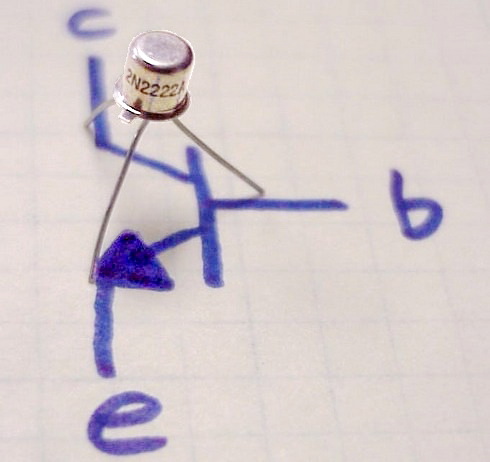|
RMA Tube Designation
In the years 1942-1944, the Radio Manufacturers Association used a descriptive nomenclature system for industrial, transmitting, and special-purpose vacuum tubes. The numbering scheme was distinct from both the numbering schemes used for standard receiving tubes, and the existing transmitting tube numbering systems used previously, such as the "800 series" numbers originated by RCA and adopted by many others. The system assigned numbers with the base form "1A21", and this numbering scheme is occasionally referred to by tube collectors and historians as the "1A21 system". The first digit of the type number was 1-9, providing a rough indication of the filament/heater power rating (and therefore the overall power handling capabilities) of the tube. The assigned numbers were as follows: *1-- No filament/heater, or cold cathode device *2-- Up to 10 W *3-- 10-20 W *4-- 20-50 W *5-- 50-100 W *6-- 100-200 W *7-- 200-500 W *8-- 500W-1 kW *9-- More than 1 kW The second character w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vacuum Tubes
A vacuum tube, electron tube, valve (British usage), or tube (North America), is a device that controls electric current flow in a high vacuum between electrodes to which an electric potential difference has been applied. The type known as a thermionic tube or thermionic valve utilizes thermionic emission of electrons from a hot cathode for fundamental electronic functions such as signal amplification and current rectification. Non-thermionic types such as a vacuum phototube, however, achieve electron emission through the photoelectric effect, and are used for such purposes as the detection of light intensities. In both types, the electrons are accelerated from the cathode to the anode by the electric field in the tube. The simplest vacuum tube, the diode (i.e. Fleming valve), invented in 1904 by John Ambrose Fleming, contains only a heated electron-emitting cathode and an anode. Electrons can only flow in one direction through the device—from the cathode to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2N2222
The 2N2222 is a common NPN bipolar junction transistor (BJT) used for general purpose low-power amplifying or switching applications. It is designed for low to medium current, low power, medium voltage, and can operate at moderately high speeds. It was originally made in the TO-18 metal can as shown in the picture. The 2N2222 is considered a very common transistor, and is used as an exemplar of an NPN transistor. It is frequently used as a small-signal transistor, and it remains a small general purpose transistor of enduring popularity. The 2N2222 was part of a family of devices described by Motorola at a 1962 IRE convention. Since then it has been made by many semiconductor companies, for example, Texas Instruments.''The Transistor and Diode Data Book for Design Engineers'', Texas Instruments Incorporated, no date, TI publication number CC413 71242-73-CSS, page 4-93 Specifications The JEDEC registration of a device number ensures particular rated values will be met by al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Night Vision
Night vision is the ability to see in low-light conditions, either naturally with scotopic vision or through a night-vision device. Night vision requires both sufficient spectral range and sufficient intensity range. Humans have poor night vision compared to many animals such as cats, foxes and rabbits, in part because the human eye lacks a tapetum lucidum, tissue behind the retina that reflects light back through the retina thus increasing the light available to the photoreceptors. Types of ranges Spectral range Night-useful spectral range techniques can sense radiation that is invisible to a human observer. Human vision is confined to a small portion of the electromagnetic spectrum called visible light. Enhanced spectral range allows the viewer to take advantage of non-visible sources of electromagnetic radiation (such as near-infrared or ultraviolet radiation). Some animals such as the mantis shrimp and trout can see using much more of the infrared and/or ultraviolet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thermionic Converter
A thermionic converter consists of a hot electrode which thermionically emits electrons over a potential energy barrier to a cooler electrode, producing a useful electric power output. Caesium vapor is used to optimize the electrode work functions and provide an ion supply (by surface ionization or electron impact ionization in a plasma) to neutralize the electron space charge. Definition From a physical electronic viewpoint, thermionic energy conversion is the direct production of electric power from heat by thermionic electron emission. From a thermodynamic viewpoint, it is the use of electron vapor as the working fluid in a power-producing cycle. A thermionic converter consists of a hot emitter electrode from which electrons are vaporized by thermionic emission and a colder collector electrode into which they are condensed after conduction through the inter-electrode plasma. The resulting current, typically several amperes per square centimeter of emitter surface, de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
X-ray Tube
An X-ray tube is a vacuum tube that converts electrical input power into X-rays. The availability of this controllable source of X-rays created the field of radiography, the imaging of partly opaque objects with penetrating radiation. In contrast to other sources of ionizing radiation, X-rays are only produced as long as the X-ray tube is energized. X-ray tubes are also used in CT scanners, airport luggage scanners, X-ray crystallography, material and structure analysis, and for industrial inspection. Increasing demand for high-performance Computed tomography (CT) scanning and angiography systems has driven development of very high performance medical X-ray tubes. History X-ray tubes evolved from experimental Crookes tubes with which X-rays were first discovered on November 8, 1895, by the German physicist Wilhelm Conrad Röntgen. The first-generation ''cold cathode'' or ''Crookes'' X-ray tubes were used until the 1920s. These tubes work by ionisation of residual gas within the tu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Travelling Wave Tube
A traveling-wave tube (TWT, pronounced "twit") or traveling-wave tube amplifier (TWTA, pronounced "tweeta") is a specialized vacuum tube that is used in electronics to amplify radio frequency (RF) signals in the microwave range. The TWT belongs to a category of "linear beam" tubes, such as the klystron, in which the radio wave is amplified by absorbing power from a beam of electrons as it passes down the tube. Although there are various types of TWT, two major categories are: *''Helix TWT'' - in which the radio waves interact with the electron beam while traveling down a wire helix which surrounds the beam. These have wide bandwidth, but output power is limited to a few hundred watts. *''Coupled cavity TWT'' - in which the radio wave interacts with the beam in a series of cavity resonators through which the beam passes. These function as narrowband power amplifiers. A major advantage of the TWT over some other microwave tubes is its ability to amplify a wide range of frequencie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flash Tube
Flash, flashes, or FLASH may refer to: Arts, entertainment, and media Fictional aliases * Flash (DC Comics character), several DC Comics superheroes with super speed: ** Flash (Barry Allen) ** Flash (Jay Garrick) ** Wally West, the first Kid Flash and third adult Flash ** Bart Allen, the second Kid Flash who also became the adult hero for a time * Flash (G.I. Joe), a character in the G.I. Joe universe * Flash, a robot in the video game ''Brave Saga 2'' * Flash, a character in the comedy film ''Daddy Day Care'' (2003) * Flash, a character in the TV science fiction drama '' Real Humans'' * Flash, a character in the 1989 American action comedy movie ''Speed Zone'' * Flash, a character in the TV sitcom '' Step by Step'' * Flash, a character in the film ''Zootopia'' (2016) * Flash Gordon, the titular hero of science fiction comic strip * Flash Sentry, in ''My Little Pony: Friendship is Magic'' * Flash Thompson, a Marvel comic book character Films * ''Flash'' (1997 film), Disney C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beam Deflection Tube
Beam deflection tubes, sometimes known as sheet beam tubes, are vacuum tubes with an electron gun, a beam intensity control grid, a screen grid, sometimes a suppressor grid, and two electrostatic deflection electrodes on opposite sides of the electron beam, that can direct the rectangular beam to either of two anodes in the same plane. They can be used as two-quadrant, single-balanced mixers or (de)modulators with very linear qualities, their mode of operation similar to one-half of a Gilbert Cell, by applying an unbalanced signal to the control grid and a balanced signal to the deflection electrodes, then extracting the balanced mixing products and from the two anodes. Similar to a pentagrid converter, the cathode and the first two grids can be made into an oscillator. Two beam deflection tubes can be combined to form a double-balanced mixer. They need extensive shielding against external magnetic fields. The ballistic deflection transistors currently under develop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Storage Tube
Storage tubes are a class of cathode-ray tubes (CRTs) that are designed to hold an image for a long period of time, typically as long as power is supplied to the tube. A specialized type of storage tube, the Williams tube, was used as a main memory system on a number of early computers, from the late 1940s into the early 1950s. They were replaced with other technologies, notably core memory, starting in the 1950s. Storage tubes made a comeback in the 1960s and 1970s for use in computer graphics, most notably the Tektronix 4010 series. Today they are obsolete, their functions provided by low-cost memory devices and liquid crystal displays. Operation Background A conventional CRT consists of an electron gun at the back of the tube that is aimed at a thin layer of phosphor at the front of the tube. Depending on the role, the beam of electrons emitted by the gun is steered around the display using magnetic (television) or electrostatic ( oscilloscope) means. When the electrons s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mercury Arc Rectifier
Mercury commonly refers to: * Mercury (planet), the nearest planet to the Sun * Mercury (element), a metallic chemical element with the symbol Hg * Mercury (mythology), a Roman god Mercury or The Mercury may also refer to: Companies * Mercury (toy manufacturer), a brand of diecast toy cars manufactured in Italy * Mercury Communications, a British telecommunications firm set up in the 1980s * Mercury Drug, a Philippine pharmacy chain * Mercury Energy, an electricity generation and retail company in New Zealand * Mercury Filmworks, a Canadian independent animation studio * Mercury General, a multiple-line American insurance organization * Mercury Interactive, a software testing tools vendor * Mercury Marine, a manufacturer of marine engines, particularly outboard motors * Mercury Systems, a defense-related information technology company Computing * Mercury (programming language), a functional logic programming language * Mercury (metadata search system), a data search ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
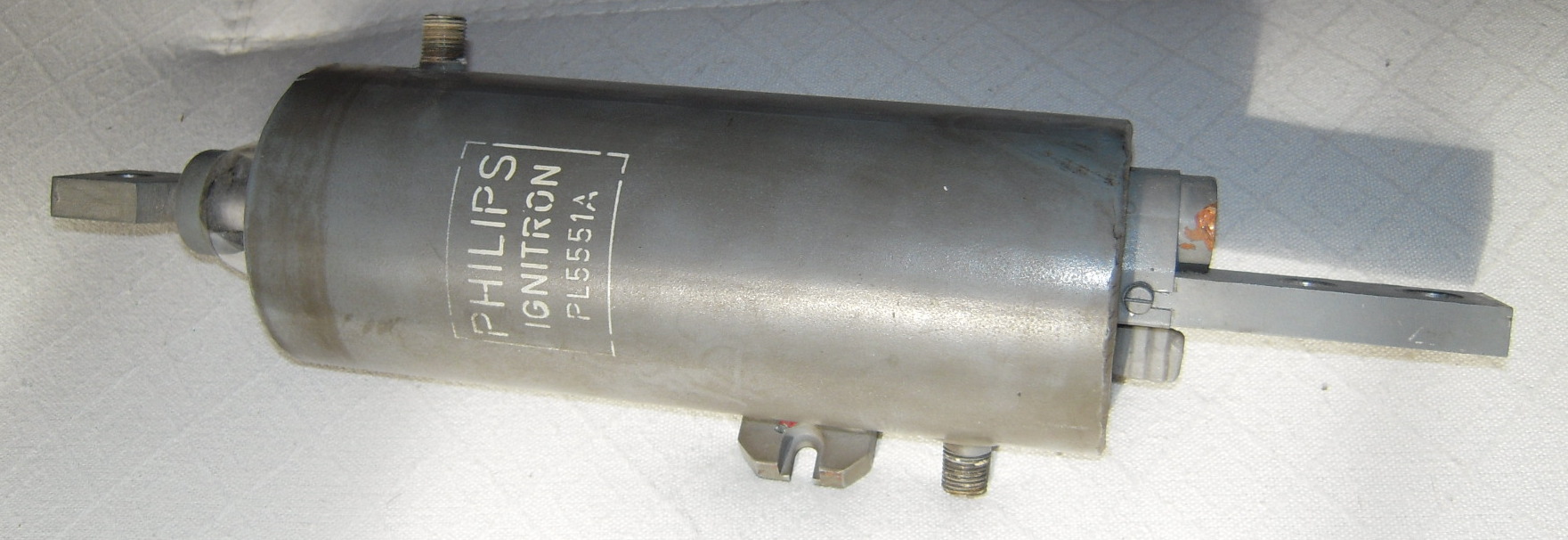
Ignitron
An ignitron is a type of gas-filled tube used as a controlled rectifier and dating from the 1930s. Invented by Joseph Slepian while employed by Westinghouse, Westinghouse was the original manufacturer and owned trademark rights to the name "Ignitron". Ignitrons are closely related to mercury-arc valves but differ in the way the arc is ignited. They function similarly to thyratrons; a triggering pulse to the igniter electrode turns the device "on", allowing a high current to flow between the cathode and anode electrodes. After it is turned on, the current through the anode must be reduced to zero to restore the device to its nonconducting state. They are used to switch high currents in heavy industrial applications. Construction and operation An ignitron is usually a large steel container with a pool of mercury in the bottom that acts as a cathode during operation. A large graphite or refractory metal cylinder, held above the pool by an insulated electrical connection, serves as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
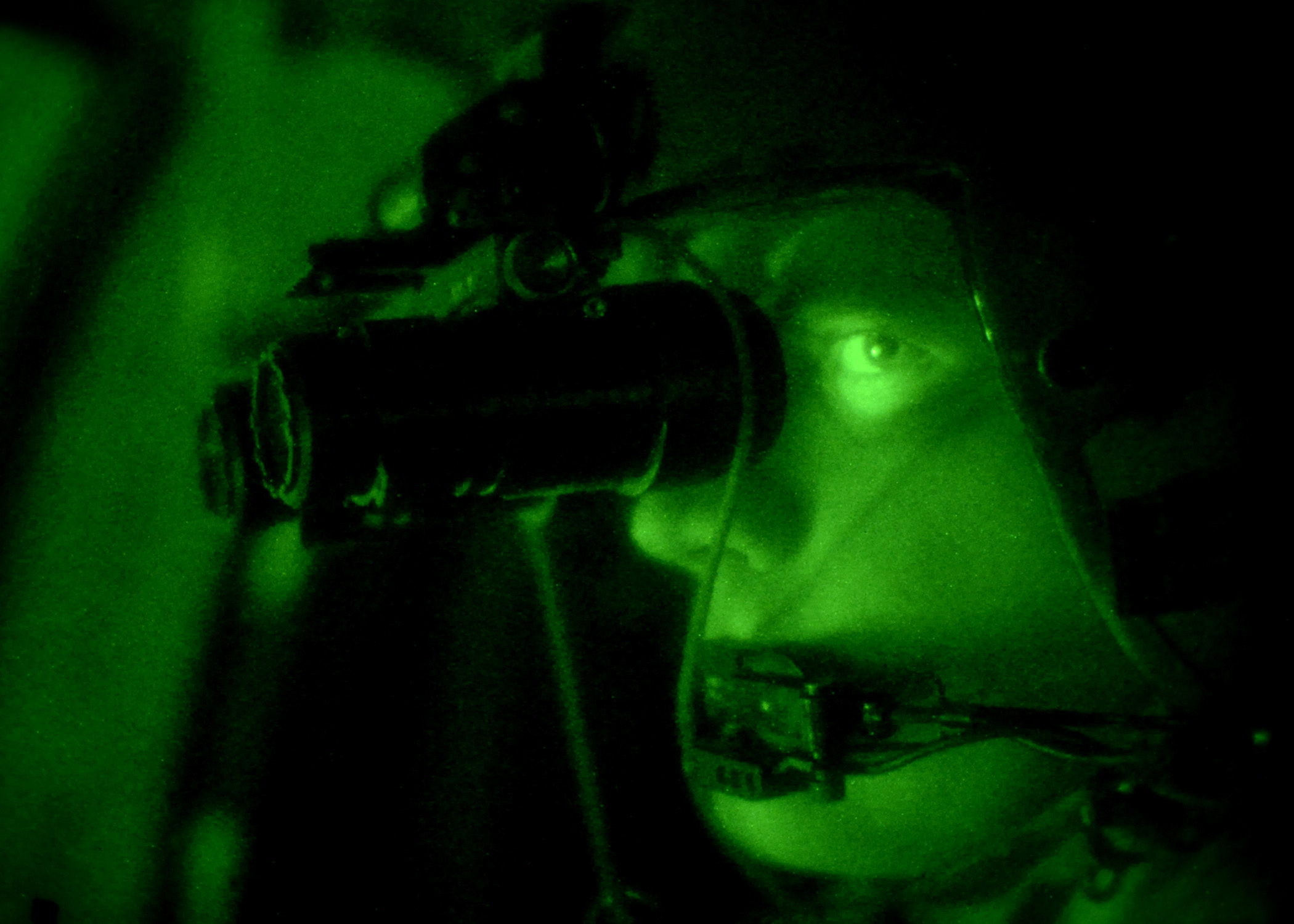
Night Vision Device
A night-vision device (NVD), also known as a night optical/observation device (NOD), night-vision goggle (NVG), is an optoelectronic device that allows visualization of images in low levels of light, improving the user's night vision. The device enhances ambient visible light and converts near-infrared light into visible light which can be seen by the user; this is known as I2 ( image intensification). By comparison, viewing of infrared thermal radiation is referred to as thermal imaging and operates in a different section of the infrared spectrum. A night vision device usually consists of an image intensifier tube, a protective housing, and may have some type of mounting system. Many NVDs also include a protective sacrificial lens, mounted over the front lens (ie. objective lens) on NVDs to protect the latter from damage by environmental hazards and some can incorporate [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |