|
Radical Retropubic Prostatectomy
Radical retropubic prostatectomy is a surgical procedure in which the prostate gland is removed through an incision in the abdomen (in comparison with perineal prostatectomy, done through the perineum). It is most often used to treat individuals who have early prostate cancer. Radical retropubic prostatectomy can be performed under general, spinal, or epidural anesthesia and requires blood transfusion less than one-fifth of the time. Radical retropubic prostatectomy is associated with complications such as urinary incontinence and impotence, but these outcomes are related to a combination of individual patient anatomy, surgical technique, and the experience and skill of the surgeon. Description Radical retropubic prostatectomy was developed in 1945 by Terence Millin at the All Saints Hospital in London. The procedure was brought to the United States by one of Millin's students, Samuel Kenneth Bacon, M.D., adjunct professor of surgery, University of Southern California, and w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1116 Muscle Of The Male Perineum
Year 1116 ( MCXVI) was a leap year starting on Saturday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar. Events By place Byzantine Empire * Autumn – Battle of Philomelion: Emperor Alexios I (Komnenos) leads an expedition into Anatolia and meets the Seljuk army under Sultan Malik Shah (near Philomelium). The Byzantines introduce a new battle formation of Alexios' devising, the ''parataxis'' (a defensive formation, consisting of a hollow square, with the baggage in the centre). During the battle, the Seljuk Turks mount several attacks on the formations, but all are repulsed. The Byzantine cavalry makes two counterattacks; the first is unsuccessful. But a second attack, led by Nikephoros Bryennios (the Younger), breaks the Seljuk forces, who then turn to flight. The following day Malik Shah again attacks, his army completely surrounding the Byzantines from all sides. The Seljuk Turks are once more repulsed, with many losses. Alexios claims the victo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pubic Bone
In vertebrates, the pubic region ( la, pubis) is the most forward-facing (ventral and anterior) of the three main regions making up the coxal bone. The left and right pubic regions are each made up of three sections, a superior ramus, inferior ramus, and a body. Structure The pubic region is made up of a ''body'', ''superior ramus'', and ''inferior ramus'' (). The left and right coxal bones join at the pubic symphysis. It is covered by a layer of fat, which is covered by the mons pubis. The pubis is the lower limit of the suprapubic region. In the female, the pubic region is anterior to the urethral sponge. Body The body forms the wide, strong, middle and flat part of the pubic region. The bodies of the left and right pubic regions join at the pubic symphysis. The rough upper edge is the pubic crest, ending laterally in the pubic tubercle. This tubercle, found roughly 3 cm from the pubic symphysis, is a distinctive feature on the lower part of the abdominal wall; important ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nerve-sparing Surgery
Nerve-sparing surgery is a type of surgery that attempts to save the nerves near the tissues being removed. It is commonly applied in radical retropubic prostatectomy, a surgical treatment for prostate cancer, in which damage to nerves during surgery can lead to complications including urinary incontinence and impotence. In nerve-sparing radical prostatectomy, initially developed by Dr. Patrick Walsh in the 1980s, surgeons identify and attempt to avoid damaging the nerves. Surgeons may visually identify the cavernous nerves of penis or apply an electrical stimulation penile plethysmograph Penile plethysmography (PPG) or phallometry is measurement of blood flow to the penis, typically used as a proxy for measurement of sexual arousal. The most commonly reported methods of conducting penile plethysmography involve the measurement of ... diagnostic test to verify the nerves, and so avoid damaging them. The bilateral approach attempts to spare the nerves on both sides of the prosta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lymphocele
A lymphocele is a collection of lymphatic fluid within the body not bordered by epithelial lining. It is usually a surgical complication seen after extensive pelvic surgery (such as cancer surgery) and is most commonly found in the retroperitoneal space. Spontaneous development is rare. Signs and symptoms Many lymphoceles are asymptomatic. Larger lymphoceles may cause symptoms related to compression of adjacent structures leading to lower abdominal pain, abdominal fullness, constipation, urinary frequency, and edema of the genitals and/or legs. Serious sequelae could develop and include infection of the lymphocele, obstruction and infection of the urinary tract, intestinal obstruction, venous thrombosis, pulmonary embolism, chylous ascites and lymphatic fistula formation. On clinical examination the skin may be reddened and swollen and a mass felt. Ultrasonography or CT scan will help to establish a diagnosis. Other fluid collections to be considered in the differential diagn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microscope
A microscope () is a laboratory instrument used to examine objects that are too small to be seen by the naked eye. Microscopy is the science of investigating small objects and structures using a microscope. Microscopic means being invisible to the eye unless aided by a microscope. There are many types of microscopes, and they may be grouped in different ways. One way is to describe the method an instrument uses to interact with a sample and produce images, either by sending a beam of light or electrons through a sample in its optical path, by detecting photon emissions from a sample, or by scanning across and a short distance from the surface of a sample using a probe. The most common microscope (and the first to be invented) is the optical microscope, which uses lenses to refract visible light that passed through a thinly sectioned sample to produce an observable image. Other major types of microscopes are the fluorescence microscope, electron microscope (both the transmi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
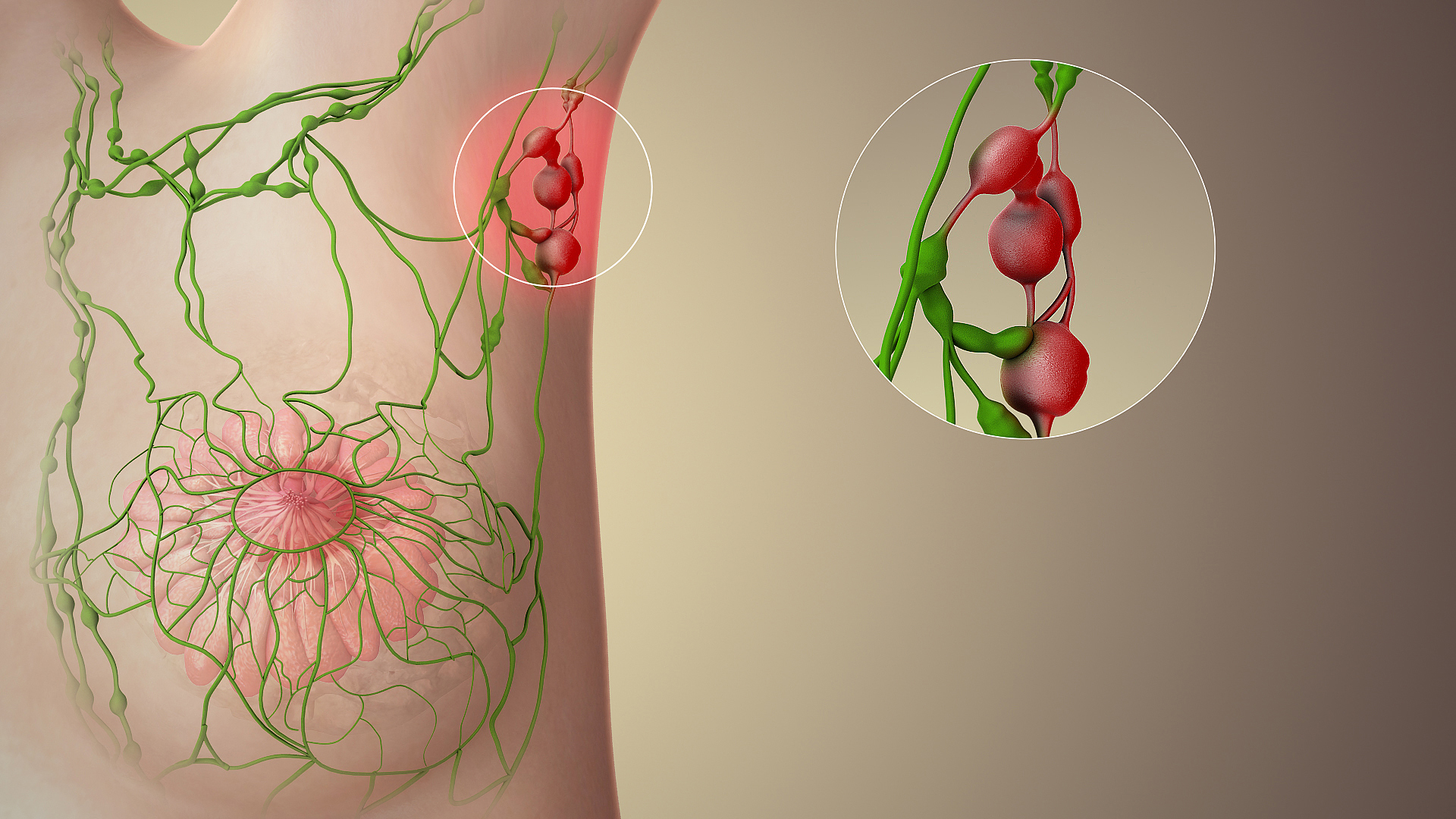
Sentinel Lymph Node
The sentinel lymph node is the hypothetical first lymph node or group of nodes draining a cancer. In case of established cancerous dissemination it is postulated that the sentinel lymph nodes are the target organs primarily reached by metastasizing cancer cells from the tumor. The sentinel node procedure (also termed sentinel lymph node biopsy or SLNB) is the identification, removal and analysis of the sentinel lymph nodes of a particular tumour. Physiology The spread of some forms of cancer usually follows an orderly progression, spreading first to regional lymph nodes, then the next echelon of lymph nodes, and so on, since the flow of lymph is directional, meaning that some cancers spread in a predictable fashion from where the cancer started. In these cases, if the cancer spreads it will spread first to lymph nodes (lymph glands) close to the tumor before it spreads to other parts of the body. The concept of sentinel lymph node surgery is to determine if the cancer has sprea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lymph Nodes
A lymph node, or lymph gland, is a kidney-shaped organ of the lymphatic system and the adaptive immune system. A large number of lymph nodes are linked throughout the body by the lymphatic vessels. They are major sites of lymphocytes that include B and T cells. Lymph nodes are important for the proper functioning of the immune system, acting as filters for foreign particles including cancer cells, but have no detoxification function. In the lymphatic system a lymph node is a secondary lymphoid organ. A lymph node is enclosed in a fibrous capsule and is made up of an outer cortex and an inner medulla. Lymph nodes become inflamed or enlarged in various diseases, which may range from trivial throat infections to life-threatening cancers. The condition of lymph nodes is very important in cancer staging, which decides the treatment to be used and determines the prognosis. Lymphadenopathy refers to glands that are enlarged or swollen. When inflamed or enlarged, lymph nodes can be fi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lymphadenectomy
Lymphadenectomy or lymph node dissection is the surgical removal of one or more groups of lymph nodes. It is almost always performed as part of the surgical management of cancer. In a regional lymph node dissection, some of the lymph nodes in the tumor area are removed; in a radical lymph node dissection, most or all of the lymph nodes in the tumor area are removed. Indications It is usually done because many types of cancer have a marked tendency to produce lymph node metastasis early in their natural history. This is particularly true of melanoma, head and neck cancer, differentiated thyroid cancer, breast cancer, lung cancer, gastric cancer and colorectal cancer. Famed British surgeon Berkeley Moynihan once remarked that "the surgery of cancer is not the surgery of organs; it is the surgery of the lymphatic system". The better-known examples of lymphadenectomy are ''axillary lymph node dissection'' for breast cancer; ''radical neck dissection'' for head and neck cancer and th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blood
Blood is a body fluid in the circulatory system of humans and other vertebrates that delivers necessary substances such as nutrients and oxygen to the cells, and transports metabolic waste products away from those same cells. Blood in the circulatory system is also known as ''peripheral blood'', and the blood cells it carries, ''peripheral blood cells''. Blood is composed of blood cells suspended in blood plasma. Plasma, which constitutes 55% of blood fluid, is mostly water (92% by volume), and contains proteins, glucose, mineral ions, hormones, carbon dioxide (plasma being the main medium for excretory product transportation), and blood cells themselves. Albumin is the main protein in plasma, and it functions to regulate the colloidal osmotic pressure of blood. The blood cells are mainly red blood cells (also called RBCs or erythrocytes), white blood cells (also called WBCs or leukocytes) and platelets (also called thrombocytes). The most abundant cells in vertebrate blo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Surgical Drain
A surgical drain is a tube used to remove pus, blood or other fluids from a wound, body cavity, or organ. They are commonly placed by surgeons or interventional radiologists after procedures or some types of injuries, but they can also be used as an intervention for decompression. There are several types of drains, and selection of which to use often depends on the placement site and how long the drain is needed. Use and Management Drains help to remove contents, usually fluids, from inside the body. This is beneficial since fluid accumulation may cause distension and pressure, which can lead to pain. For example, nasogastric (NG) tubes inserted through the nose and into the stomach can help remove stomach contents for patients who have a blockage further along in their gastrointestinal tract. After surgery, drains can be placed to remove blood, lymph, or other fluids that accumulate in the wound bed. This helps to promote wound healing and allows healthcare providers to moni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Foley Catheter
In urology, a Foley catheter (named for Frederic Foley, who produced the original design in 1929) is a flexible tube that a clinician passes through the urethra and into the bladder to drain urine. It is the most common type of indwelling urinary catheter. The tube has two separated channels, or ''lumens'', running down its length. One lumen, open at both ends, drains urine into a collection bag. The other has a valve on the outside end and connects to a balloon at the inside tip. The balloon is inflated with sterile water when it lies inside the bladder to stop it from slipping out. Manufacturers usually produce Foley catheters using silicone or coated natural latex. Coatings include polytetrafluoroethylene, hydrogel, or a silicon elastomer – the different properties of these surface coatings determine whether the catheter is suitable for 28-day or 3-month indwelling duration. Foley catheters should be used only when indicated, as use increases the risk of catheter-ass ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nerve
A nerve is an enclosed, cable-like bundle of nerve fibers (called axons) in the peripheral nervous system. A nerve transmits electrical impulses. It is the basic unit of the peripheral nervous system. A nerve provides a common pathway for the electrochemical nerve impulses called action potentials that are transmitted along each of the axons to peripheral organs or, in the case of sensory nerves, from the periphery back to the central nervous system. Each axon, within the nerve, is an extension of an individual neuron, along with other supportive cells such as some Schwann cells that coat the axons in myelin. Within a nerve, each axon is surrounded by a layer of connective tissue called the endoneurium. The axons are bundled together into groups called fascicles, and each fascicle is wrapped in a layer of connective tissue called the perineurium. Finally, the entire nerve is wrapped in a layer of connective tissue called the epineurium. Nerve cells (often called neurons) are f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

_mini.jpg)

.jpg)

.jpg)
