac, Pontack Inn, Pontiac Inn, Pontack Hotel, Pontack House, Pontac Tavern) was a large three-story building, erected by the Hon. John Butler (and run by John Willis ), previous to 1754, at the corner of Duke and Water Streets in Halifax, Nova Scotia. (Present-day sites of the Waterside Centre and the Pontac House at the Historic Properties (Halifax).) It was named after the famous Pontack Club in London. The first resident professional company in Canada was The American Company of Comedians, believed to have performed at The Great Pontack, Halifax, in the summer and fall of 1768. (A lively garrison and amateur theatrical tradition emerged in the Maritimes, among these was a romantic comedy called Acadius: or, Love in a Calm, the first recorded English Canadian play, performed in Halifax in 1774.) The most famous event to take place at the establishment was on May 24, 1758, when James Wolfe, who was headquartered on Hollis Street, Halif ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saint Patrick's Day
Saint Patrick's Day, or the Feast of Saint Patrick ( ga, Lá Fhéile Pádraig, lit=the Day of the Festival of Patrick), is a cultural and religious celebration held on 17 March, the traditional death date of Saint Patrick (), the foremost patron saint of Ireland. Saint Patrick's Day was made an official Christian feast day in the early 17th century and is observed by the Catholic Church, the Anglican Communion (especially the Church of Ireland), the Eastern Orthodox Church, and the Lutheran Church. The day commemorates Saint Patrick and the arrival of Christianity in Ireland, and celebrates the heritage and culture of the Irish in general. Celebrations generally involve public parades and festivals, céilithe, and the wearing of green attire or shamrocks. Christians who belong to liturgical denominations also attend church services and historically the Lenten restrictions on eating and drinking alcohol were lifted for the day, which has encouraged and propagated the holida ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
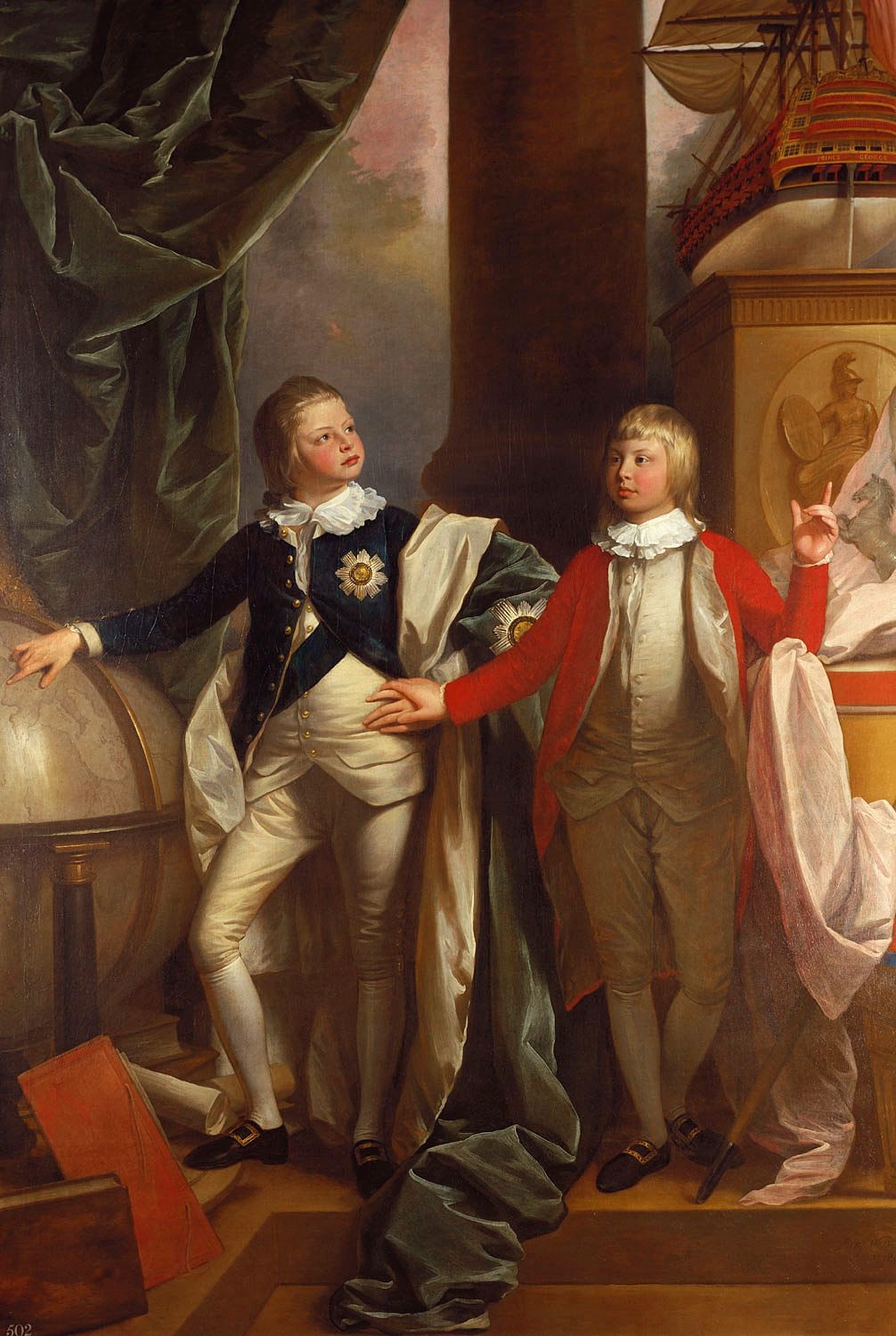
Charlotte Of Mecklenburg-Strelitz
Charlotte of Mecklenburg-Strelitz (Sophia Charlotte; 19 May 1744 – 17 November 1818) was Queen of Great Britain and of Ireland as the wife of King George III from their marriage on 8 September 1761 until the union of the two kingdoms on 1 January 1801, after which she was Queen of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland until her death in 1818. As George's wife, she was also Electress of Hanover until becoming Queen of Hanover on 12 October 1814, when the electorate became a kingdom. Charlotte was Britain's longest-serving queen consort. Charlotte was born into the royal family of Mecklenburg-Strelitz, a duchy in northern Germany. In 1760, the young and unmarried George III inherited the British throne. As Charlotte was a minor German princess with no interest in politics, George considered her a suitable consort, and they married in 1761. The marriage lasted 57 years, and produced 15 children, 13 of whom survived to adulthood. They included two fu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Year's Day
