|
Russell J. Howard
Russell J. Howard is an Australian-born executive, entrepreneur and scientist. He was a pioneer in the fields of molecular parasitology, especially malaria, and in leading the commercialisation of one of the most important methods used widely today in molecular biology today called “ DNA shuffling" or "Molecular breeding", a form of "Directed evolution". His contributions to malaria research over an 18-year period began in Australia at the Walter and Eliza Hall Institute of Medical Research, then continued as a tenured Principal Investigator at the National Institutes of Health (NIH) in Bethesda, MD, USA, and continued at the biotechnology companies DNAX (now Schering-Plough Biopharma) anAffymaxin California. Thirteen years of his group's malaria research on antigenic variation in malaria culminated in the first molecular cloning of the malarial antigen PfEMP1, a parasite protein that this human malaria parasite expresses on the surface of malaria-infected red cells This antig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biotechnology
Biotechnology is the integration of natural sciences and engineering sciences in order to achieve the application of organisms, cells, parts thereof and molecular analogues for products and services. The term ''biotechnology'' was first used by Károly Ereky in 1919, meaning the production of products from raw materials with the aid of living organisms. Definition The concept of biotechnology encompasses a wide range of procedures for modifying living organisms according to human purposes, going back to domestication of animals, cultivation of the plants, and "improvements" to these through breeding programs that employ artificial selection and hybridization. Modern usage also includes genetic engineering as well as cell and tissue culture technologies. The American Chemical Society defines biotechnology as the application of biological organisms, systems, or processes by various industries to learning about the science of life and the improvement of the value of materials ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Melbourne
The University of Melbourne is a public research university located in Melbourne, Australia. Founded in 1853, it is Australia's second oldest university and the oldest in Victoria. Its main campus is located in Parkville, an inner suburb north of Melbourne's central business district, with several other campuses located across Victoria. Incorporated in the 19th century by the colony of Victoria, the University of Melbourne is one of Australia's six sandstone universities and a member of the Group of Eight, Universitas 21, Washington University's McDonnell International Scholars Academy, and the Association of Pacific Rim Universities. Since 1872, many residential colleges have become affiliated with the university, providing accommodation for students and faculty, and academic, sporting and cultural programs. There are ten colleges located on the main campus and in nearby suburbs. The university comprises ten separate academic units and is associated with numerous institut ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Immunomodulatory
Immunotherapy or biological therapy is the treatment of disease by activating or suppressing the immune system. Immunotherapies designed to elicit or amplify an immune response are classified as ''activation immunotherapies,'' while immunotherapies that reduce or suppress are classified as '' suppression immunotherapies''. Immunotherapy is under preliminary research for its potential to treat various forms of cancer. Cell-based immunotherapies are effective for some cancers. Immune effector cells such as lymphocytes, macrophages, dendritic cells, natural killer cells, and cytotoxic T lymphocytes work together to defend the body against cancer by targeting abnormal antigens expressed on the surface of tumor cells. Vaccine-induced immunity to COVID-19 relies mostly on an immunomodulatory T cell response. Therapies such as granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF), interferons, imiquimod and cellular membrane fractions from bacteria are licensed for medical use. Others includin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alphavirus
''Alphavirus'' is a genus of RNA viruses, the sole genus in the ''Togaviridae'' family. Alphaviruses belong to group IV of the Baltimore classification of viruses, with a positive-sense, single-stranded RNA genome. There are 32 alphaviruses, which infect various vertebrates such as humans, rodents, fish, birds, and larger mammals such as horses, as well as invertebrates. Alphaviruses that could infect both vertebrates and arthropods are referred dual-host alphaviruses, while insect-specific alphaviruses such as Eilat virus and Yada yada virus are restricted to their competent arthropod vector. Transmission between species and individuals occurs mainly via mosquitoes, making the alphaviruses a member of the collection of arboviruses – or arthropod-borne viruses. Alphavirus particles are enveloped, have a 70 nm diameter, tend to be spherical (although slightly pleomorphic), and have a 40 nm isometric nucleocapsid. Genome The alphaviruses are small, spherical, e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
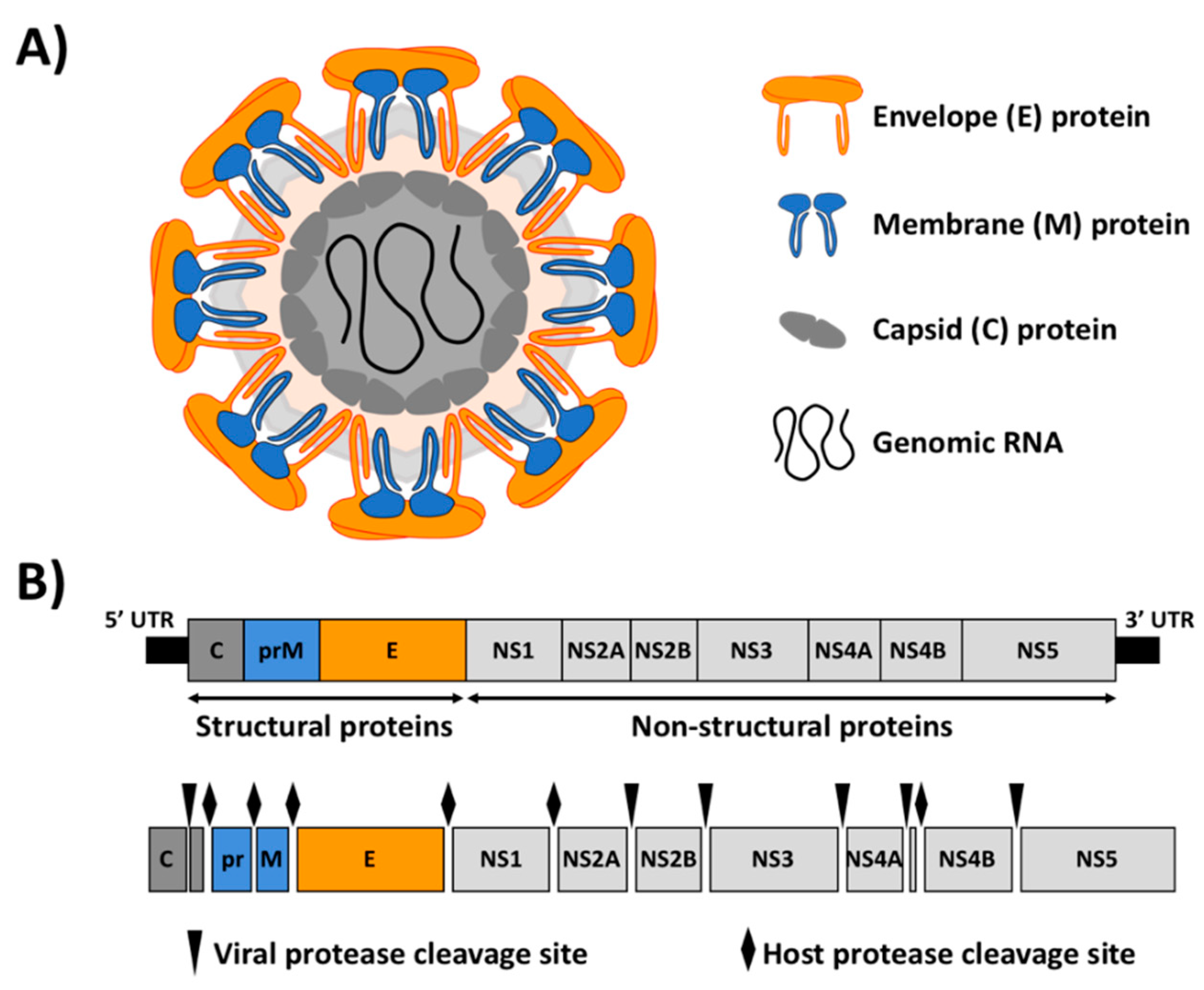
Flavivirus
''Flavivirus'' is a genus of positive-strand RNA viruses in the family ''Flaviviridae''. The genus includes the West Nile virus, dengue virus, tick-borne encephalitis virus, yellow fever virus, Zika virus and several other viruses which may cause encephalitis, as well as insect-specific flaviviruses (ISFs) such as cell fusing agent virus (CFAV), Palm Creek virus (PCV), and Parramatta River virus (PaRV). While dual-host flaviviruses can infect vertebrates as well as arthropods, insect-specific flaviviruses are restricted to their competent arthropods. The means by which flaviviruses establish persistent infection in their competent vectors and cause disease in humans depends upon several virus-host interactions, including the intricate interplay between flavivirus-encoded immune antagonists and the host antiviral innate immune effector molecules. Flaviviruses are named for the yellow fever virus; the word ''flavus'' means 'yellow' in Latin, and yellow fever in turn is named from i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polynucleotide
A polynucleotide molecule is a biopolymer composed of 13 or more nucleotide Nucleotides are organic molecules consisting of a nucleoside and a phosphate. They serve as monomeric units of the nucleic acid polymers – deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA), both of which are essential biomolecules wi ... monomers covalently bonded in a chain. DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) and RNA (ribonucleic acid) are examples of polynucleotides with distinct biological function. The prefix ''poly'' comes from the ancient Greek πολυς (polys, ''many''). DNA consists of two chains of polynucleotides, with each chain in the form of a helix (like a spiral staircase). Sequence Although DNA and RNA do not generally occur in the same polynucleotide, the four species of nucleotides may occur in any order in the chain. The sequence of DNA or RNA species for a given polynucleotide is the main factor determining its function in a living organism or a scientific experiment. Polynu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cerebral Malaria
Malaria is a Mosquito-borne disease, mosquito-borne infectious disease that affects humans and other animals. Malaria causes Signs and symptoms, symptoms that typically include fever, fatigue (medical), tiredness, vomiting, and headaches. In severe cases, it can cause jaundice, Epileptic seizure, seizures, coma, or death. Symptoms usually begin ten to fifteen days after being bitten by an infected mosquito. If not properly treated, people may have recurrences of the disease months later. In those who have recently survived an infection, reinfection usually causes milder symptoms. This partial Immunity (medical), resistance disappears over months to years if the person has no continuing exposure to malaria. Malaria is caused by protozoa, single-celled microorganisms of the ''Plasmodium'' group. It is spread exclusively through bites of infected ''Anopheles'' mosquitoes. The mosquito bite introduces the parasites from the mosquito's saliva into a person's blood. The parasites trav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pathogenesis
Pathogenesis is the process by which a disease or disorder develops. It can include factors which contribute not only to the onset of the disease or disorder, but also to its progression and maintenance. The word comes from Greek πάθος ''pathos'' 'suffering, disease' and γένεσις ''genesis'' 'creation'. Description Types of pathogenesis include microbial infection, inflammation, malignancy and tissue breakdown. For example, bacterial pathogenesis is the process by which bacteria cause infectious illness. Most diseases are caused by multiple processes. For example, certain cancers arise from dysfunction of the immune system (skin tumors and lymphoma after a renal transplant, which requires immunosuppression), Streptococcus pneumoniae is spread through contact with respiratory secretions, such as saliva, mucus, or cough droplets from an infected person and colonizes the upper respiratory tract and begins to multiply. The pathogenic mechanisms of a disease (or cond ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Queensland
, mottoeng = By means of knowledge and hard work , established = , endowment = A$224.3 million , budget = A$2.1 billion , type = Public research university , chancellor = Peter Varghese , vice_chancellor = Deborah Terry , city = Brisbane, Queensland, Australia , students = 55,305 (2019) , undergrad = 35,051 (2019) , postgrad = 19,939 (2019) , faculty = 2,854 , campus = Multiple sites , colours = Purple , affiliations = Group of EightUniversitas 21 ASAIHL EdX , website = , logo = Logo of the University of Queensland.svg , coor = The University of Queensland (UQ, or Queensland University) is a public research university located primarily in Brisbane, the capital city of the Australian state of Queensland. Founded in 1909 by the Queensland parliament, UQ is one of the six sandstone universities, an informal designation of the oldest university in each state. As per 2023, The University of Queensland is ranked as 2nd in Australia and 42nd in the world. Al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Technology
An institute of technology (also referred to as: technological university, technical university, university of technology, technological educational institute, technical college, polytechnic university or just polytechnic) is an institution of tertiary education (such as a university or college) that specializes in engineering, technology, applied science, and natural sciences. Institutes of technology versus polytechnics The institutes of technology and polytechnics have been in existence since at least the 18th century, but became popular after World War II with the expansion of engineering and applied science education, associated with the new needs created by industrialization. The world's first institution of technology, the Berg-Schola (today its legal successor is the University of Miskolc), was founded by the Court Chamber of Vienna in Selmecbánya, Kingdom of Hungary (now Banská Štiavnica, Slovakia), in 1735 in order to train specialists of precious metal and copper mi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Green House Gas
A greenhouse gas (GHG or GhG) is a gas that absorbs and emits radiant energy within the thermal infrared range, causing the greenhouse effect. The primary greenhouse gases in Earth's atmosphere are water vapor (), carbon dioxide (), methane (), nitrous oxide (), and ozone (). Without greenhouse gases, the average temperature of Earth's surface would be about , rather than the present average of . The atmospheres of Venus, Mars and Titan also contain greenhouse gases. Human activities since the beginning of the Industrial Revolution (around 1750) have increased the atmospheric concentration of carbon dioxide by over 50%, from 280 ppm in 1750 to 421 ppm in 2022. The last time the atmospheric concentration of carbon dioxide was this high was over 3 million years ago. This increase has occurred despite the absorption of more than half of the emissions by various natural carbon sinks in the carbon cycle. At current greenhouse gas emission rates, temperatures could increa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemosynthetic
In biochemistry, chemosynthesis is the biological conversion of one or more carbon-containing molecules (usually carbon dioxide or methane) and nutrients into organic matter using the oxidation of inorganic compounds (e.g., hydrogen gas, hydrogen sulfide) or ferrous ions as a source of energy, rather than sunlight, as in photosynthesis. Chemoautotrophs, organisms that obtain carbon from carbon dioxide through chemosynthesis, are phylogenetically diverse. Groups that include conspicuous or biogeochemically-important taxa include the sulfur-oxidizing Gammaproteobacteria, the Campylobacterota, the Aquificota, the methanogenic archaea, and the neutrophilic iron-oxidizing bacteria. Many microorganisms in dark regions of the oceans use chemosynthesis to produce biomass from single-carbon molecules. Two categories can be distinguished. In the rare sites where hydrogen molecules (H2) are available, the energy available from the reaction between CO2 and H2 (leading to production of m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |