
 A night-vision device (NVD), also known as a night optical/observation device (NOD), night-vision goggle (NVG), is an optoelectronic device that allows visualization of images in low levels of light, improving the user's night vision. The device enhances ambient visible light and converts
A night-vision device (NVD), also known as a night optical/observation device (NOD), night-vision goggle (NVG), is an optoelectronic device that allows visualization of images in low levels of light, improving the user's night vision. The device enhances ambient visible light and converts near-infrared
Infrared (IR), sometimes called infrared light, is electromagnetic radiation (EMR) with wavelengths longer than those of visible light. It is therefore invisible to the human eye. IR is generally understood to encompass wavelengths from around ...
light into visible light which can be seen by the user; this is known as I2 ( image intensification). By comparison, viewing of infrared thermal radiation
Thermal radiation is electromagnetic radiation generated by the thermal motion of particles in matter. Thermal radiation is generated when heat from the movement of charges in the material (electrons and protons in common forms of matter) is ...
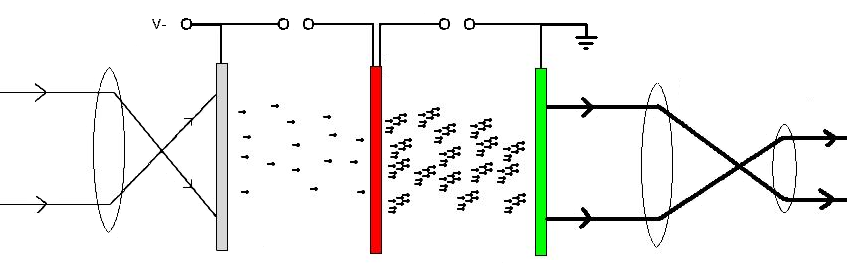
is referred to as thermal imaging and operates in a different section of the infrared spectrum. A night vision device usually consists of an image intensifier tube, a protective housing, and may have some type of mounting system. Many NVDs also include a protective sacrificial lens, mounted over the front lens (ie. objective lens) on NVDs to protect the latter from damage by environmental hazards and some can incorporate telescopic lenses. The image produced by an NVD is typically monochrome green, as green was considered to be the easiest color to look at for prolonged periods in the dark. Night vision devices may be passive, relying solely on ambient light, or may be active, using an IR (infrared) illuminator to better visualize the environment.
Night vision devices can be handheld but many are head-mounted and attach to helmets
A helmet is a form of protective gear worn to protect the head. More specifically, a helmet complements the skull in protecting the human brain. Ceremonial or symbolic helmets (e.g., a policeman's helmet in the United Kingdom) without prote ...
. When used with firearms, an IR laser sight is often mounted to the user's weapon. The laser sight produces an infrared beam that is only visible through an NVD and aids with aiming. Some night vision devices are specially made to be mounted to firearms. These can used in conjunction with weapon sights like rifle scopes or can be used as standalone sights; some thermal weapon sights have been designed to provide similar capabilities.
These devices were first used in World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the World War II by country, vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great power ...
and came into wide use during the Vietnam War
The Vietnam War (also known by #Names, other names) was a conflict in Vietnam, Laos, and Cambodia from 1 November 1955 to the fall of Saigon on 30 April 1975. It was the second of the Indochina Wars and was officially fought between North Vie ...
. The technology has evolved greatly since its introduction, leading to several "generations" of night-vision equipment with performance increases and price reductions. Consequently, though they are commonly used by the military and law enforcement
Law enforcement is the activity of some members of government who act in an organized manner to enforce the law by discovering, deterring, rehabilitating, or punishing people who violate the rules and norms governing that society. The term ...
agencies, night vision devices are available to civilian
Civilians under international humanitarian law are "persons who are not members of the armed forces" and they are not " combatants if they carry arms openly and respect the laws and customs of war". It is slightly different from a non-combatan ...
users for a wide range of applications including aviation, driving, demining, etc.
History
Early night vision technology used prior to the end of World War II has been described as Generation 0. In 1929 Hungarian physicist Kálmán Tihanyi invented an infrared-sensitive electronic television camera for anti-aircraft defense in the UK. Night-vision devices were introduced in the German Army as early as 1939 and were used inWorld War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the World War II by country, vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great power ...
. AEG started developing the first devices in 1935. In mid-1943, the German Army began the first tests with infrared night-vision (german: Nachtjäger) devices and telescopic rangefinders mounted on Panther tanks. Two different arrangements were constructed and used on Panther tanks. The Sperber FG 1250 ("Sparrow Hawk"), with a range of up to 600 m, had a 30 cm infrared searchlight and an image converter operated by the tank commander.
An experimental Soviet device called the PAU-2 was field-tested in 1942.
From late 1944 to March 1945 the German military conducted successful tests of FG 1250 sets mounted on Panther Ausf. G tanks (and other variants). Before World War II ended in 1945, approximately 50 (or 63) Panthers had been equipped with the FG 1250 and saw combat on both the Eastern and Western Fronts. The "Vampir" man-portable system for infantry was used with StG 44
The StG 44 (abbreviation of Sturmgewehr 44, "assault rifle 44") is a German assault rifle developed during World War II by Hugo Schmeisser. It is also known by its early designations as the MP 43 and MP 44 (''Maschinenpistole 43'' and ''44''). ...
assault rifles.
Parallel development of night-vision systems occurred in the US. The M1 and M3 infrared night-sighting devices, also known as the "sniperscope" or "snooperscope", saw limited service with the US Army in World War II and in the Korean War
{{Infobox military conflict
, conflict = Korean War
, partof = the Cold War and the Korean conflict
, image = Korean War Montage 2.png
, image_size = 300px
, caption = Clockwise from top: ...
, to assist snipers. These were active devices, using a large infrared light source to illuminate targets. Their image-intensifier tubes used an anode
An anode is an electrode of a polarized electrical device through which conventional current enters the device. This contrasts with a cathode, an electrode of the device through which conventional current leaves the device. A common mnemoni ...
and an S-1 photocathode, made primarily of silver
Silver is a chemical element with the Symbol (chemistry), symbol Ag (from the Latin ', derived from the Proto-Indo-European wikt:Reconstruction:Proto-Indo-European/h₂erǵ-, ''h₂erǵ'': "shiny" or "white") and atomic number 47. A soft, whi ...
, cesium
Caesium ( IUPAC spelling) (or cesium in American English) is a chemical element with the symbol Cs and atomic number 55. It is a soft, silvery-golden alkali metal with a melting point of , which makes it one of only five elemental metals that ...
, and oxygen
Oxygen is the chemical element with the symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group in the periodic table, a highly reactive nonmetal, and an oxidizing agent that readily forms oxides with most elements as we ...
, and electrostatic inversion with electron acceleration was used to achieve gain.
Examples
* PAU-2
* PNV-57A tanker goggles
* SU-49/PAS-5
* T-120 Sniperscope, 1st model (World War II)
* M2 Sniperscope, 2nd model (World War II)
* M3 Sniperscope, 4th model (Korean War)
* AN/PAS-4 (early Vietnam War)
After World War II, Vladimir K. Zworykin
Vladimir Kosma Zworykin; or with the patronymic as ''Kosmich''; or russian: Кузьмич, translit=Kuz'mich, label=none. Zworykin anglicized his name to ''Vladimir Kosma Zworykin'', replacing the patronymic with the name ''Kosma'' as a middle na ...
developed the first practical commercial night-vision device at Radio Corporation of America, intended for civilian use. Zworykin's idea came from a former radio-guided missile. At that time, infrared was commonly called '' black light'', a term later restricted to ultraviolet
Ultraviolet (UV) is a form of electromagnetic radiation with wavelength from 10 nm (with a corresponding frequency around 30 PHz) to 400 nm (750 THz), shorter than that of visible light, but longer than X-rays. UV radiati ...
. Zworykin's invention was not a success due to its size and cost.
United States
Generation 1
First-generation passive devices developed and patented by theUS Army
The United States Army (USA) is the land service branch of the United States Armed Forces. It is one of the eight U.S. uniformed services, and is designated as the Army of the United States in the U.S. Constitution.Article II, section 2, c ...
in the 1960s, introduced during the Vietnam War
The Vietnam War (also known by #Names, other names) was a conflict in Vietnam, Laos, and Cambodia from 1 November 1955 to the fall of Saigon on 30 April 1975. It was the second of the Indochina Wars and was officially fought between North Vie ...
, were an adaptation of earlier active GEN 0 technology and relied on ambient light instead of using an extra infrared light source. Using an S-20 photocathode, their image intensifiers produced a light amplification of around , but they were quite bulky and required moonlight to function properly.
Examples:
* AN/PVS-1 Starlight scope
* AN/PVS-2 Starlight scope
* AN/PAS 6 Varo Metascope
Generation 2 (GEN II)
Second-generation devices developed in the 1970s, featuring an improved image-intensifier tube using a micro-channel plate (MCP) with an S-25 photocathode, and resulted in a much brighter image, especially around the edges of the lens. This led to increased clarity in low ambient-light environments, such as moonless nights. Light amplification was around .Image resolution
Image resolution is the detail an image holds. The term applies to digital images, film images, and other types of images. "Higher resolution" means more image detail.
Image resolution can be measured in various ways. Resolution quantifies how cl ...
and reliability
Reliability, reliable, or unreliable may refer to:
Science, technology, and mathematics Computing
* Data reliability (disambiguation), a property of some disk arrays in computer storage
* High availability
* Reliability (computer networking), ...
were also improved.
Examples:
* AN/PVS-3 Miniaturized night vision sight
* AN/PVS-4
* AN/PVS-5
* SUPERGEN
Later advances in GEN II technology brought the tactical characteristics of "GEN II+" devices (equipped with better optics, SUPERGEN tubes, improved resolution and better signal-to-noise ratios), though GEN II+ is not formally recognized by the NVESD.
