|
Russian Astronomy
This list of Russian astronomers and astrophysicists includes the famous astronomers, astrophysicists and cosmologists from the Russian Empire, the Soviet Union and the Russian Federation. Alphabetical list __NOTOC__ A *Tateos Agekian, one of the pioneers of Russian and world Stellar dynamics, discoverer of two evolutionary sequences of stellar systems: nearly spherical and strongly flattened *Vladimir Albitsky, discovered a significant number of asteroids *Viktor Ambartsumian, one of the founders of theoretical astrophysics, discoverer of stellar associations, founder of Byurakan Observatory in Armenia *Andrejs Auzāns, director of the Tashkent observatory, 1911-1916 B * Nikolai P. Barabashov, co-author of the ground breaking publication of the first pictures of the far side of the Moon in 1961, called ''Atlas of the Other Side of the Moon''; a crater and a planet were named after him *Vladimir Belinski, an author of the BKL singularity model of the Universe evolution * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pulkovo
Pulkovo may refer to: *Pulkovo Heights marking the southern limit of Saint Petersburg, Russia *Pulkovo Airport serving Saint Petersburg, Russia *Pulkovo Aviation Enterprise, a former (until 2006) state airline based in Saint Petersburg, Russia *Pulkovo Observatory, The Central Astronomical Observatory of the Russian Academy of Sciences at Pulkovo, 19 km south of Saint Petersburg {{Disambig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tashkent
Tashkent (, uz, Toshkent, Тошкент/, ) (from russian: Ташкент), or Toshkent (; ), also historically known as Chach is the capital and largest city of Uzbekistan. It is the most populous city in Central Asia, with a population of 2,909,500 (2022). It is in northeastern Uzbekistan, near the border with Kazakhstan. Tashkent comes from the Turkic ''tash'' and ''kent'', literally translated as "Stone City" or "City of Stones". Before Islamic influence started in the mid-8th century AD, Tashkent was influenced by the Sogdian and Turkic cultures. After Genghis Khan destroyed it in 1219, it was rebuilt and profited from the Silk Road. From the 18th to the 19th century, the city became an independent city-state, before being re-conquered by the Khanate of Kokand. In 1865, Tashkent fell to the Russian Empire; it became the capital of Russian Turkestan. In Soviet times, it witnessed major growth and demographic changes due to forced deportations from throughout the Sov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
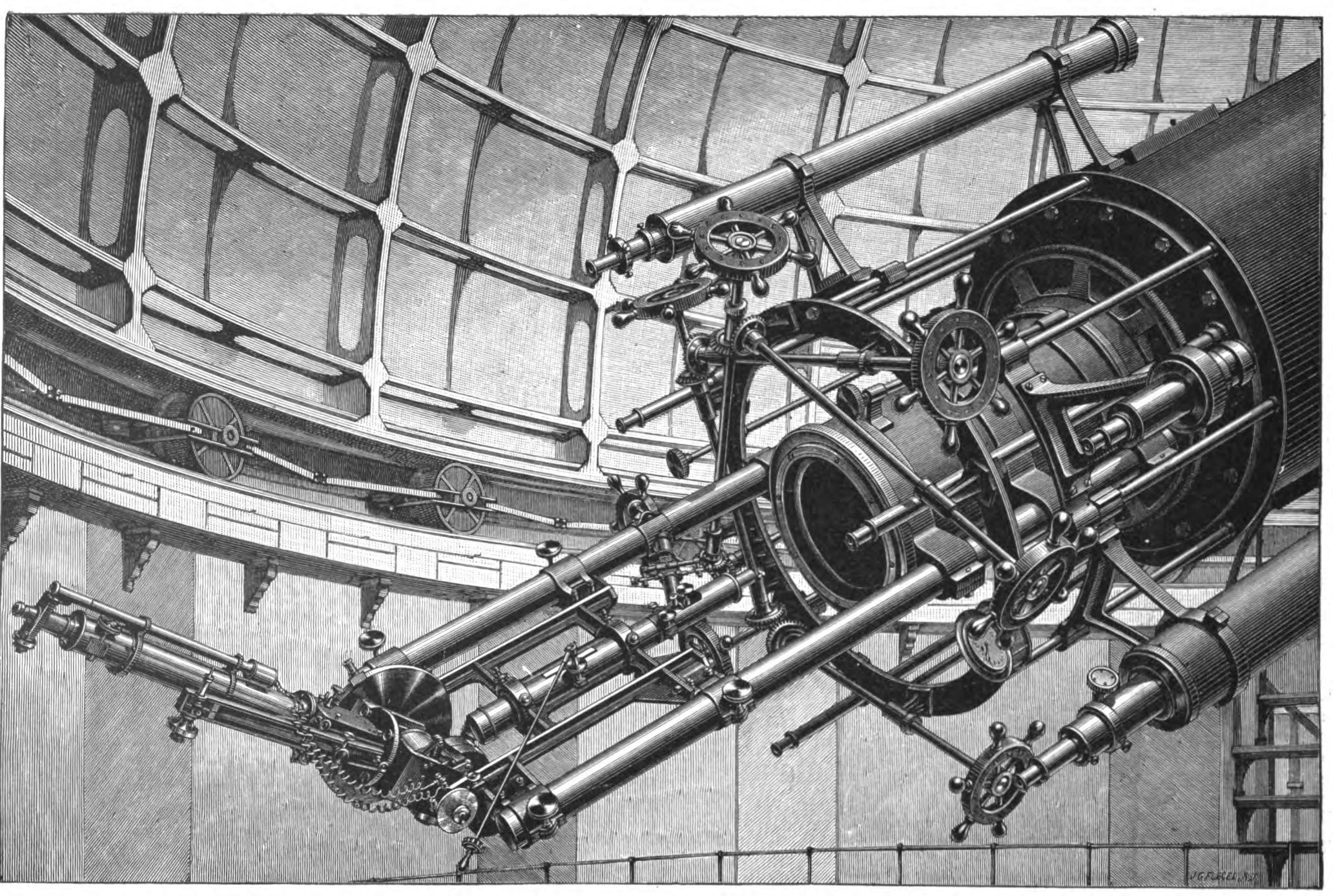
Fyodor Bredikhin
Fyodor Aleksandrovich Bredikhin (russian: Фёдор Александрович Бредихин, 8 December 1831 – 14 May 1904 ( O.S.: 1 May)) was a Russian astronomer. His surname is sometimes given as Bredichin in the literature, and non-Russian sources sometimes render his first name as Theodor. Information In 1857 he joined the staff of the observatory at Moscow University, becoming its director in 1873. In 1890 he became director of Pulkovo Observatory (until 1894) and in the same year became a member of the Russian Academy of Sciences. He studied the theory of comet tails, and also studied meteors and meteor showers. The asteroid 786 Bredichina and the crater Bredikhin on the Moon are named after him. The is awarded by the Russian Academy of Sciences The Russian Academy of Sciences (RAS; russian: Росси́йская акаде́мия нау́к (РАН) ''Rossíyskaya akadémiya naúk'') consists of the national academy of Russia; a network of scientific ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Semion Braude
Semion Yakovlevich Braude ( uk, Семен Якович Брауде; 28 January 1911 – 29 June 2003) was a Soviet and Ukrainian physicist and radio astronomer. Of Ashkenazi Jewish descent, Braude was born in Poltava, Ukraine, and pursued his higher education at the National University of Kharkiv, receiving his undergraduate degree from the Physics and Mathematics Department in 1932. He then joined the staff of the Laboratory of Electromagnetic Oscillations (LEMO) at the Ukrainian Physico-Technical Institute (UPTI), and also began graduate work at KU. His mentor was Abram A. Slutskin, professor at KU as well as head of the LEMO. Much of the activities of the LEMO involved the development of magnetrons for generating ultra high frequency (UHF) signals. In 1936, the LEMO was tasked to study the application of magnetrons in a pulsed radio-location (radar) system for use by anti-aircraft batteries. For this project, Braude designed a superheterodyne receiver, using a low-power, tunabl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sergey Blazhko
Sergey Nikolayevich Blazhko (''Сергей Николаевич Блажко'' in Russian) (November 17, 1870 – February 11, 1956, Moscow) was a Russian and Soviet astronomer, a corresponding member of the Academy of Sciences of the Soviet Union (1929). He was a graduate of Moscow State University and held a number of positions there including head of the Moscow Observatory from 1920-1931. He discovered a secondary variation of the amplitude and period of some RR Lyrae stars and related pulsating variables, now known as the Blazhko effect. Sergey Blazhko was awarded the Stalin Prize (1952), two Orders of Lenin, two other orders and numerous medals. The crater Blazhko on the Moon The Moon is Earth's only natural satellite. It is the fifth largest satellite in the Solar System and the largest and most massive relative to its parent planet, with a diameter about one-quarter that of Earth (comparable to the width of ... is named after him. References {{DEFAULTSORT:B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gennady S
Gennady ( rus, Геннадий, p=ɡʲɪˈnadʲɪj), also spelled Gennadi or Gennadiy, is a Russian male name. They are derived from the Greek given name Gennadius. People *Gennady Gladkov, Soviet and Russian composer *Gennady Golovkin, Kazakh boxer *Gennady Gudkov, Russian politician and businessman *Gennadi Karponosov, Soviet and Russian Olympic and world champion ice dancer and coach *Gennady Korotkevich, Belarusian sport programmer *Gennady Logofet, Soviet and Russian footballer and football coach *Gennady Semenovich Makanin, Russian mathematician *Gennady Mikhasevich, prolific Soviet serial killer and rapist *Gennady of Novgorod, Russian archbishop *Gennady Padalka, Russian cosmonaut *Gennady Rozhdestvensky, Soviet and Russian conductor *Gennadi Syomin, Russian footballer and football coach *Genndy Tartakovsky, Russian-American cartoonist *Gennady Yanayev, the only vice president of the Soviet Union *Gennady Zyuganov, Russian political party leader and assemblyman *Giennadij J ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sergey Belyavsky
Sergey Ivanovich Belyavsky (russian: Серге́й Ива́нович Беля́вский; December 7, 1883 (Julian calendar: November 25) – October 13, 1953) was a Soviet/Russian astronomer and a discoverer of 36 numbered minor planets. His last name is also alternatively spelled Beljavskij (name under which the Minor Planet Center credits him) or Beljawskij. His first name is occasionally given as "Sergius". He was born in St. Petersburg and was a member of the Academy of Sciences of the Soviet Union. His field of work included astrophotometry, astrometry, and the study of variable stars. He died in Leningrad. He discovered the bright naked-eye comet C/1911 S3 (Beljawsky), also known according to the nomenclature of the time as "Comet 1911 IV" or "Comet 1911g". Belyavsky observed at Simeiz Observatory (Симеиз) in Crimea. Between 1937 and 1944, Belyavsky was the seventh director of the Pulkovo Observatory The Pulkovo Astronomical Observatory (russian: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stellar Spectra
Astronomical spectroscopy is the study of astronomy using the techniques of spectroscopy to measure the spectrum of electromagnetic radiation, including visible light, ultraviolet, X-ray, infrared and radio waves that radiate from stars and other celestial objects. A stellar spectrum can reveal many properties of stars, such as their chemical composition, temperature, density, mass, distance and luminosity. Spectroscopy can show the velocity of motion towards or away from the observer by measuring the Doppler shift. Spectroscopy is also used to study the physical properties of many other types of celestial objects such as planets, nebulae, galaxies, and active galactic nuclei. Background Astronomical spectroscopy is used to measure three major bands of radiation in the electromagnetic spectrum: visible light, radio waves, and X-rays. While all spectroscopy looks at specific bands of the spectrum, different methods are required to acquire the signal depending on the frequency. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Doppler Effect
The Doppler effect or Doppler shift (or simply Doppler, when in context) is the change in frequency of a wave in relation to an observer who is moving relative to the wave source. It is named after the Austrian physicist Christian Doppler, who described the phenomenon in 1842. A common example of Doppler shift is the change of pitch heard when a vehicle sounding a horn approaches and recedes from an observer. Compared to the emitted frequency, the received frequency is higher during the approach, identical at the instant of passing by, and lower during the recession. The reason for the Doppler effect is that when the source of the waves is moving towards the observer, each successive wave crest is emitted from a position closer to the observer than the crest of the previous wave. Therefore, each wave takes slightly less time to reach the observer than the previous wave. Hence, the time between the arrivals of successive wave crests at the observer is reduced, causing an increa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spectrograph
An optical spectrometer (spectrophotometer, spectrograph or spectroscope) is an instrument used to measure properties of light over a specific portion of the electromagnetic spectrum, typically used in spectroscopic analysis to identify materials. The variable measured is most often the light's intensity but could also, for instance, be the polarization state. The independent variable is usually the wavelength of the light or a unit directly proportional to the photon energy, such as reciprocal centimeters or electron volts, which has a reciprocal relationship to wavelength. A spectrometer is used in spectroscopy for producing spectral lines and measuring their wavelengths and intensities. Spectrometers may operate over a wide range of non-optical wavelengths, from gamma rays and X-rays into the far infrared. If the instrument is designed to measure the spectrum on an absolute scale rather than a relative one, then it is typically called a spectrophotometer. The majority o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aristarkh Belopolsky
Aristarkh Apollonovich Belopolsky (Аристарх Аполлонович Белопольский) (, Moscow – 16 May 1934, Pulkovo, Leningrad) was a Russian astronomer. He was born in Moscow but his father's ancestors are from a Serbian town called Belo Polje. Life Belopolsky got his degree at Moscow University in 1876, and in 1878, he became the assistant to Fyodor Aleksandrovich Bredikhin at Moscow Observatory. In 1888, he joined the staff of Pulkovo Observatory. He worked in spectroscopy and discovered a number of spectroscopic binaries. Among others, he discovered that Castor B was a spectroscopic binary with a period of 2.92 days. Belopolsky was known for his fine instrument making, and in 1900 he built a device for measuring the Doppler shift of spectra. He pioneered the use of optical Doppler shift to measure the rotational rates of distant objects. He was the first to discover that the equator of Jupiter rotates more rapidly than higher latitudes, and that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Igor Belkovich
Igor Vladimirovich Belkovich (Игорь Владимирович Белькович) (October 15, 1904 ( OS: October 2) – May 30, 1949) was a Soviet astronomer. His son Oleg Igorevich Belkovich was also an astronomer. The crater Belkovich on the Moon The Moon is Earth's only natural satellite. It is the fifth largest satellite in the Solar System and the largest and most massive relative to its parent planet, with a diameter about one-quarter that of Earth (comparable to the width of ... is named after him. External links *Biography by his son Soviet astronomers 1904 births 1949 deaths {{europe-astronomer-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |