|
Reuben Thwaites
Reuben Gold Thwaites ( May 15, 1853 – October 22, 1913) was an American librarian and historical writer. Biography Thwaites was born in 1853 in Dorchester, Massachusetts. His parents were William George and Sarah Bibbs Thwaites, who had moved to Dorchester in 1850 from Yorkshire, England. The family moved to Omro, Wisconsin, in 1866, where Reuben worked on the farm, studied college-level coursework and reported for the Oshkosh ''Times''. In 1874–1875 he studied English literature, economic history and international law at Yale University. Thwaites studied at Yale as a special student, and beyond that never formally studied at the collegiate level, although later in his life he was awarded an LLD from the University of Wisconsin. From 1876 to 1886, Thwaites was managing editor of the ''Wisconsin State Journal'', at Madison. In 1885 he became assistant corresponding secretary of the State Historical Society of Wisconsin, and when Lyman Draper retired as secretary 1887, Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Presidents Of The American Library Association
The American Library Association, founded in 1876 and chartered in 1879, is the largest professional organization for librarians in the United States. The headquarters of the American Library Association The American Library Association (ALA) is a nonprofit organization based in the United States that promotes libraries and library education internationally. It is the oldest and largest library association in the world, with 49,727 members a ... is in Chicago, Illinois. Table of ALA presidents References External linksAla.org Handbook {{ALA Presidents Presidents of the American Library Association [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles Floyd (explorer)
Charles Floyd (1782 – August 20, 1804) was an American explorer, a non-commissioned officer in the U.S. Army, and the quartermaster of the Lewis and Clark Expedition. A native of Kentucky, he was a son of Robert Clark Floyd, a nephew of James John Floyd, a cousin of Virginia governor John Floyd, and possibly a relative of William Clark. He was one of the first men to join the expedition, and the only member of the Corps of Discovery to die during the expedition. Lewis and Clark Expedition While exploring the Louisiana Purchase with Lewis and Clark, he took ill at the end of July 1804. On July 31, Floyd wrote in his diary, "I am very sick and have been for sometime but have recovered my health again." However, this apparent recovery was soon followed by a severe turn for the worse. William Clark described Floyd's death as one "with a great deal of composure" and that before Floyd died he said to Clark, "I am going away. Please write me a letter." A funeral was held and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lyman Copeland Draper
Lyman Copeland Draper (September 4, 1815August 26, 1891) was a librarian and historian who served as secretary for the State Historical Society of Wisconsin at Madison, Wisconsin. Draper also served as Superintendent of Public Instruction of Wisconsin from 1858 to 1860. Biography Lyman Copeland Draper was born on September 4, 1815, in Evans, New York, a descendant of early Massachusetts settler James Draper (1618–1694). Growing up he often heard about the exploits of his grandfathers and father in the Revolution and the War of 1812. He developed a keen interest in the history of those times. Starting in the 1838, Lyman Draper corresponded with people who were early settlers in the Trans-Allegheny region during the second half of the 18th century. He also traveled extensively in the region to gain a better feel for the territory. Draper's professed purpose was to shed light on the era and gain knowledge before it was completely forgotten. He planned to write a series of biograph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexander Scott Withers
Alexander Scott Withers (12 October 1792, near Warrenton, Virginia – 23 January 1865, near Parkersburg, West Virginia) was a Virginia slave owner, lawyer, planter, magistrate, teacher and delegate to the First Wheeling Convention (1861) establishing the state of West Virginia. He is celebrated as the author of ''Chronicles of Border Warfare'' (1831), a history of (and important primary source on) the early white settlement of western Virginia and consequent conflicts with American Indians. He sold two of the children he fathered with a slave to slave traders further South. Biography Youth and education Withers was a son of Enoch Keene Withers and Jennet Chinn Withers and was born at the family home, an estate known as "Green Meadows" about 6 miles from Warrenton, Fauquier County, Virginia. His mother was a second cousin of Sir Walter Scott. He was educated at home and in private schools, later attending Washington College and finally learning law at William and Mary, desp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geomorphologist
Geomorphology (from Ancient Greek: , ', "earth"; , ', "form"; and , ', "study") is the scientific study of the origin and evolution of topographic and bathymetric features created by physical, chemical or biological processes operating at or near Earth's surface. Geomorphologists seek to understand why landscapes look the way they do, to understand landform and terrain history and dynamics and to predict changes through a combination of field observations, physical experiments and numerical modeling. Geomorphologists work within disciplines such as physical geography, geology, geodesy, engineering geology, archaeology, climatology, and geotechnical engineering. This broad base of interests contributes to many research styles and interests within the field. Overview Earth's surface is modified by a combination of surface processes that shape landscapes, and geologic processes that cause tectonic uplift and subsidence, and shape the coastal geography. Surface processes com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glaciology
Glaciology (; ) is the scientific study of glaciers, or more generally ice and natural phenomena that involve ice. Glaciology is an interdisciplinary Earth science that integrates geophysics, geology, physical geography, geomorphology, climatology, meteorology, hydrology, biology, and ecology. The impact of glaciers on people includes the fields of human geography and anthropology. The discoveries of water ice on the Moon, Mars, Europa and Pluto add an extraterrestrial component to the field, which is referred to as "astroglaciology". Overview A glacier is an extended mass of ice formed from snow falling and accumulating over a long period of time; glaciers move very slowly, either descending from high mountains, as in valley glaciers, or moving outward from centers of accumulation, as in continental glaciers. Areas of study within glaciology include glacial history and the reconstruction of past glaciation. A glaciologist is a person who studies glaciers. A glac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fredrik T
Fredrik is a masculine Germanic given name derived from the German name '' Friedrich'' or Friederich, from the Old High German ''fridu'' meaning "peace" and ''rîhhi'' meaning "ruler" or "power". It is the common form of Frederick in Norway, Finland and Sweden. The name means "peaceful ruler" The most common variant spelling of this name is Frederik which is used in Denmark, although the English spelling Frederick is more common than either. Fredrik replaced the Anglo-Saxon name Freodheric, and has been a rare first name in England since this time. In Sweden, Fredrik first fell into usage in the 14th century, and became increasingly common after the 18th century. It is the 19th most popular male name in Sweden and the 41st most popular in Norway. |
Donald Dean Jackson
Donald Dean Jackson (June 10, 1919 – December 9, 1987) was an American journalist, historian, and professor of American history involving early America and the Civil War mostly. He was the founding editor of the University of Virginia's George Washington Papers project. Apart from his editing and publishing of those papers, Jackson was also noted for his consulting and editorship in the Lewis and Clark project, gathering and compiling related manuscripts into one comprehensive study. Jackson was also considered an expert historian of the American West and its exploration and authored many books and journals in that area of study. Life Early life Jackson was born on June 10, 1919, in Glenwood, Iowa. He earned a Bachelor of Science from Iowa State University in 1942, with a degree in technical journalism, after which he became a reporter for the ''Des Moines Register'', and then a radio news editor for WOI in Ames, Iowa. In 1946 he earned his master's degree in English from th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ohio River
The Ohio River is a long river in the United States. It is located at the boundary of the Midwestern and Southern United States, flowing southwesterly from western Pennsylvania to its mouth on the Mississippi River at the southern tip of Illinois. It is the third largest river by discharge volume in the United States and the largest tributary by volume of the north-south flowing Mississippi River that divides the eastern from western United States. It is also the 6th oldest river on the North American continent. The river flows through or along the border of six states, and its drainage basin includes parts of 14 states. Through its largest tributary, the Tennessee River, the basin includes several states of the southeastern U.S. It is the source of drinking water for five million people. The lower Ohio River just below Louisville is obstructed by rapids known as the Falls of the Ohio where the elevation falls in restricting larger commercial navigation, although i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rock River (Mississippi River)
The Rock River is a tributary of the Mississippi River, approximately long,U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline dataThe National Map accessed May 13, 2011 in the U.S. states of Wisconsin and Illinois. The river was known as the Sinnissippi to Sauk and Fox Indians; the name means "rocky waters". The river, which has a notable higher western bank, begins with three separate branches which flow into the Horicon Marsh. The northernmost branch, the West Branch, begins just to the west of the village of Brandon in Fond du Lac County, Wisconsin and flows east and then south to Horicon Marsh. The South Branch rises north of Fox Lake in Dodge County and flows east through Waupun to the marsh. The East Branch rises southeast of Allenton in Washington County just west of the Niagara Escarpment, and flows north and west through Theresa to the marsh. Leaving the marsh, it meanders southward to the Illinois border, ending about 300 miles later at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fox River (Wisconsin)
The Fox River is a river in eastern Wisconsin in the Great Lakes region of the United States. It is the principal tributary of the Bay of Green Bay, and via the Bay, the largest tributary of Lake Michigan. The well-known city of Green Bay, one of the first European settlements in North America, is on the river at its mouth on lower Green Bay. Hydrographers divide the Fox into two distinct sections, the Upper Fox River, flowing from its headwaters in south-central Wisconsin northeasterly into Lake Winnebago, and the Lower Fox River, flowing from Lake Winnebago northeasterly to lower Green Bay. Together, the two sections give the Fox River a length of .U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline dataThe National Map, accessed December 19, 2011 Counting the distance through Lake Winnebago gives a total of . The Fox River (Green Bay tributary) should not be confused with the Fox River (Illinois River tributary) which also flows through Wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
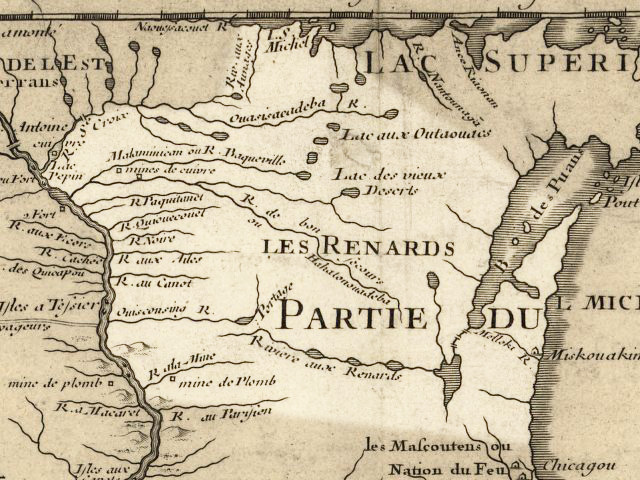
Wisconsin River
The Wisconsin River is a tributary of the Mississippi River in the U.S. state of Wisconsin. At approximately 430 miles (692 km) long, it is the state's longest river. The river's name, first recorded in 1673 by Jacques Marquette as "Meskousing", is rooted in the Algonquian languages used by the area's American Indian tribes, but its original meaning is obscure. French explorers who followed in the wake of Marquette later modified the name to "Ouisconsin", and so it appears on Guillaume de L'Isle's map (Paris, 1718). This was simplified to "Wisconsin" in the early 19th century before being applied to Wisconsin Territory and finally the state of Wisconsin. The Wisconsin River originates in the forests of the North Woods Lake District of northern Wisconsin, in Lac Vieux Desert near the border of the Upper Peninsula of Michigan. It flows south across the glacial plain of central Wisconsin, passing through Wausau, Stevens Point, and Wisconsin Rapids. In southern Wisconsi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |