|
Relaxed Intersection
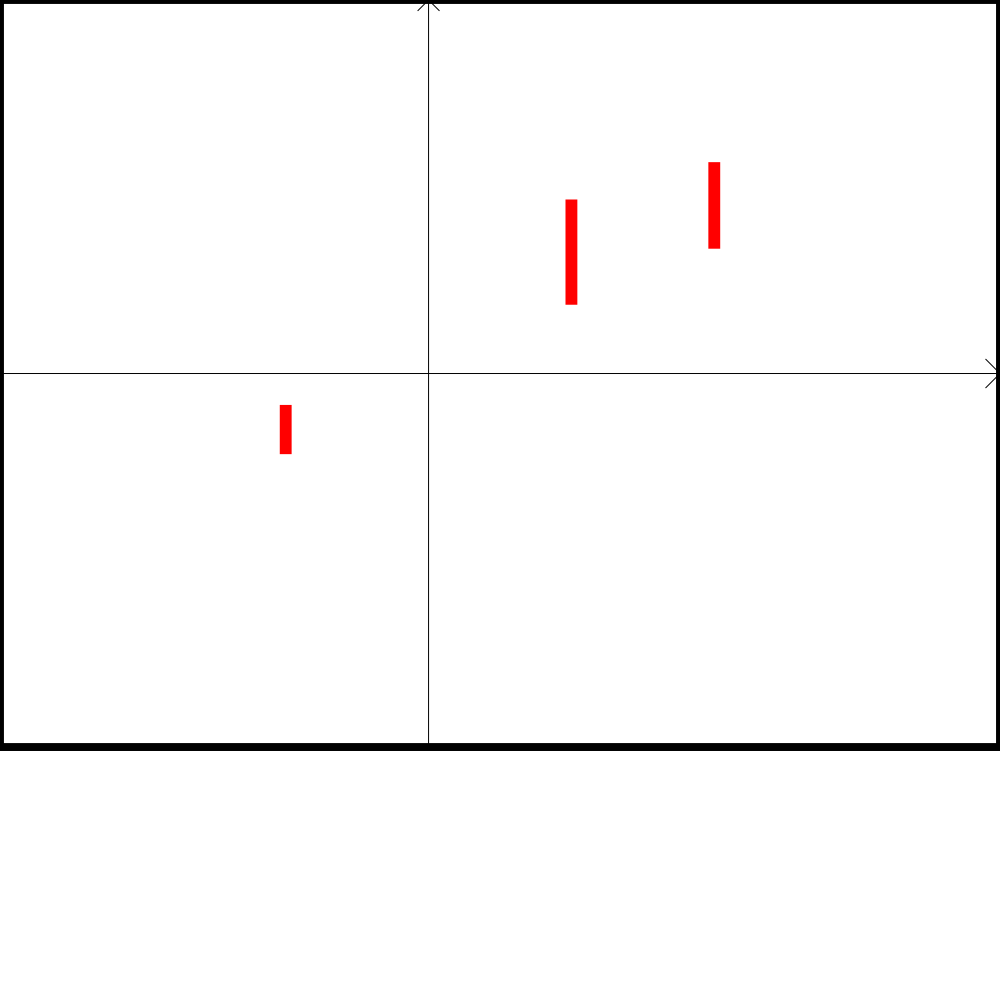
The ''relaxed intersection'' of ''m'' sets corresponds to the classical intersection between sets except that it is allowed to relax few sets in order to avoid an empty intersection. This notion can be used to solve Constraints Satisfaction Problems that are inconsistent by relaxing a small number of constraints. When a bounded-error approach is considered for parameter estimation, the relaxed intersection makes it possible to be robust with respect to some outliers. Definition The ''q''-relaxed intersection of the ''m'' subsets X_,\dots ,X_ of R^, denoted by X^=\bigcap^X_ is the set of all x \in R^ which belong to all X_ 's, except q at most. This definition is illustrated by Figure 1. Define \lambda (x) =\text \left\. We have X^=\lambda ^( -q,m . Characterizing the q-relaxed intersection is a thus a set inversion problem. Example Consider 8 intervals: X_= ,4 X_=\ ,4 X_= ,7 X_= ,9 X_= ,4 X_= ,7 We have X^ = \emptyset, X^= ,4 X^= ,4 X^ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Constraint Satisfaction Problem
Constraint satisfaction problems (CSPs) are mathematical questions defined as a set of objects whose state must satisfy a number of constraints or limitations. CSPs represent the entities in a problem as a homogeneous collection of finite constraints over variables, which is solved by constraint satisfaction methods. CSPs are the subject of research in both artificial intelligence and operations research, since the regularity in their formulation provides a common basis to analyze and solve problems of many seemingly unrelated families. CSPs often exhibit high complexity, requiring a combination of heuristics and combinatorial search methods to be solved in a reasonable time. Constraint programming (CP) is the field of research that specifically focuses on tackling these kinds of problems. Additionally, Boolean satisfiability problem (SAT), the satisfiability modulo theories (SMT), mixed integer programming (MIP) and answer set programming (ASP) are all fields of research focusin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maximum Satisfiability Problem
In computational complexity theory, the maximum satisfiability problem (MAX-SAT) is the problem of determining the maximum number of clauses, of a given Boolean formula in conjunctive normal form, that can be made true by an assignment of truth values to the variables of the formula. It is a generalization of the Boolean satisfiability problem, which asks whether there exists a truth assignment that makes all clauses true. Example The conjunctive normal form formula : (x_0\lor x_1)\land(x_0\lor\lnot x_1)\land(\lnot x_0\lor x_1)\land(\lnot x_0\lor\lnot x_1) is not satisfiable: no matter which truth values are assigned to its two variables, at least one of its four clauses will be false. However, it is possible to assign truth values in such a way as to make three out of four clauses true; indeed, every truth assignment will do this. Therefore, if this formula is given as an instance of the MAX-SAT problem, the solution to the problem is the number three. Hardness The MAX-SAT problem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Set Estimation
In statistics, a random vector ''x'' is classically represented by a probability density function. In a set-membership approach or set estimation, ''x'' is represented by a set ''X'' to which ''x'' is assumed to belong. This means that the support of the probability distribution function of ''x'' is included inside ''X''. On the one hand, representing random vectors by sets makes it possible to provide fewer assumptions on the random variables (such as independence) and dealing with nonlinearities is easier. On the other hand, a probability distribution function provides a more accurate information than a set enclosing its support. Set-membership estimation Set membership estimation (or ''set estimation'' for short) is an estimation approach which considers that measurements are represented by a set ''Y'' (most of the time a box of R''m'', where ''m'' is the number of measurements) of the measurement space. If ''p'' is the parameter vector and ''f'' is the model function, then t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parameter Estimation
Estimation theory is a branch of statistics that deals with estimating the values of parameters based on measured empirical data that has a random component. The parameters describe an underlying physical setting in such a way that their value affects the distribution of the measured data. An ''estimator'' attempts to approximate the unknown parameters using the measurements. In estimation theory, two approaches are generally considered: * The probabilistic approach (described in this article) assumes that the measured data is random with probability distribution dependent on the parameters of interest * The set-membership approach assumes that the measured data vector belongs to a set which depends on the parameter vector. Examples For example, it is desired to estimate the proportion of a population of voters who will vote for a particular candidate. That proportion is the parameter sought; the estimate is based on a small random sample of voters. Alternatively, it is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Outlier
In statistics, an outlier is a data point that differs significantly from other observations. An outlier may be due to a variability in the measurement, an indication of novel data, or it may be the result of experimental error; the latter are sometimes excluded from the data set. An outlier can be an indication of exciting possibility, but can also cause serious problems in statistical analyses. Outliers can occur by chance in any distribution, but they can indicate novel behaviour or structures in the data-set, measurement error, or that the population has a heavy-tailed distribution. In the case of measurement error, one wishes to discard them or use statistics that are robust to outliers, while in the case of heavy-tailed distributions, they indicate that the distribution has high skewness and that one should be very cautious in using tools or intuitions that assume a normal distribution. A frequent cause of outliers is a mixture of two distributions, which may be two dist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wiki Q Inter Def
A wiki ( ) is an online hypertext publication collaboratively edited and managed by its own audience, using a web browser. A typical wiki contains multiple pages for the subjects or scope of the project, and could be either open to the public or limited to use within an organization for maintaining its internal knowledge base. Wikis are enabled by wiki software, otherwise known as wiki engines. A wiki engine, being a form of a content management system, differs from other web-based systems such as blog software, in that the content is created without any defined owner or leader, and wikis have little inherent structure, allowing structure to emerge according to the needs of the users. Wiki engines usually allow content to be written using a simplified markup language and sometimes edited with the help of a rich-text editor. There are dozens of different wiki engines in use, both standalone and part of other software, such as bug tracking systems. Some wiki engines are open ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
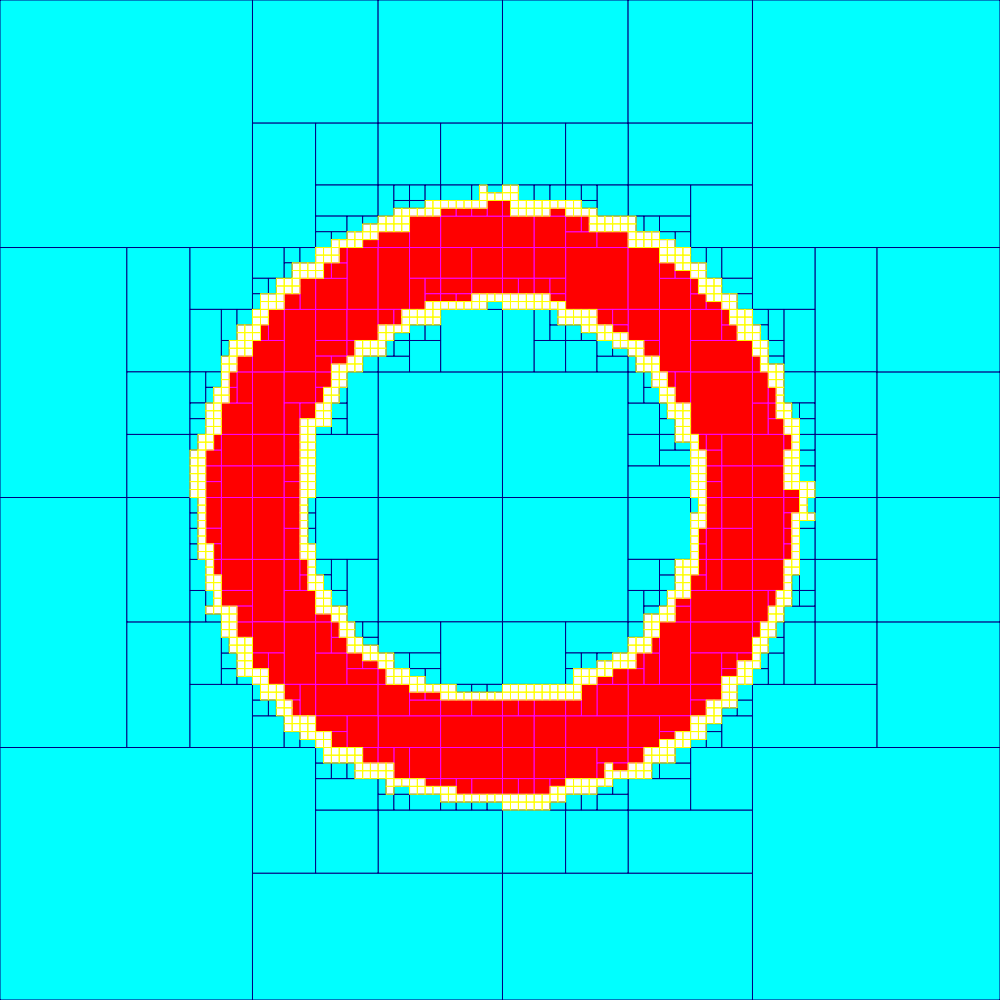
Set Inversion
In mathematics, set inversion is the problem of characterizing the preimage ''X'' of a set ''Y'' by a function ''f'', i.e., ''X'' = ''f'' −1(''Y'' ) = . It can also be viewed as the problem of describing the solution set of the quantified constraint "''Y''(''f'' (''x''))", where ''Y''( ''y'') is a constraint, e.g. an inequality, describing the set ''Y''. In most applications, ''f'' is a function from R''n'' to R''p'' and the set ''Y'' is a box of R''p'' (i.e. a Cartesian product of ''p'' intervals of R). When ''f'' is nonlinear the set inversion problem can be solved using interval analysis combined with a branch-and-bound algorithm. The main idea consists in building a paving of R''p'' made with non-overlapping boxes. For each box 'x'' we perform the following tests: # if ''f'' ( 'x'' ⊂ ''Y'' we conclude that 'x''⊂ ''X''; # if ''f'' ( 'x'' ∩ ''Y'' = ∅ we conclude that 'x''∩ ''X'' = ∅; # Otherwise, the box 'x''t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marzullo's Algorithm
Marzullo's algorithm, invented by Keith Marzullo for his Ph.D. dissertation in 1984, is an agreement algorithm used to select sources for estimating accurate time from a number of noisy time sources. A refined version of it, renamed the "intersection algorithm", forms part of the modern Network Time Protocol. Marzullo's algorithm is also used to compute the relaxed intersection of n boxes (or more generally ''n'' subsets of R''n''), as required by several robust set estimation methods. Purpose Marzullo's algorithm is efficient in terms of time for producing an optimal value from a set of estimates with confidence intervals where the actual value may be outside the confidence interval for some sources. In this case the best estimate is taken to be the smallest interval consistent with the largest number of sources. If we have the estimates 10 ± 2, 12 ± 1 and 11 ± 1 then these intervals are ,12 1,13and 0,12which intersect to form 1,12or 11.5& ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wiki Qinter Intervals
A wiki ( ) is an online hypertext publication Collaborative editing, collaboratively edited and managed by its own audience, using a web browser. A typical wiki contains multiple pages for the subjects or scope of the project, and could be either open to the public or limited to use within an organization for maintaining its internal knowledge base. Wikis are enabled by wiki software, otherwise known as wiki engines. A wiki engine, being a form of a content management system, differs from other web application, web-based systems such as blog software, in that the content is created without any defined owner or leader, and wikis have little inherent structure, allowing structure to emerge according to the needs of the users. Wiki engines usually allow content to be written using a simplified markup language and sometimes edited with the help of a Online rich-text editor, rich-text editor. There are dozens of different wiki engines in use, both standalone and part of other sof ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |