|
Ruppy
Ruppy (short for Ruby Puppy) is the world's first transgenic dog. A cloned beagle, Ruppy and four other beagles produce a fluorescent protein that glows red upon excitation with ultraviolet light. Ruppy was created in 2009 by a group of scientists in South Korea, led by Byeong-Chun Lee. The dog was cloned using viral transfection of fibroblasts cells which expresses the red fluorescent gene. The nucleus of the transfected fibroblast was then inserted into the enucleated oocyte of another dog, leading to generation of dog oocytes expressing the red fluorescent protein. These cloned embryos were then implanted into the uterus of a surrogate mother. It was hoped to use this procedure to investigate the effect of the hormone oestrogen Estrogen or oestrogen is a category of sex hormone responsible for the development and regulation of the female reproductive system and secondary sex characteristics. There are three major endogenous estrogens that have estrogenic hormonal activ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transgenic
A transgene is a gene that has been transferred naturally, or by any of a number of genetic engineering techniques, from one organism to another. The introduction of a transgene, in a process known as transgenesis, has the potential to change the phenotype of an organism. ''Transgene'' describes a segment of DNA containing a gene sequence that has been isolated from one organism and is introduced into a different organism. This non-native segment of DNA may either retain the ability to produce RNA or protein in the transgenic organism or alter the normal function of the transgenic organism's genetic code. In general, the DNA is incorporated into the organism's germ line. For example, in higher vertebrates this can be accomplished by injecting the foreign DNA into the nucleus of a fertilized ovum. This technique is routinely used to introduce human disease genes or other genes of interest into strains of laboratory mice to study the function or pathology involved with that particula ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beagle
The beagle is a breed of small scent hound, similar in appearance to the much larger foxhound. The beagle was developed primarily for hunting hare, known as beagling. Possessing a great sense of smell and superior tracking instincts, the beagle is the primary breed used as a detection dog for prohibited agricultural imports and foodstuffs in quarantine around the world. The beagle is intelligent and is a popular pet due to its size, good temper, and a lack of inherited health problems. The modern breed was developed in Great Britain around the 1830s from several breeds, including the Talbot Hound, the North Country Beagle, the Southern Hound, and possibly the Harrier. Beagles have been depicted in popular culture since Elizabethan times in literature and paintings and more recently in film, television, and comic books. History The origin of the beagle is not known. In the 11th century, William the Conqueror brought the St. Hubert Hound and the Talbot hound to Br ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fibroblast
A fibroblast is a type of cell (biology), biological cell that synthesizes the extracellular matrix and collagen, produces the structural framework (Stroma (tissue), stroma) for animal Tissue (biology), tissues, and plays a critical role in wound healing. Fibroblasts are the most common cells of connective tissue in animals. Structure Fibroblasts have a branched cytoplasm surrounding an elliptical, speckled cell nucleus, nucleus having two or more nucleoli. Active fibroblasts can be recognized by their abundant Endoplasmic reticulum#Rough endoplasmic reticulum, rough endoplasmic reticulum. Inactive fibroblasts (called fibrocytes) are smaller, spindle-shaped, and have a reduced amount of rough endoplasmic reticulum. Although disjointed and scattered when they have to cover a large space, fibroblasts, when crowded, often locally align in parallel clusters. Unlike the epithelial cells lining the body structures, fibroblasts do not form flat monolayers and are not restricted by a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enucleation (microbiology)
In the context of microbiology, enucleation refers to removing the nucleus of a cell and replacing it with a different nucleus. This is used mainly in cloning but can also be used for creating hybrids of plants or animals. List of enucleated cells Humans *Red blood cell *Platelets See also * Cytoplasmic hybrid * Cell nucleus The cell nucleus (pl. nuclei; from Latin or , meaning ''kernel'' or ''seed'') is a membrane-bound organelle found in eukaryotic cells. Eukaryotic cells usually have a single nucleus, but a few cell types, such as mammalian red blood cells, h ... References __notoc__ Cell biology Cloning {{cell-biology-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
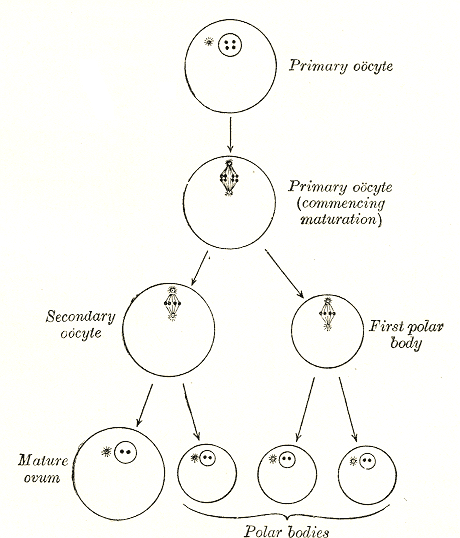
Oocyte
An oocyte (, ), oöcyte, or ovocyte is a female gametocyte or germ cell involved in reproduction. In other words, it is an immature ovum, or egg cell. An oocyte is produced in a female fetus in the ovary during female gametogenesis. The female germ cells produce a primordial germ cell (PGC), which then undergoes mitosis, forming oogonia. During oogenesis, the oogonia become primary oocytes. An oocyte is a form of genetic material that can be collected for cryoconservation. Formation The formation of an oocyte is called oocytogenesis, which is a part of oogenesis. Oogenesis results in the formation of both primary oocytes during fetal period, and of secondary oocytes after it as part of ovulation. Characteristics Cytoplasm Oocytes are rich in cytoplasm, which contains yolk granules to nourish the cell early in development. Nucleus During the primary oocyte stage of oogenesis, the nucleus is called a germinal vesicle. The only normal human type of secondary oocyte has t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uterus
The uterus (from Latin ''uterus'', plural ''uteri'') or womb () is the organ in the reproductive system of most female mammals, including humans that accommodates the embryonic and fetal development of one or more embryos until birth. The uterus is a hormone-responsive sex organ that contains glands in its lining that secrete uterine milk for embryonic nourishment. In the human, the lower end of the uterus, is a narrow part known as the isthmus that connects to the cervix, leading to the vagina. The upper end, the body of the uterus, is connected to the fallopian tubes, at the uterine horns, and the rounded part above the openings to the fallopian tubes is the fundus. The connection of the uterine cavity with a fallopian tube is called the uterotubal junction. The fertilized egg is carried to the uterus along the fallopian tube. It will have divided on its journey to form a blastocyst that will implant itself into the lining of the uterus – the endometrium, where it will ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Surrogate Pregnancy
Surrogacy is an arrangement, often supported by a legal agreement, whereby a woman agrees to delivery/labour for another person or people, who will become the child's parent(s) after birth. People may seek a surrogacy arrangement when pregnancy is medically impossible, when pregnancy risks are dangerous for the intended mother, or when a single man or a male couple wish to have a child. In surrogacy arrangements, monetary compensation may or may not be involved. Receiving money for the arrangement is known as commercial surrogacy. The legality and cost of surrogacy varies widely between jurisdictions, sometimes resulting in problematic international or interstate surrogacy arrangements. Couples seeking a surrogacy arrangement in a country where it is banned sometimes travel to a jurisdiction that permits it. In some countries, surrogacy is legal only if money does not exchange hands. Where commercial surrogacy is legal, couples may use the help of third-party agencies to a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oestrogen
Estrogen or oestrogen is a category of sex hormone responsible for the development and regulation of the female reproductive system and secondary sex characteristics. There are three major endogenous estrogens that have estrogenic hormonal activity: estrone (E1), estradiol (E2), and estriol (E3). Estradiol, an estrane, is the most potent and prevalent. Another estrogen called estetrol (E4) is produced only during pregnancy. Estrogens are synthesized in all vertebrates and some insects. Their presence in both vertebrates and insects suggests that estrogenic sex hormones have an ancient evolutionary history. Quantitatively, estrogens circulate at lower levels than androgens in both men and women. While estrogen levels are significantly lower in males than in females, estrogens nevertheless have important physiological roles in males. Like all steroid hormones, estrogens readily diffuse across the cell membrane. Once inside the cell, they bind to and activate estrogen receptors (ER ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2009 Animal Births
9 (nine) is the natural number following and preceding . Evolution of the Arabic digit In the beginning, various Indians wrote a digit 9 similar in shape to the modern closing question mark without the bottom dot. The Kshatrapa, Andhra and Gupta started curving the bottom vertical line coming up with a -look-alike. The Nagari continued the bottom stroke to make a circle and enclose the 3-look-alike, in much the same way that the sign @ encircles a lowercase ''a''. As time went on, the enclosing circle became bigger and its line continued beyond the circle downwards, as the 3-look-alike became smaller. Soon, all that was left of the 3-look-alike was a squiggle. The Arabs simply connected that squiggle to the downward stroke at the middle and subsequent European change was purely cosmetic. While the shape of the glyph for the digit 9 has an ascender in most modern typefaces, in typefaces with text figures the character usually has a descender, as, for example, in . The mod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cloned Dogs
Cloning is the process of producing individual organisms with identical or virtually identical DNA, either by natural or artificial means. In nature, some organisms produce clones through asexual reproduction. In the field of biotechnology, cloning is the process of creating cloned organisms (copies) of cells and of DNA fragments (molecular cloning). Etymology Coined by Herbert J. Webber, the term clone derives from the Ancient Greek word (), ''twig'', which is the process whereby a new plant is created from a twig. In botany, the term ''lusus'' was used. In horticulture, the spelling ''clon'' was used until the early twentieth century; the final ''e'' came into use to indicate the vowel is a "long o" instead of a "short o". Since the term entered the popular lexicon in a more general context, the spelling ''clone'' has been used exclusively. Natural cloning Cloning is a natural form of reproduction that has allowed life forms to spread for hundreds of millions of years. It ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)