Generation 3 (GEN III)
Third-generation night-vision systems, developed in the late 1980s, maintained the MCP from Gen II, but used a photocathode made with gallium arsenide, which further improved image resolution. Gallium arsenide photocathodes are primarily manufactured by L3Harris Technologies and Elbit Systems of America and image light from 500-900 nm. In addition, the MCP is coated with an ion barrier film to increase tube life. However, the ion barrier causes fewer electrons to pass through, thus diminishing the improvement that the gallium-arsenide photocathode provides. Because of the ion barrier, the "halo" effect around bright spots or light sources is larger as well. Light amplification with these devices is improved to around –. Power consumption is higher than in GEN II tubes. Examples: * AN/PVS-7 * AN/NVS-7 * AN/PVS-10 * AN/PVS-14 * AN/PNVS-14 * AN/PVS-17 * CNVS-4949 * PN-21KAuto-gating
Autogating (ATG) is a function which rapidly switches the power supply's voltage to the photocathode on and off. However, these switches are rapid enough that they are not detectable to the human eye and peak voltage supplied to the night vision device is maintained. This achieves several purposes: first, it reduces the " duty cycle" (ie. the amount of time that the tube has power running through it) which increases the device's lifespan. Second, autogating enhances the BSP (Bright-Source Protection), which is the built-in system that reduces the voltage supplied to the photocathode in response to ambient light levels. ABC (Automatic Brightness Control) is a similar function which modulates the amount of voltage supplied to the microchannel plate (rather than the photocathode) in response to ambient light. Together, BSP and ABC (alongside the autogating function) serve to prevent temporary blindness for the user and prevent damage to the tube when the night vision device is exposed to sudden bright sources of light, like amuzzle flash
Muzzle flash is the light — both visible and infrared — created by a muzzle blast, which is caused by the sudden release and expansion of high-temperature, high-pressure gases from the muzzle of a firearm during shooting. Both the bl ...
or artificial lighting being switched on. These modulation systems also help maintain a steady illumination level in the user's view which improves the ability to keep "eyes on target" in spite of temporary flashes of light. These functions are especially useful for pilots, soldiers in urban environments, and special operations forces who may be exposed to dynamic, rapidly changing light levels.
Generation 3+ (GEN III OMNI I–IX)
 OMNI, or OMNIBUS, refers to a series of contracts through which the US Army purchased GEN III night vision devices. This started with OMNI I which procured AN/PVS-7A and AN/PVS-7B devices, then continued with OMNI II (1990), OMNI III (1992), OMNI IV (1996), OMNI V (1998), OMNI VI (2002), OMNI VII (2005), OMNI VIII, and OMNI IX.
However, OMNI is not a specification in and of itself. The performance of a particular GEN III OMNI device generally depends upon the tube which is used. For example, a GEN III OMNI III MX-10160A/AVS-6 tube will perform similarly to a GEN III VII MX-10160A/AVS-6 tube, even though the former was manufactured in ~1992 and the latter ~2005.
One particular technology, PINNACLE©, is often mentioned as well. It is a proprietary thin-film microchannel plate technology created by
OMNI, or OMNIBUS, refers to a series of contracts through which the US Army purchased GEN III night vision devices. This started with OMNI I which procured AN/PVS-7A and AN/PVS-7B devices, then continued with OMNI II (1990), OMNI III (1992), OMNI IV (1996), OMNI V (1998), OMNI VI (2002), OMNI VII (2005), OMNI VIII, and OMNI IX.
However, OMNI is not a specification in and of itself. The performance of a particular GEN III OMNI device generally depends upon the tube which is used. For example, a GEN III OMNI III MX-10160A/AVS-6 tube will perform similarly to a GEN III VII MX-10160A/AVS-6 tube, even though the former was manufactured in ~1992 and the latter ~2005.
One particular technology, PINNACLE©, is often mentioned as well. It is a proprietary thin-film microchannel plate technology created by ITT
ITT may refer to:
Communication
* Infantry-Tank Telephone, a device allowing infantrymen to speak to the occupants of armoured vehicles.
Mathematics
*Intuitionistic type theory, other name of Martin-Löf Type Theory
*Intensional type theory
B ...
(since combined with Exelis
''Exelis'' is a genus of moths in the family Geometridae erected by Achille Guenée in 1857.
Species
*''Exelis dicolus'' Rindge, 1952
*''Exelis mundaria'' Dyar, 1916
*''Exelis ophiurus'' Rindge, 1952
*''Exelis pyrolaria
''Exelis pyrolaria'', t ...
, acquired by Harris, then sold to Elbit Systems of America) that was included in the OMNI VII contract. The thin-film improves performance.
That being said, GEN III OMNI V–IX devices developed in the 2000s and onward can differ from standard GEN III and earlier GEN III OMNI I-IV devices in one or both of two important ways:
# An automatic gated power supply
A power supply is an electrical device that supplies electric power to an electrical load. The main purpose of a power supply is to convert electric current from a source to the correct voltage, current, and frequency to power the load. As a ...
system regulates the photocathode voltage, allowing the NVD to instantaneously adapt to changing light conditions.
# A removed or greatly thinned ion barrier (thin film) which decreases the number of electrons that are usually rejected by the standard GEN III MCP, hence resulting in less image noise. The disadvantage to a thin or removed ion barrier is the overall decrease in tube life from a theoretical mean time to failure ( MTTF) for standard Gen III type, to MTTF for thin film types. However, this is largely negated by the low number of image-intensifier tubes that reach of operation before requiring replacement.
While the consumer market sometimes classifies this type of system as ''generation 4'', the United States military describes these systems as ''generation 3 autogated'' tubes (GEN III OMNI V-IX). Moreover, as autogating power supplies can now be added to any previous generation of night-vision devices, "autogating" capability does not automatically class the devices as belonging to a particular OMNI classification. Any postnominals appearing after a generation type (i.e., Gen II+, Gen III+) do not change the generation type of the device, but instead indicate improvement(s) over the original specification's requirements.
Examples:
* AN/PVS-22
* NVS-22
* Binocular Night Vision Device (BNVD) ( AN/PVS-15, AN/PVS-21, AN/PVS-23, AN/PVS-31A, AN/PVS-31D)
* Ground Panoramic Night Vision Goggle ( GPNVG-18)
Figure of merit
Figure of merit (FoM) is a number which gives a quantitative measure of a night vision device's effectiveness and clarity. It is calculated using the number of line pairs per millimeter which a user can detect while using the device multiplied by the image intensifier's signal-to-noise ratio. In the late 1990s, innovations in photocathode technology significantly increased the signal-to-noise ratio, with newly developed tubes starting to surpass the performance of standard Gen 3 tubes. By 2001, the United States federal government concluded that a tube's "generation" was not a determinant factor of a tube's global performance, making the term "generation" irrelevant in determining the performance of an image-intensifier tube, and therefore eliminated the term as a basis of export regulations. Though image-intensification technology employed by different manufacturers varies, from the tactical point of view, a night-vision system is an optical device that enables vision in conditions of low light. The US government itself has recognized the fact that the technology itself makes little difference, as long as an operator can see clearly at night. Consequently, the United States bases export regulations not on the generation, but on the figure of merit. ITAR regulations specify that US-made tubes with a FOM greater than 1400 are not exportable outside the US; however, the Defense Technology Security Administration (DTSA) can waive that policy on a case-by-case basis.Fusion night vision
 Fusion night vision is a newer advance in night vision technology which combines I² ( image intensification) with thermal imaging, which functions in the medium (MWIR 3-5
Fusion night vision is a newer advance in night vision technology which combines I² ( image intensification) with thermal imaging, which functions in the medium (MWIR 3-5 µm
The micrometre ( international spelling as used by the International Bureau of Weights and Measures; SI symbol: μm) or micrometer (American spelling), also commonly known as a micron, is a unit of length in the International System of Unit ...
) and/or long (LWIR 8-14 µm) wavelength range. Initial models appeared in the 2000s and progressed in the 2010s. Some devices are dedicated fusion devices while others are clip-on thermal imagers which can add a thermal overlay to standard I² night vision devices. Fusion technologies combines the strengths of traditional I², which is excellent for navigation and discernment of fine details, with the strengths of thermal imaging, which excels in spotting the heat signatures of targets. Fusion systems have offered a number of different imaging modes including "fused" night vision with thermal overlay, night vision only, thermal only, and various special fusion modes like outline (which outlines objects that have thermal signatures) or "decamouflage", which highlights all objects that are of near-human temperatures. Fusion devices do struggle with weight and power usage and are often heavier and have shorter run times than contemporary I²-only devices.
Aside from fusion of I² and thermal imaging within a single device, some users have tried using an I² device over one eye and a thermal device over the other eye, relying on the human visual system to provide a binocular combined view of the two. Some, but not all, thermal imaging systems can also be viewed through a night vision device (ie. lining up the thermal imager in front of the I² night vision device) to produce a form of fusion vision.
Examples:
* AN/PSQ-20 ENVG (Enhanced Night Vision Goggles)
* AN/PSQ-36 FGE (Fusion Goggle Enhanced, previously FGS for Fusion Goggle System)
* AN/PSQ-42 ENVG-B (Enhanced Night Vision Goggles-Binocular)
* AN/PSQ-44 ENVG-B (Enhanced Night Vision Goggles-Binocular)
* AN/PAS-29 COTI/E-COTI: (Enhanced) Clip-On Thermal Imager
Out of Band (OOB)
Out of Band (OOB) refers to night vision technologies which operate outside of the 500-900 nm NIR (near infrared) range that traditional Gen III gallium arsenide tubes detect. Imaging outside the usual spectrum is possible with dedicated OOB image intensifier tubes or with clip-on devices. Two examples include Photonis' 4G HyMa (Hybrid Multi-Alkali) image intensifier tubes (bandwidth of 350-1100 nm, fromnear UV
NEAR or Near may refer to:
People
* Thomas J. Near, US evolutionary ichthyologist
* Near, a developer who created the higan emulator
Science, mathematics, technology, biology, and medicine
* National Emergency Alarm Repeater (NEAR), a former ...
to IR) and Safran Optics 1's AN/PAS-34 E-COSI (Enhanced Clip-On SWIR Imager), which clips onto standard night vision devices and provides an overlay (in the 900-1700 nm range), respectively.
OOB provides several advantages. First, OOB imaging makes better use of ambient light; while a standard Gen III/III+ device can only intensify light in the 500-900 nm NIR range, an OOB device also intensifies any UV light or SWIR light in the environment. As a result, an OOB device might be able to see more on a starlit night than a standard GEN III/III+ device could. Second, OOB imaging can help JTACs and other FACs when marking targets with a laser designator. Many laser designators use 1064nm light, which is barely visible to standard Gen III/III+ devices, so ground personnel may need to use a separate "see-spot" device to visually confirm that the designator's targeting laser is on target. OOB night vision devices, however, can easily image the 1064nm range.
Third, OOB light is not visible to most commercially available night vision devices. Despite ITAR restrictions, night vision technologies have proliferated among peer and near-peer countries and have also made their way into terrorist hands. For example, there has been documented use of night vision equipment by the Taliban
The Taliban (; ps, طالبان, ṭālibān, lit=students or 'seekers'), which also refers to itself by its state name, the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan, is a Deobandi Islamic fundamentalist, militant Islamist, jihadist, and Pas ...
