|
Radioresistance
Radioresistance is the level of ionizing radiation that organisms are able to withstand. Ionizing-radiation-resistant organisms (IRRO) were defined as organisms for which the dose of acute ionizing radiation (IR) required to achieve 90% reduction (D10) is greater than 1000 gray (Gy) Radioresistance is surprisingly high in many organisms, in contrast to previously held views. For example, the study of environment, animals and plants around the Chernobyl disaster area has revealed an unexpected survival of many species, despite the high radiation levels. A Brazilian study in a hill in the state of Minas Gerais which has high natural radiation levels from uranium deposits, has also shown many radioresistant insects, worms and plants. Certain extremophiles, such as the bacteria ''Deinococcus radiodurans'' and the tardigrades, can withstand large doses of ionizing radiation on the order of 5,000 Gy. Induced radioresistance In the graph on left, a dose/survival curve for a hyp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deinococcus Radiodurans
''Deinococcus radiodurans'' is an extremophilic bacterium and one of the most radiation-resistant organisms known. It can survive cold, dehydration, vacuum, and acid, and therefore is known as a polyextremophile. It has been listed as the world's toughest known bacterium in ''The Guinness Book Of World Records''. Name and classification The name ''Deinococcus radiodurans'' derives from the Ancient Greek δεινός () and κόκκος () meaning "terrible grain/berry" and the Latin and , meaning "radiation surviving". The species was formerly called ''Micrococcus radiodurans''. As a consequence of its hardiness, it has been nicknamed “Conan the Bacterium”, in reference to Conan the Barbarian. Initially, it was placed in the genus ''Micrococcus''. After evaluation of ribosomal RNA sequences and other evidence, it was placed in its own genus ''Deinococcus'', which is closely related to the genus ''Thermus''. ''Deinococcus'' is one genus of three in the order ''Deinococcale ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extremophiles
An extremophile (from Latin ' meaning "extreme" and Greek ' () meaning "love") is an organism that is able to live (or in some cases thrive) in extreme environments, i.e. environments that make survival challenging such as due to extreme temperature, radiation, salinity, or pH level. These organisms are ecologically dominant in the evolutionary history of the planet. Some spores and cocooned bacteria samples have been dormant for more than 40 million years, extremophiles have continued to thrive in the most extreme conditions, making them one of the most abundant lifeforms. Characteristics In the 1980s and 1990s, biologists found that microbial life has great flexibility for surviving in extreme environments—niches that are acidic, extraordinarily hot or within irregular air pressure for example—that would be completely inhospitable to complex organisms. Some scientists even concluded that life may have begun on Earth in hydrothermal vents far under the ocean's surfac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ionizing Radiation
Ionizing radiation (or ionising radiation), including nuclear radiation, consists of subatomic particles or electromagnetic waves that have sufficient energy to ionize atoms or molecules by detaching electrons from them. Some particles can travel up to 99% of the speed of light, and the electromagnetic waves are on the high-energy portion of the electromagnetic spectrum. Gamma rays, X-rays, and the higher energy ultraviolet part of the electromagnetic spectrum are ionizing radiation, whereas the lower energy ultraviolet, visible light, nearly all types of laser light, infrared, microwaves, and radio waves are non-ionizing radiation. The boundary between ionizing and non-ionizing radiation in the ultraviolet area is not sharply defined, as different molecules and atoms ionize at different energies. The energy of ionizing radiation starts between 10 electronvolts (eV) and 33 eV. Typical ionizing subatomic particles include alpha particles, beta particles, and neutrons. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mammal
Mammals () are a group of vertebrate animals constituting the class Mammalia (), characterized by the presence of mammary glands which in females produce milk for feeding (nursing) their young, a neocortex (a region of the brain), fur or hair, and three middle ear bones. These characteristics distinguish them from reptiles (including birds) from which they diverged in the Carboniferous, over 300 million years ago. Around 6,400 extant species of mammals have been described divided into 29 orders. The largest orders, in terms of number of species, are the rodents, bats, and Eulipotyphla ( hedgehogs, moles, shrews, and others). The next three are the Primates (including humans, apes, monkeys, and others), the Artiodactyla (cetaceans and even-toed ungulates), and the Carnivora ( cats, dogs, seals, and others). In terms of cladistics, which reflects evolutionary history, mammals are the only living members of the Synapsida (synapsids); this clade, toget ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blood Cells
A blood cell, also called a hematopoietic cell, hemocyte, or hematocyte, is a cell produced through hematopoiesis and found mainly in the blood. Major types of blood cells include red blood cells (erythrocytes), white blood cells (leukocytes), and platelets (thrombocytes). Together, these three kinds of blood cells add up to a total 45% of the blood tissue by volume, with the remaining 55% of the volume composed of plasma, the liquid component of blood. Red blood cells Red blood cells or ''erythrocytes'', primarily carry oxygen and collect carbon dioxide through the use of hemoglobin. Hemoglobin is an iron-containing protein that gives red blood cells their color and facilitates transportation of oxygen from the lungs to tissues and carbon dioxide from tissues to the lungs to be exhaled. Red blood cells are the most abundant cell in the blood, accounting for about 40-45% of its volume. Red blood cells are circular, biconcave, disk-shaped and deformable to allow them to squeeze ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cell (biology)
The cell is the basic structural and functional unit of life forms. Every cell consists of a cytoplasm enclosed within a membrane, and contains many biomolecules such as proteins, DNA and RNA, as well as many small molecules of nutrients and metabolites.Cell Movements and the Shaping of the Vertebrate Body in Chapter 21 of Molecular Biology of the Cell '' fourth edition, edited by Bruce Alberts (2002) published by Garland Science. The Alberts text discusses how the "cellular building blocks" move to shape developing embryos. It is also common to describe small molecules such ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cell Death
Cell death is the event of a biological cell ceasing to carry out its functions. This may be the result of the natural process of old cells dying and being replaced by new ones, as in programmed cell death, or may result from factors such as diseases, localized injury, or the death of the organism of which the cells are part. Apoptosis or Type I cell-death, and autophagy or Type II cell-death are both forms of programmed cell death, while necrosis is a non-physiological process that occurs as a result of infection or injury. Programmed cell death Programmed cell death (PCD) is cell death mediated by an intracellular program. PCD is carried out in a regulated process, which usually confers advantage during an organism's life-cycle. For example, the differentiation of fingers and toes in a developing human embryo occurs because cells between the fingers apoptose; the result is that the digits separate. PCD serves fundamental functions during both plant and metazoa (multicel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radiation Biology
Radiobiology (also known as radiation biology, and uncommonly as actinobiology) is a field of clinical and basic medical sciences that involves the study of the action of ionizing radiation on living things, especially health effects of radiation. Ionizing radiation is generally harmful and potentially lethal to living things but can have health benefits in radiation therapy for the treatment of cancer and thyrotoxicosis. Its most common impact is the induction of cancer with a latent period of years or decades after exposure. High doses can cause visually dramatic radiation burns, and/or rapid fatality through acute radiation syndrome. Controlled doses are used for medical imaging and radiotherapy. Health effects In general, ionizing radiation is harmful and potentially lethal to living beings but can have health benefits in radiation therapy for the treatment of cancer and thyrotoxicosis. Most adverse health effects of radiation exposure may be grouped in two general categorie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
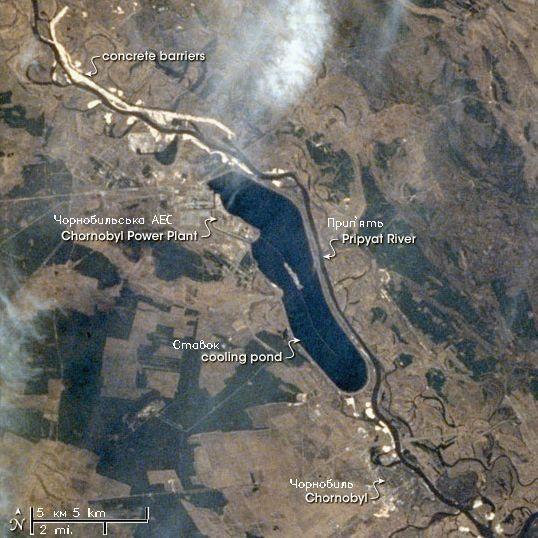
Chernobyl
Chernobyl ( , ; russian: Чернобыль, ) or Chornobyl ( uk, Чорнобиль, ) is a partially abandoned city in the Chernobyl Exclusion Zone, situated in the Vyshhorod Raion of northern Kyiv Oblast, Ukraine. Chernobyl is about north of Kyiv, and southwest of the Belarusian city of Gomel. Before its evacuation, the city had about 14,000 residents, while around 1,000 people live in the city today. First mentioned as a ducal hunting lodge in 1193, the city has changed hands multiple times over the course of history. Jews moved into the city in the 16th century, and a now-defunct monastery was established in the area in 1626. By the end of the 18th century, Chernobyl was a major centre of Hasidic Judaism under the Twersky Dynasty, who left Chernobyl after the city was subject to pogroms in the early 20th century. The Jewish community was later murdered during the Holocaust. Chernobyl was chosen as the site of Ukraine's first nuclear power plant in 1972, loc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Goiânia Accident
The Goiânia accident was a radioactive contamination accident that occurred on September 13, 1987, in Goiânia, Goiás, Brazil, after a forgotten radiotherapy source was stolen from an abandoned hospital site in the city. It was subsequently handled by many people, resulting in four deaths. About 112,000 people were examined for radioactive contamination and 249 of them were found to have been contaminated. In the consequent cleanup operation, topsoil had to be removed from several sites, and several houses were demolished. All the objects from within those houses, including personal possessions, were seized and incinerated. ''Time'' magazine has identified the accident as one of the world's "worst nuclear disasters" and the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) called it "one of the world's worst radiological incidents". Description of the source The radiation source in the Goiânia accident was a small capsule containing about of highly radioactive caesium chlori ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DNA Repair
DNA repair is a collection of processes by which a cell identifies and corrects damage to the DNA molecules that encode its genome. In human cells, both normal metabolic activities and environmental factors such as radiation can cause DNA damage, resulting in tens of thousands of individual molecular lesions per cell per day. Many of these lesions cause structural damage to the DNA molecule and can alter or eliminate the cell's ability to transcribe the gene that the affected DNA encodes. Other lesions induce potentially harmful mutations in the cell's genome, which affect the survival of its daughter cells after it undergoes mitosis. As a consequence, the DNA repair process is constantly active as it responds to damage in the DNA structure. When normal repair processes fail, and when cellular apoptosis does not occur, irreparable DNA damage may occur, including double-strand breaks and DNA crosslinkages (interstrand crosslinks or ICLs). This can eventually lead to malig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gene Expression
Gene expression is the process by which information from a gene is used in the synthesis of a functional gene product that enables it to produce end products, protein or non-coding RNA, and ultimately affect a phenotype, as the final effect. These products are often proteins, but in non-protein-coding genes such as transfer RNA (tRNA) and small nuclear RNA (snRNA), the product is a functional non-coding RNA. Gene expression is summarized in the central dogma of molecular biology first formulated by Francis Crick in 1958, further developed in his 1970 article, and expanded by the subsequent discoveries of reverse transcription and RNA replication. The process of gene expression is used by all known life— eukaryotes (including multicellular organisms), prokaryotes (bacteria and archaea), and utilized by viruses—to generate the macromolecular machinery for life. In genetics, gene expression is the most fundamental level at which the genotype gives rise to the phenot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)