New Year's Day is a festival observed in most of the world on 1 January, the first day of the year in the modern Gregorian calendar. 1 January is also New Year's Day on the Julian calendar, but this is not the same day as the Gregorian one. Whilst most solar calendars (like the Gregorian and Julian) begin the year regularly at or near the northern winter solstice, cultures that observe a lunisolar or lunar calendar celebrate their New Year (such as the Chinese New Year and the Islamic New Year) at less fixed points relative to the solar year. In pre-Christian Rome under the Julian calendar, the day was dedicated to Janus, god of gateways and beginnings, for whom January is also named. From Roman times until the middle of the 18th century, the new year was celebrated at various stages and in various parts of Christian Europe on 25 December, on 1 March, on 25 March and on the movable feast of Easter. In the present day, with most countries now using the Gregorian calendar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Queen Victoria
Victoria (Alexandrina Victoria; 24 May 1819 – 22 January 1901) was Queen of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland from 20 June 1837 until Death and state funeral of Queen Victoria, her death in 1901. Her reign of 63 years and 216 days was longer than that of List of monarchs in Britain by length of reign, any previous British monarch and is known as the Victorian era. It was a period of industrial, political, scientific, and military change within the United Kingdom, and was marked by a great expansion of the British Empire. In 1876, the British Parliament voted to grant her the additional title of Empress of India. Victoria was the daughter of Prince Edward, Duke of Kent and Strathearn (the fourth son of King George III), and Princess Victoria of Saxe-Coburg-Saalfeld. After the deaths of her father and grandfather in 1820, she was Kensington System, raised under close supervision by her mother and her comptroller, John Conroy. She inherited the throne aged 18 af ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prince Edward, Duke Of Kent And Strathearn
Prince Edward, Duke of Kent and Strathearn, (Edward Augustus; 2 November 1767 – 23 January 1820) was the fourth son and fifth child of King George III. His only legitimate child became Queen Victoria. Prince Edward was created Duke of Kent and Strathearn and Earl of Dublin on 23 April 1799''Whitehall, 23 April 1799.''The King has been pleased to grant to His Most Dearly-Beloved Son Prince Edward, and to the Heirs Male of His Royal Highness's Body lawfully begotten, the Dignities of Duke of the Kingdom of Great Britain, and of Earl of the Kingdom of Ireland, by the Names, Styles, and Titles of Duke of Kent, and of Strathern, in the Kingdom of Great Britain, and of Earl of Dublin, in the Kingdom of Ireland. and, a few weeks later, appointed a General and commander-in-chief of British forces in the Maritime Provinces of North America. On 23 March 1802, he was appointed Governor of Gibraltar and nominally retained that post until his death. The Duke was appointed Field-Marshal of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William IV Of The United Kingdom
William IV (William Henry; 21 August 1765 – 20 June 1837) was King of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland and King of Hanover from 26 June 1830 until his death in 1837. The third son of George III, William succeeded his elder brother George IV, becoming the last king and penultimate monarch of Britain's House of Hanover. William served in the Royal Navy in his youth, spending time in North America and the Caribbean, and was later nicknamed the "Sailor King". In 1789, he was created Duke of Clarence and St Andrews. In 1827, he was appointed Britain's first Lord High Admiral since 1709. As his two elder brothers died without leaving legitimate issue, he inherited the throne when he was 64 years old. His reign saw several reforms: the Poor Law was updated, child labour restricted, slavery abolished in nearly all of the British Empire, and the electoral system refashioned by the Reform Acts of 1832. Although William did not engage in politics as m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siege Of Louisbourg (1758)
The siege of Louisbourg was a pivotal operation of the Seven Years' War (known in the United States as the French and Indian War) in 1758 that ended the French colonial era in Atlantic Canada and led to the subsequent British campaign to capture Quebec in 1759 and the remainder of French North America the following year. Background The British government realized that with the Fortress of Louisbourg under French control, the Royal Navy could not sail up the St. Lawrence River unmolested for an attack on Quebec. After an expedition against Louisbourg in 1757 led by Lord Loudon was turned back due to a strong French naval deployment, the British under the leadership of William Pitt resolved to try again with new commanders. Pitt assigned the task of capturing the fortress to Major General Jeffery Amherst. Amherst's brigadiers were Charles Lawrence, James Wolfe and Edward Whitmore, and command of naval operations was assigned to Admiral Edward Boscawen. The chief engineer w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Carleton
The Carleton (also known as the Carleton House and Carleton Hotel) is a building on Argyle Street in Halifax, Nova Scotia, built in 1760 as the home of Richard Bulkeley. Apart from two churches, Bulkeley's home is the oldest building in Halifax, Nova Scotia (1760). It was reported to have been made from the ruins of Fortress Louisbourg. Since 1786 his residence has been known as "The Carleton". History Bulkeley built his new home on Argyle Street on the land of Captain James Bannerman, who died during Father Le Loutre's War in the Attack at Jeddore. He also had installed the black marble mantel from the Governor's house in the King's Bastion at Louisbourg. He is also reported to have brought the stone from the ruins of Louisbourg (1758) to build the house. At his new home in the 1780s, Bulkeley regularly entertained the future King William IV (abolished slavery in British Empire; had an affair with Governor Wentworth's wife Francis) as well as Prince Edward (father of Queen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Cobbett
William Cobbett (9 March 1763 – 18 June 1835) was an English pamphleteer, journalist, politician, and farmer born in Farnham, Surrey. He was one of an agrarian faction seeking to reform Parliament, abolish "rotten boroughs", restrain foreign activity, and raise wages, with the goal of easing poverty among farm labourers and small land holders. Cobbett backed lower taxes, saving, reversing commons enclosures and resisting the 1821 gold standard. He opposed borough-mongers, sinecurists, bureaucratic "tax-eaters" and stockbrokers. His radicalism furthered the Reform Act 1832 and gained him one of two newly created seats in Parliament for the borough of Oldham. His polemics range from political reform to religion, including Catholic emancipation. His best known book is ''Rural Rides'' (1830, in print). He argued against Malthusianism, saying economic betterment could support global population growth. Early life (1763–1791) William Cobbett was born in Farnham, Surrey, on 9 Mar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
_Bulkeley%2C_Old_Burying_Ground%2C_Halifax%2C_Nova_Scotia.jpg)





GeorgeDawe.jpg)