Red Unit. As a result, if friendly forces are using night vision equipment like IR illuminators, IR strobe
A beacon is an intentionally conspicuous device designed to attract attention to a specific location. A common example is the lighthouse, which draws attention to a fixed point that can be used to navigate around obstacles or into port. More mode ...
s, IR lasers, etc. then hostile forces using night vision equipment could spot them as well. OOB strobes, illuminators, and lasers, on the other hand, are easily visible when using OOOB night vision but much more difficult to spot with current Gen III/III+ night vision equipment as they appear faintly if at all (depending on wavelength and intensity).
Additionally, depending on the wavelengths covered by an OOB imaging device, users might be able to observe the lasers used in laser rangefinders as they often operate in the 1550nm range.
Examples (ground personnel, helmet-mounted imagers):
*Photonis 4G INTENS image intensifier tubes (350-1100 nm)
*Optics 1 AN/PAS-34 E-COSI (Enhanced Clip-On SWIR Imager) (900-1700 nm)
*Optics 1 COSMO (Clip-On SWIR Monocular)
Examples (ground personnel, weapon-mounted lasers):
*B.E. Meyers & Co. MAWL-CLAD (Modular Aiming Weapon Laser--Covert Laser Aiming Device) (1064 nm laser)
*LA-17/PEQ D-PILS (Dual-band Pointer and Illuminator Laser System) (1400-1600 nm)
* Rheinmetall LM-VAMPIR (Laser Module--VAriable Multi Purpose InfraRed)
* AN/PSQ-23 STORM, STORM-PI, STORM-SLX, STORM II; and L3Harris SPEAR (1570 nm)
*Optics 1 ICUGR (Integrated Compact Ultralight Gun-mounted Rangefinder) (1550 nm)
*Rheinmetall FCS-RPAL (Fire Control System--Rheinmetall Precision Aiming Laser) (1550 nm)
*Rheinmetall FCS-TRB (Fire Control System--TacRay Ballistic) (1550 nm)
*Wilcox RAPTAR S (Rapid Targeting and Ranging Module) (1550 nm)
*Wilcox MRF Xe (Micro Range Finder--Enhanced) (1550 nm)
*B.E. Meyers & Co. IZLID Ultra 1064 and 1550 (Infrared Zoom Laser Illuminator Designator) (1064 nm, 1550 nm)
*Optics 1 CTAM (Coded Target Acquisition Marker) (1064 nm)
Wide Field of View (WFoV)
Night vision devices, whether monocular or binocular, typically have a limited field of view (FoV); the commonly used AN/PVS-14 has a FoV of 40° which is rather less than the 95° monocular horizontal FoV and 190° binocular horizontal FoV that humans possess. Due to the limited FoV, users must visually scan about to fully check their surroundings, which is a time consuming process. This limitation is particularly evident when using night vision devices for flying, driving, or CQB where split second decisions must be made. Because of these limitations, many SOF troops preferred to use white light rather than night vision when conducting CQB. As a result, much time and effort has gone into research to develop a wider FoV solution for night vision devices. As of 2021, there were three primary methods for increasing peripheral vision in night vision devices (each with their own advantages and disadvantages): *Panoramic night vision goggles (PNVG) *Foveated night vision goggles (F-NVG) *Diverging image tube night vision goggles (DIT-NVG) Panoramic night vision goggles (PNVG) increase field of view by increasing the number of sensors: if tubes are generally limited to 40°, then one can add more tubes to increase peripheral vision. This solution works well and does not compromise device performance or visual clarity but comes at the cost of size, weight, power requirements, and complexity. A well-known set of peripheral NVGs is the GPNVG-18 (Ground Peripheral Night Vision Goggle), which was used in the raid in Abottabad that killed Osama Bin Laden. These goggles, and the aviation AN/AVS-10 PNVG from which they were derived, offer a 97° FoV. Foveated night vision (F-NVG) uses specialized WFoV optics to increase the field of view through a night vision intensifier tube. Thefovea
Fovea () (Latin for "pit"; plural foveae ) is a term in anatomy. It refers to a pit or depression in a structure.
Human anatomy
* Fovea centralis of the retina
* Fovea buccalis or Dimple
* Fovea of the femoral head
*Trochlear fovea of the f ...
refers to the part of the retina
The retina (from la, rete "net") is the innermost, light-sensitive layer of tissue of the eye of most vertebrates and some molluscs. The optics of the eye create a focused two-dimensional image of the visual world on the retina, which then ...
which is responsible for central vision. These night vision devices have users still look "straight through" the tubes so light passing through the center of the tube falls on the foveal retina, as is the case with traditional binocular NVGs. While these devices increase FoV, it comes at the price of image quality and edge distortions. A US Naval contract for US$47.6 million was awarded to Kent Optronics to retrofit AN/PVS-15 units with WFoV optics that expanded them to 80° FoV with less than 4% distortion.
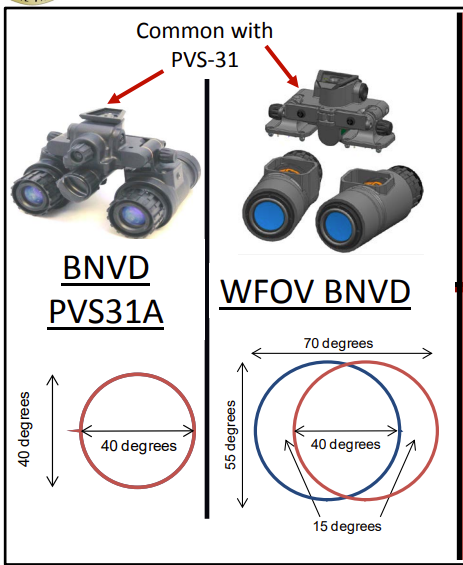 Diverging image tube (DIT) night vision increases FoV by positioning the night vision tubes so they are no longer parallel but are angled slightly outward. This increases peripheral FoV but causes distortion and reduced image quality. Unfortunately, optical clarity is best when looking through the center of an image intensifier tube. With DIT, users are no longer looking "straight through" the center of the tubes (which provides the clearest images) and light passing through the center of the tubes no longer falls on the fovea (the area of clearest vision). The AN/PVS-25 was one such example of DIT night vision from the late 2000s. The WFoV BNVD is a variant of the AN/PVS-31A which incorporates both F-NVG and DIT-NVG concepts: the foveal WFoV optics increase the FoV of each tube from 40° to 55°, while the slight angulation of the tubes positions them so there is a 40° overlap of binocular vision in the center and a total 70° bi-ocular FoV. With the performance of the modified AN/PVS-31A tubes used, the WFoV BNVD has a FoM of 2706 which is better than the FoM in both the GPNVG-18 and the standard AN/PVS-31A.
Examples:
*Panoramic NVG (PNVG):
** GPNVG-18
** AN/AVS-10 (PNVG)
*Foveated NVG (F-NVG):
**WFoV F-NVG retrofit AN/PVS-15 goggles
**WFoV BNVD (combined F-NVG and DIT-NVG variant of AN/PVS-31A)
*Diverging Image Tube NVG (DIT-NVG)
** AN/PVS-25
**WFoV BNVD (combined F-NVG and DIT-NVG variant of AN/PVS-31A)
**Noise Fighters Panobridge: binocular bridge mount which combines two AN/PVS-14 monoculars and allows them to be angulated outward or positioned parallel for DIT or traditional configuration
Diverging image tube (DIT) night vision increases FoV by positioning the night vision tubes so they are no longer parallel but are angled slightly outward. This increases peripheral FoV but causes distortion and reduced image quality. Unfortunately, optical clarity is best when looking through the center of an image intensifier tube. With DIT, users are no longer looking "straight through" the center of the tubes (which provides the clearest images) and light passing through the center of the tubes no longer falls on the fovea (the area of clearest vision). The AN/PVS-25 was one such example of DIT night vision from the late 2000s. The WFoV BNVD is a variant of the AN/PVS-31A which incorporates both F-NVG and DIT-NVG concepts: the foveal WFoV optics increase the FoV of each tube from 40° to 55°, while the slight angulation of the tubes positions them so there is a 40° overlap of binocular vision in the center and a total 70° bi-ocular FoV. With the performance of the modified AN/PVS-31A tubes used, the WFoV BNVD has a FoM of 2706 which is better than the FoM in both the GPNVG-18 and the standard AN/PVS-31A.
Examples:
*Panoramic NVG (PNVG):
** GPNVG-18
** AN/AVS-10 (PNVG)
*Foveated NVG (F-NVG):
**WFoV F-NVG retrofit AN/PVS-15 goggles
**WFoV BNVD (combined F-NVG and DIT-NVG variant of AN/PVS-31A)
*Diverging Image Tube NVG (DIT-NVG)
** AN/PVS-25
**WFoV BNVD (combined F-NVG and DIT-NVG variant of AN/PVS-31A)
**Noise Fighters Panobridge: binocular bridge mount which combines two AN/PVS-14 monoculars and allows them to be angulated outward or positioned parallel for DIT or traditional configuration
Digital
Some night vision devices, including several of the ENVG models, are digital, which allows electronic transmission of the device's night vision view, though this often comes at the price of size, weight, power usage.Other technologies
Ceramic Optical Ruggedized Engine (CORE) is a technology which was first shown at the 2012 SHOT Show in Las Vegas, NV by Armasight. CORE produces a higher-performance Gen 1 tubes. The main difference between CORE tubes and standard Gen 1 tubes is introduction of a ceramic plate instead of a glass one. This plate is produced from specially formulated ceramic and metal alloys. Edge distortion is improved, photo sensitivity is increased, and the resolution can be as high as 60 /mm. CORE is still considered Gen 1, as it does not utilize a microchannel plate. Scientists at theUniversity of Michigan
, mottoeng = "Arts, Knowledge, Truth"
, former_names = Catholepistemiad, or University of Michigania (1817–1821)
, budget = $10.3 billion (2021)
, endowment = $17 billion (2021)As o ...
have developed a contact lens that can act as a night-vision device. The lens has a thin strip of graphene
Graphene () is an allotrope of carbon consisting of a Single-layer materials, single layer of atoms arranged in a hexagonal lattice nanostructure.
between layers of glass that reacts to photons to make dark images look brighter. Current prototypes only absorb 2.3% of light, so the percentage of light pickup has to rise before the lens can be viable. The graphene technology can be expanded into other uses, like car windshields, to improve night-driving. The US. Army is interested in the technology to potentially replace night-vision goggles.
The Sensor and Electron Devices Directorate (SEDD) of the United States Army Research Laboratory, US Army Research Laboratory developed quantum-well infrared detector (QWID) technology. This technology's epitaxial layers, which result in diode formation, compose a gallium arsenide or aluminum gallium arsenide system (GaAs or AlGaAs). It is particularly sensitive to infrared waves that are mid-long lengths. The Corrugated QWIP (CQWIP) broadens detection capacity by using a resonance superstructure to orient more of the electric field parallel, so that it can be absorbed. Although cryogenic cooling between 77 K and 85 K is required, QWID technology is considered for constant surveillance viewing due to its claimed low cost and uniformity in materials.
Materials from the II–VI compounds, such as HgCdTe, are used for high-performing infrared light-sensing cameras. In 2017 the US Army Research Labs in collaboration with Stony Brook University
Stony Brook University (SBU), officially the State University of New York at Stony Brook, is a public research university in Stony Brook, New York. Along with the University at Buffalo, it is one of the State University of New York syste ...
developed an alternative within the III–V family of compounds. InAsSb, a III–V compound, is commonly used commercially for opto-electronics in items such as DVDs and cell phones. To counteract this possibility in implementing InAsSb, scientists added a graded layer with increased atomic spacing and an intermediate layer of the substrate GaAs to trap any potential defects. This technology was designed with night-time military operations in mind.
Soviet Union and Russia


 The
The Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, ...
, and after 1991 the Russian Federation
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and Northern Asia
North Asia or Northern Asia, also referred to as Siberia, is the northern region of Asia, which is defined in geographic ...
, have developed a range of night-vision devices. Models used after 1960 by the Russian/Soviet Army are designated ''1PNxx'' ( rus, 1ПНxx), where ''1PN'' is the GRAU index
The Main Missile and Artillery Directorate of the Ministry of Defense of the Russian Federation (), commonly referred to by its transliterated Russian acronym GRAU (), is a department of the Russian Ministry of Defense. It is subordinate to the ...
of night-vision devices. The PN stands for ''pritsel nochnoy'' ( rus, прицел ночной), meaning "night sight", and the ''xx'' is the model number. Different models introduced around the same time use the same type of batteries and mechanism for mounting on the weapon. The multi-weapon models have replaceable elevation scales, with one scale for the ballistic arc of each supported weapon. The weapons supported include the AK family, sniper rifle
A sniper rifle is a high-precision, long-range rifle. Requirements include accuracy, reliability, mobility, concealment and optics for anti-personnel, anti-materiel and surveillance uses of the military sniper. The modern sniper rifle is a ...
s, light machine gun
A light machine gun (LMG) is a light-weight machine gun designed to be operated by a single infantryman, with or without an assistant, as an infantry support weapon. LMGs firing cartridges of the same caliber as the other riflemen of the ...
s and hand-held grenade launchers.
* 1PN34 refractor-based night sight for a range of small arms and grenade launchers, see photo.
* 1PN50 refractor-based night observation binoculars.
* 1PN51 1PN51 ( rus, 1ПН51) is the GRAU index for a Soviet designed passive night scope for a range of Soviet designed small arms and grenade launchers. ''1PN'' is the GRAU index of night vision devices, where PN stands for ''Nochnoy Pritsel'' ( rus, Н� ...
reflector-based night sight for a range of small arms and grenade launchers.
* 1PN51-2 1PN51-2 ( rus, 1ПН51-2) is the GRAU index for a Soviet designed passive night scope for the RPG-29 rocket launcher. ''1PN'' is the GRAU index of night vision devices, where PN stands for ''Nochnoy Pritsel'' ( rus, Ночной прицел) meanin ...
reflector-based night sight for the RPG-29.
* 1PN58
1PN58 ( rus, 1ПН58) is the GRAU index for a Soviet designed passive night scope for a range of Soviet designed small arms and grenade launchers. ''1PN'' is the GRAU index of night vision devices, where PN stands for ''Nochnoy Pritsel'' ( rus, Н ...
refractor-based night sight for a range of small arms and grenade launchers.
* 1PN93-2 reflector-based night sight for the RPG-7D3, see photo.
* 1PN110, a more recent (~Gen 3) night sight for the RPG-29.
* 1PN113, a night sight similar to the 1PN110, for the SV-98 sniper rifle.
The Russian army has also contracted the development of and fielded a series of so-called ( ru , Антиснайпер , translit = Antisnayper). The counter-sniper night sight is an active system that uses laser pulses from a laser diode to detect reflections from the focal elements of enemy optical systems and estimate their range. The vendor claims that this system is unparalleled:
* 1PN106 counter-sniper night sight for the SVD sniper rifle and its SVDS variant.
* 1PN119 counter-sniper night sight for the PKMN and Pecheneg light machine guns.
* 1PN120 counter-sniper night sight for the SVDK sniper rifle.
* 1PN121 counter-sniper night sight for the ASVK
The KSVK 12.7 (russian: Крупнокалиберная Снайперская Винтовка Ковровская (''Krupnokalibernaya Snayperskaya Vintovka Kovrovskaya''); en, Large-Caliber Kovrov Sniper Rifle) or Degtyarev sniper rifle is ...
large caliber sniper rifle.
* 1PN123 counter-sniper night sight for the SV-98 sniper rifle.
Legality
*Belgium
Belgium, ; french: Belgique ; german: Belgien officially the Kingdom of Belgium, is a country in Northwestern Europe. The country is bordered by the Netherlands to the north, Germany to the east, Luxembourg to the southeast, France to ...
: firearms legislation forbids any night-vision device if it can be mounted on a firearm; even if not mounted, they are considered illegal.
* Czech Republic
The Czech Republic, or simply Czechia, is a landlocked country in Central Europe. Historically known as Bohemia, it is bordered by Austria to the south, Germany to the west, Poland to the northeast, and Slovakia to the southeast. Th ...
: not regulated.,
Previously only available for hunting.
* Germany
Germany, officially the Federal Republic of Germany (FRG),, is a country in Central Europe. It is the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany lies between the Baltic and North Sea to the north and the Alps to the sou ...
: law forbids such devices if their purpose is to be mounted on firearms. Due to the African swine fever virus exceptions for hunting wild boar
The wild boar (''Sus scrofa''), also known as the wild swine, common wild pig, Eurasian wild pig, or simply wild pig, is a suid native to much of Eurasia and North Africa, and has been introduced to the Americas and Oceania. The species is ...
s were made around 2021.
* Iceland
Iceland ( is, Ísland; ) is a Nordic island country in the North Atlantic Ocean and in the Arctic Ocean. Iceland is the most sparsely populated country in Europe. Iceland's capital and largest city is Reykjavík, which (along with its ...
: the use of night-vision devices for hunting is prohibited, while there are no restrictions on the devices themselves.
* India
India, officially the Republic of India ( Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the ...
: civilian possession and trading of night-vision scopes is illegal. Permission is needed from Union home ministry for possession.
* Netherlands
)
, anthem = ( en, "William of Nassau")
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, subdivision_type = Sovereign state
, subdivision_name = Kingdom of the Netherlands
, established_title = Before independence
, established_date = Spanish Netherl ...
: the possession of night-vision devices is not regulated, night-vision devices mounted on firearms are forbidden unless a permit is granted. The usage of night-vision equipment for night-time hunting (weapon mounted) is allowed only with a special permit in certain areas (the Veluwe) for hunting wild boar.
* New Zealand
New Zealand ( mi, Aotearoa ) is an island country in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It consists of two main landmasses—the North Island () and the South Island ()—and over 700 List of islands of New Zealand, smaller islands. It is the ...
: rescue helicopter services use several sets of 3rd-generation night-vision goggles imported from the US, and the country is required to restrict access to the equipment to comply with the strict regulations regarding their export."Seeing in the Dark", ''Vector'', magazine of the Civil Aviation Authority of New Zealand, January/February 2008, pages 10–11. There are no prohibitions on the ownership or use of night-vision equipment for shooting non-indigenous game animals, such as rabbits, hares, deer, pigs, tahr
Tahrs ( , ) or tehrs ( ) are large artiodactyl ungulates related to goats and sheep. There are three species, all native to Asia. Previously thought to be closely related to each other and placed in a single genus, ''Hemitragus'', genetic ...
, chamois, goats, wallabies, etc.
* United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 U.S. state, states, a Washington, D.C., federal district, five ma ...
: a 2010–2011 summary of state hunting regulations for the use of night-vision equipment in hunting listed 13 states in which the equipment is prohibited, 17 states with various restrictions (e.g. only for certain non-game species, and/or in a certain date range), and 20 states without restrictions. It did not summarize the regulations for thermal-imaging equipment.
** California
California is a state in the Western United States, located along the Pacific Coast. With nearly 39.2million residents across a total area of approximately , it is the most populous U.S. state and the 3rd largest by area. It is also the ...
: it is a misdemeanor to possess a device "designed for or adaptable to use on a firearm which, through the use of a projected infrared light source and electronic telescope, enables the operator thereof to visually determine and locate the presence of objects during the night-time". This essentially covers scopes using Gen0 technology, but not the subsequent generations. There was an effort in 1995 to further expand restrictions to forbid night-vision devices that did not incorporate a light source, but it did not become law.
** Minnesota
Minnesota () is a state in the upper midwestern region of the United States. It is the 12th largest U.S. state in area and the List of U.S. states and territories by population, 22nd most populous, with over 5.75 million residents. Minne ...
, as of 2014, "A person may not possess night vision or thermal imaging equipment while taking wild animals or while having in possession n uncased and loaded weaponthat could be used to take wild animals." There is an exception for law-enforcement and military use. The night-vision prohibition was enacted in 2007, and the thermal-imaging prohibition was added in 2014. Two bills were introduced in the Minnesota Legislature in 2016, proposing to allow night-vision and thermal-imaging equipment for, respectively, 1) "predator" or 2) "unprotected wild animal" hunting.
See also
* * * * * * *References
External links
TNVC guide to night vision generations and specifications
on 19 July 2021
Nitewalker guide to night vision equipment
on 15 August 2021
Night Vision Devices Modeling and Optimal Design
on 6 May 2022 * * * *
US patents
* * * * * * {{DEFAULTSORT:Night Vision Device Armoured fighting vehicle vision and sighting equipment Military electronics Military sensor technology Night vision devices