|
Railways On The Isle Of Wight
There once existed a network of railway lines on the Isle of Wight, which operated both as a self-contained railway network, and as links to ferry services between the island and the South coast of Great Britain. The routes were opened by several companies between 1862 and 1901 and modernised after The Grouping in the 1920s. Most of them were permanently closed between 1952 and 1966, whilst the Island Line was temporarily closed in 1966 and rebuilt for electric train services, introduced in 1967. Replacement trains were introduced in 1990, and again in 2021 along with a major renewal of the line. A further have reopened as a heritage line known as the Isle of Wight Steam Railway and there have been several proposals to expand the network further since the 1960s, either with conventional heavy rail or by conversion to light rail. Early beginnings The first railway to be built on the island ran for a distance of . It was opened in 1833 on the Nash Estate near Yarmouth. Its us ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Isle Of Wight RJD 135
''The'' () is a grammatical article in English, denoting persons or things already mentioned, under discussion, implied or otherwise presumed familiar to listeners, readers, or speakers. It is the definite article in English. ''The'' is the most frequently used word in the English language; studies and analyses of texts have found it to account for seven percent of all printed English-language words. It is derived from gendered articles in Old English which combined in Middle English and now has a single form used with pronouns of any gender. The word can be used with both singular and plural nouns, and with a noun that starts with any letter. This is different from many other languages, which have different forms of the definite article for different genders or numbers. Pronunciation In most dialects, "the" is pronounced as (with the voiced dental fricative followed by a schwa) when followed by a consonant sound, and as (homophone of pronoun ''thee'') when followed by a v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
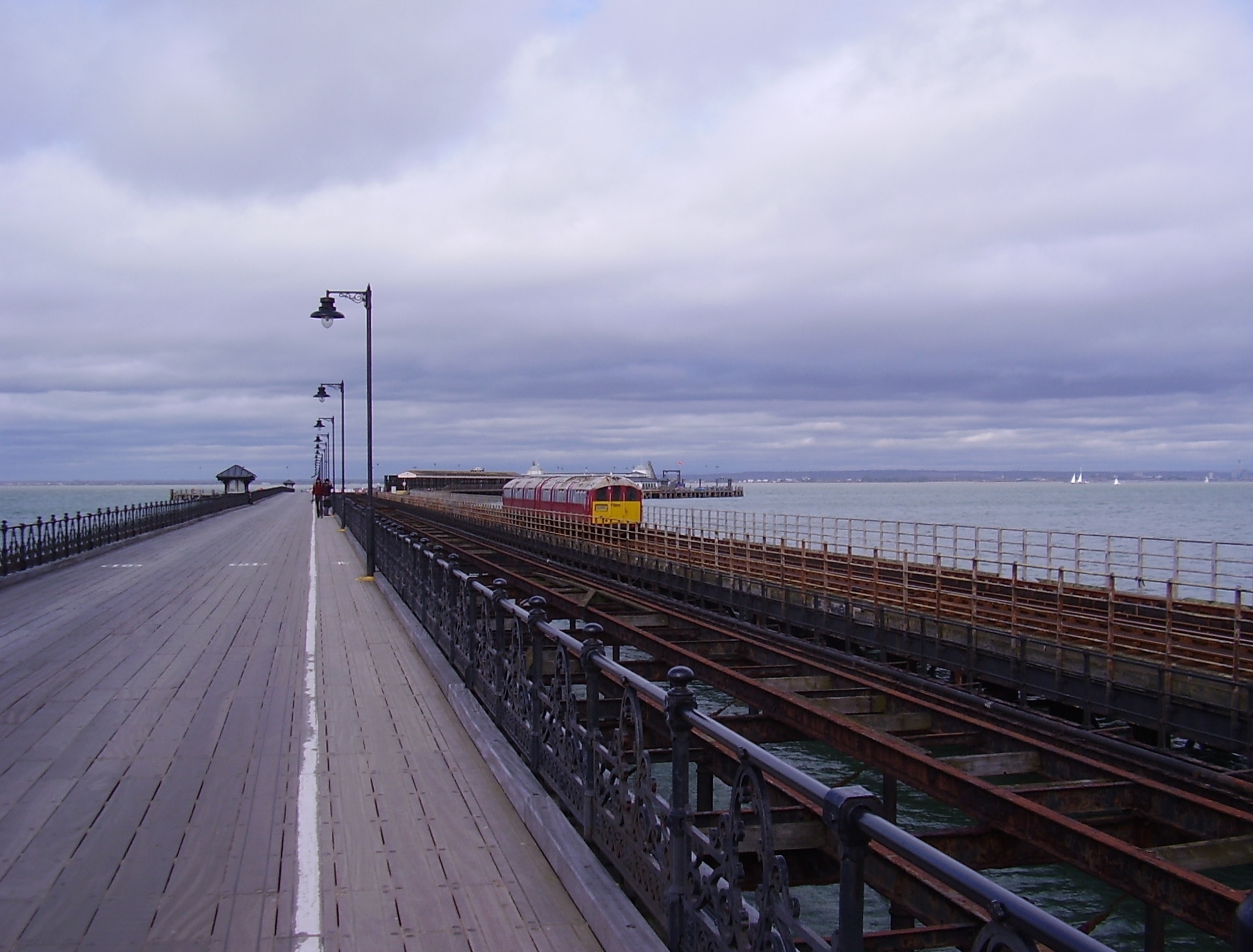
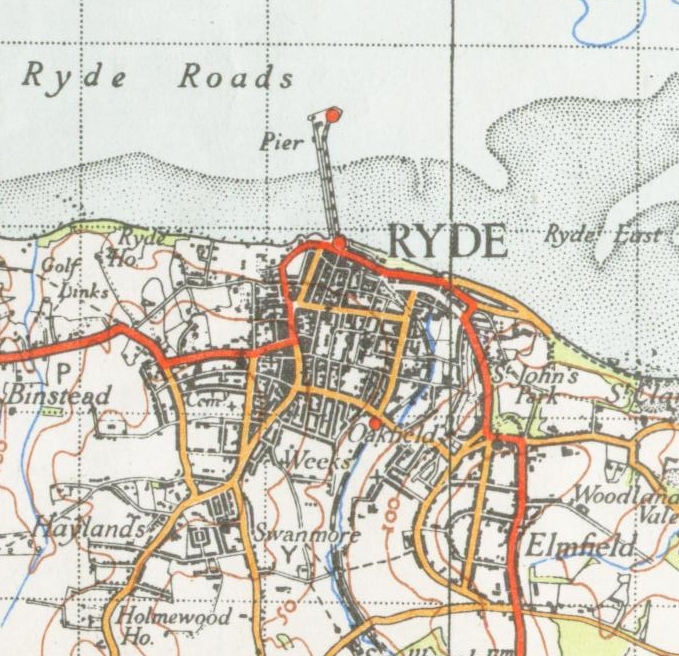
Ryde Pier
Ryde Pier is an early 19th century pier serving the town of Ryde, on the Isle of Wight, off the south coast of England. It is the world's oldest seaside pleasure pier. Ryde Pier Head railway station is at the sea end of the pier, and Ryde Esplanade railway station at the land end, both served by Island Line trains. Before the pier Before the pier was built, passengers had the uncomfortable experience of coming ashore on the back of a porter and then, depending on the state of the tide, having to walk as far as half a mile across wet sand before reaching the town. The need for a pier was obvious, especially if the town was to attract the wealthy and fashionable visitors who were beginning to patronise other seaside resorts. The original pier The pier was designed by John Kent of Southampton, and its foundation stone laid on 29 June 1813. The pier opened on 26 July 1814, with, as it still has, a timber-planked promenade. The structure was originally wholly timber and measured ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
W29 Alverstone 1965
W, or w, is the twenty-third and fourth-to-last letter of the Latin alphabet, used in the modern English alphabet, the alphabets of other western European languages and others worldwide. It represents a consonant, but in some languages it represents a vowel. Its name in English is ''double-u'',Pronounced in formal situations, but colloquially often , , or , with a silent ''l''. plural ''double-ues''. History The classical Latin alphabet, from which the modern European alphabets derived, did not have the "W' character. The "W" sounds were represented by the Latin letter " V" (at the time, not yet distinct from " U"). The sounds (spelled ) and (spelled ) of Classical Latin developed into a bilabial fricative between vowels in Early Medieval Latin. Therefore, no longer adequately represented the labial-velar approximant sound of Germanic phonology. The Germanic phoneme was therefore written as or ( and becoming distinct only by the Early Modern period) by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ventnor West Railway Station
Ventnor West railway station was in operation from 1900 to 1952 in Ventnor, Isle of Wight. History The station was opened on 1 June 1900 as the final addition to the railway network on the Isle of Wight. It opened as Ventnor Town but was renamed in 1923 by the Southern Railway. Built on the former stables of the Steephill Castle estate, the station was inconveniently situated for the town, being some distance west of the town centre and 168 feet above sea level. Consequently, it never lived up to the expectations of the operators and was an early casualty of the pruning of the railway network. Plans were made to extend the line beyond the station to a new terminus, closer to the town centre. Continuing to run along Park Avenue, the Ventnor Central Terminus would have been sited where Park Avenue meets Zig Zag Road – opposite the Royal Hotel. However, the combination of newly built housing on the proposed formation along Park Avenue and the company's ailing finances meant t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ventnor West Branch
The Ventnor West Branch was the final addition to the Isle of Wight railway network, and used an earlier scheme to run a railway from Shanklin to the railwayless south-west part of the island. History The branch was opened by the Newport, Godshill & St Lawrence Railway between Merstone and St. Lawrence on 20 July 1897. From the day of opening, the branch was operated by the Isle of Wight Central Railway. A temporary terminus was provided at St Lawrence until the extension was opened to Ventnor Town on 1 June 1900. The terminus was renamed Ventnor West by the Southern Railway. In the days prior to the Grouping of the railways in 1923, the line struggled to make financial ends meet. However, after 1923 the services did improve and some of the increasing competition from road transport was lessened. An extensive programme of modernisation was undertaken by the Southern Railway, albeit with secondhand equipment from the mainland. Some economies were made on the branch by the Sout ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
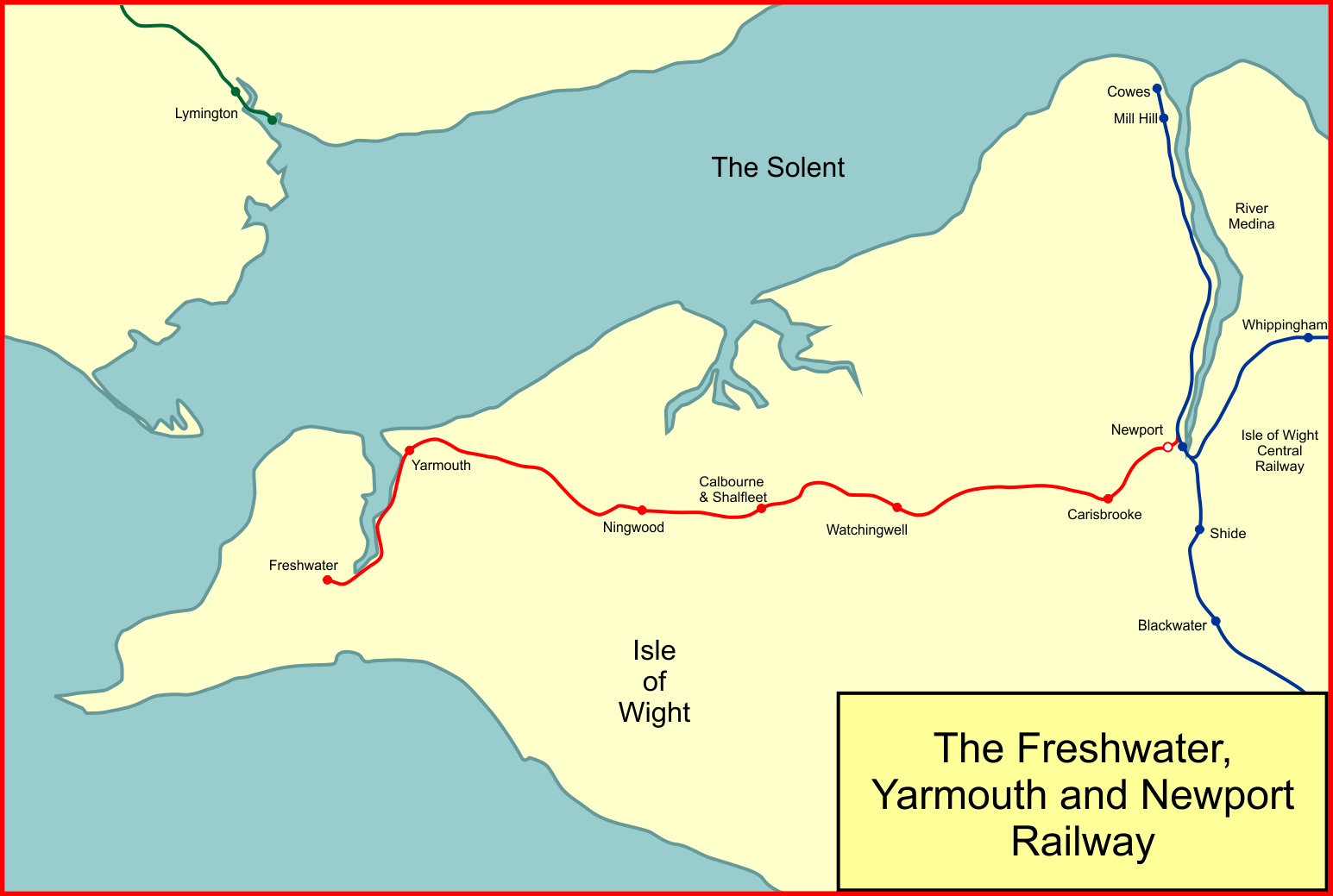
Freshwater, Yarmouth And Newport Railway
The Freshwater, Yarmouth and Newport Railway was a railway line on the Isle of Wight, United Kingdom, connecting Freshwater and Yarmouth to Newport. It was intended to connect the thinly populated west of the island, and it opened in 1889. At Newport it relied on the existing Isle of Wight Central Railway's station, but trains entering it had to shunt back from the junction. The IoWCR worked the line until 1913. The line was never commercially successful, and a break with the IoWCR in 1913 obliged the FY&NR hastily to build its own Newport station and acquire locomotives and rolling stock while in receivership. After the Southern Railway absorbed the FY&NR in 1923, the SR developed holiday traffic, but it was highly seasonal and the heavy losses resulted in the line's closure in 1953. Concept and construction By 1880 the Isle of Wight was well supplied with railways in its eastern and northern areas, connecting Ryde with Newport and Cowes, and Ryde and Newport with Sandow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
W8 Freshwater At Havenstreet Thumb
W8 or W-8 may be: * W8, a postcode district in the W postcode area * W8 engine, an eight-cylinder piston engine in a W configuration * Cargojet, IATA airline designator * Worms 3D, the eighth game in the Worms series * Vector W8, a sports car produced by Vector Aeromotive * London bus W8, a London bus route * a specific size of I-beam * Windows 8, an operating system * W8 (loading gauge) on the British rail system * W8 (tram), a class of electric trams modified by Yarra Trams from SW6, W6 and W7 trams. * Form W-8, a series of IRS tax forms See also * Wait * Weight In science and engineering, the weight of an object is the force acting on the object due to gravity. Some standard textbooks define weight as a Euclidean vector, vector quantity, the gravitational force acting on the object. Others define weigh ... {{Letter-NumberCombDisambig de:Liste von Abkürzungen (Netzjargon)#W ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hayling Island Branch Line
The Hayling Island branch was a short railway branch line in Hampshire, England, that connected a station on Hayling Island with the main line network at Havant. It was built by the Hayling Railway; at first the company planned to run it along a new embankment built along tidal mudflats, but this proved impractical. The line was opened along firm ground in 1867. The line included a bridge and viaduct over tidal water at Langstone; there was a low weight restriction on the viaduct, and only small locomotives were allowed to use it; this resulted in the survival in active service of former LB&SCR A1 class tank engines (known as "Terriers" until closure of the line). In the early 1960s large numbers of holidaymakers were carried on the line in high season, but heavy expenditure on repairs to the viaduct would have been necessary, and the cost was unsupportable; the line closed in 1963. History Before the Hayling Railway Hayling Island had long been isolated, situated off the s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ryde Pier Head Railway Station
Ryde Pier Head railway station is one of three stations in the town of Ryde on the Isle of Wight. Situated at the end of the town's pier, it is adjacent to the terminal for the Wightlink fast catamaran service connecting the island with Portsmouth on the English mainland. Passengers can use this to connect with the rest of the National Rail network at Portsmouth Harbour station, which is adjacent to the Portsmouth terminal. Through rail tickets for travel via Pier Head station are available to and from other stations on the Isle of Wight. These include travel on the catamaran service to or from Portsmouth as appropriate. Trains run down the eastern coast of the Isle of Wight to Shanklin (the Island Line), the last remnant of a network of railways on the island. Because of the restricted loading gauge, particularly through the tunnel under Ryde, services are operated by former London Underground stock. The ticket office at the station is run by Wightlink and not Island Line ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
London And South Western Railway
The London and South Western Railway (LSWR, sometimes written L&SWR) was a railway company in England from 1838 to 1922. Originating as the London and Southampton Railway, its network extended to Dorchester and Weymouth, to Salisbury, Exeter and Plymouth, and to Padstow, Ilfracombe and Bude. It developed a network of routes in Hampshire, Surrey and Berkshire, including Portsmouth and Reading. The LSWR became famous for its express passenger trains to Bournemouth and Weymouth, and to Devon and Cornwall. Nearer London it developed a dense suburban network and was pioneering in the introduction of a widespread suburban electrified passenger network. It was the prime mover of the development of Southampton Docks, which became an important ocean terminal as well as a harbour for cross channel services and for Isle of Wight ferries. Although the LSWR's area of influence was not the home of large-scale heavy industry, the transport goods and mineral traffic was a major activity, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
London, Brighton And South Coast Railway
The London, Brighton and South Coast Railway (LB&SCR; known also as the Brighton line, the Brighton Railway or the Brighton) was a railway company in the United Kingdom from 1846 to 1922. Its territory formed a rough triangle, with London at its apex, practically the whole coastline of Sussex as its base, and a large part of Surrey. It was bounded on its western side by the London and South Western Railway (L&SWR), which provided an alternative route to Portsmouth. On its eastern side the LB&SCR was bounded by the South Eastern Railway (SER)—later one component of the South Eastern and Chatham Railway (SE&CR)—which provided an alternative route to Bexhill, St Leonards-on-Sea, and Hastings. The LB&SCR had the most direct routes from London to the south coast seaside resorts of Brighton, Eastbourne, Worthing, Littlehampton and Bognor Regis, and to the ports of Newhaven and Shoreham-by-Sea. It served the inland towns and cities of Chichester, Horsham, East Grinstead and Lewes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isle Of Wight Central Railway
The Isle of Wight Central Railway (IoWCR) was a railway company on the Isle of Wight, United Kingdom. It was formed in 1887 by the merging of three earlier railways, the Cowes and Newport Railway (opened 1862), the Ryde and Newport Railway (opened 1875) and the Isle of Wight (Newport Junction) Railway, (opened in stages 1875 and 1879). Its network ran from near Ryde to Cowes and from Sandown to Newport. It also worked the Freshwater, Yarmouth and Newport Railway until 1913 and in that year it purchased the Newport, Godshill and Ventnor Railway. The IoWCR was always short of money, and operated with antiquated equipment. The heavily seasonal traffic and, later, competition from buses and cars limited profitable income. In 1923 it was absorbed by the new Southern Railway, and the new owner put financial resources into worthwhile modernisation, but by the 1960s the financial situation became difficult and the whole of the former IoWCR network was closed in 1966. The Isle of Wight S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.png)





_railway_bridge_over_Battersea_Park_Road%2C_SW8.jpg)
