|
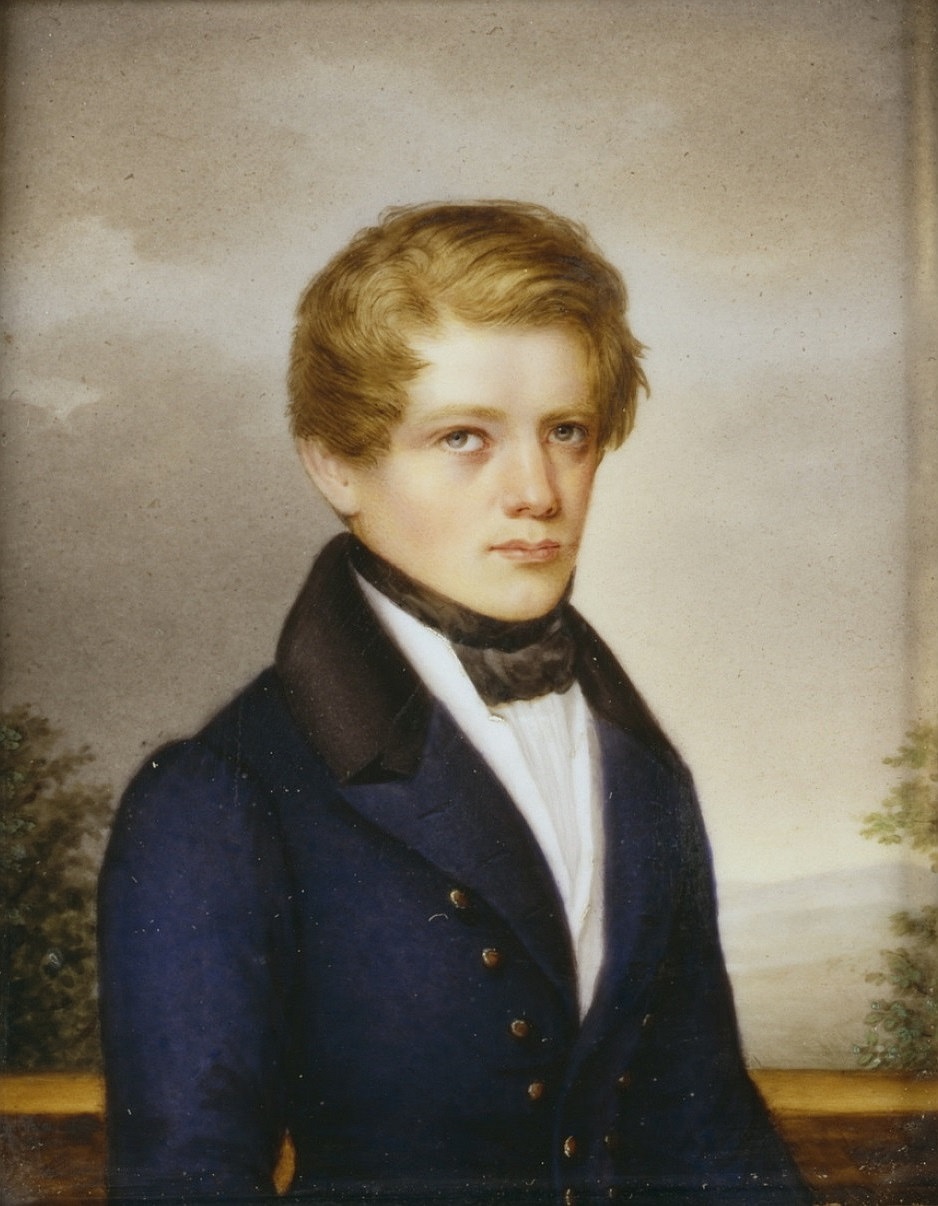
Rostislav Sementkovsky
Rostislav Ivanovich Sementkovsky (russian: ąĀąŠčüčéąĖčüą╗ą░ą▓ ąśą▓ą░ąĮąŠą▓ąĖčć ąĪąĄą╝ąĄąĮčéą║ąŠą▓čüą║ąĖą╣, 1846 ŌĆō 1918) was a Russian writer, publicist and translator, also known under the pen name Ratov. A professional lawyer, and a Saint Petersburg University's law faculty graduate, Sementkovsky started his career in journalism in 1873, first in '' Novoye Vremya'', then ''Finansovoye Obozreniye'' (Finance Review), '' Birzhevyie Vedomosti'', ''Telegraf'' and ''Novosti'', where in 1880-1890 he was the head of the Foreign Affairs section. In 1897 he became the editor-in-chief of the popular and influential '' Niva'' magazine (where for some years he had edited the Literary News section), while still writing on the broad range of subjects concerning politics, jurisprudence, philosophy and history of literature. A devoted Francophile and a proponent of the closest possible Franco-Russian relations, Sementkovsky (as Ratov) published in 1897 a book called ''Pending the War'' (ąÆ ąŠą ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moscow
Moscow ( , US chiefly ; rus, links=no, ą£ąŠčüą║ą▓ą░, r=Moskva, p=m╔Ésk╦łva, a=ą£ąŠčüą║ą▓ą░.ogg) is the capital and largest city of Russia. The city stands on the Moskva River in Central Russia, with a population estimated at 13.0 million residents within the city limits, over 17 million residents in the urban area, and over 21.5 million residents in the metropolitan area. The city covers an area of , while the urban area covers , and the metropolitan area covers over . Moscow is among the world's largest cities; being the most populous city entirely in Europe, the largest urban and metropolitan area in Europe, and the largest city by land area on the European continent. First documented in 1147, Moscow grew to become a prosperous and powerful city that served as the capital of the Grand Duchy that bears its name. When the Grand Duchy of Moscow evolved into the Tsardom of Russia, Moscow remained the political and economic center for most of the Tsardom's history. When th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French Language
French ( or ) is a Romance language of the Indo-European family. It descended from the Vulgar Latin of the Roman Empire, as did all Romance languages. French evolved from Gallo-Romance, the Latin spoken in Gaul, and more specifically in Northern Gaul. Its closest relatives are the other langues d'o├»lŌĆölanguages historically spoken in northern France and in southern Belgium, which French ( Francien) largely supplanted. French was also influenced by native Celtic languages of Northern Roman Gaul like Gallia Belgica and by the ( Germanic) Frankish language of the post-Roman Frankish invaders. Today, owing to France's past overseas expansion, there are numerous French-based creole languages, most notably Haitian Creole. A French-speaking person or nation may be referred to as Francophone in both English and French. French is an official language in 29 countries across multiple continents, most of which are members of the ''Organisation internationale de la Francophonie'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Denis Diderot
Denis Diderot (; ; 5 October 171331 July 1784) was a French philosopher, art critic, and writer, best known for serving as co-founder, chief editor, and contributor to the ''Encyclop├®die'' along with Jean le Rond d'Alembert. He was a prominent figure during the Age of Enlightenment. Diderot initially studied philosophy at a Jesuit college, then considered working in the church clergy before briefly studying law. When he decided to become a writer in 1734, his father disowned him. He lived a bohemian existence for the next decade. In the 1740s he wrote many of his best-known works in both fiction and non-fiction, including the 1748 novel ''The Indiscreet Jewels''. In 1751, Diderot co-created the ''Encyclop├®die'' with Jean le Rond d'Alembert. It was the first encyclopedia to include contributions from many named contributors and the first to describe the mechanical arts. Its secular tone, which included articles skeptical about Biblical miracles, angered both religious and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Otto Von Bismarck
Otto, Prince of Bismarck, Count of Bismarck-Sch├Čnhausen, Duke of Lauenburg (, ; 1 April 1815 ŌĆō 30 July 1898), born Otto Eduard Leopold von Bismarck, was a conservative German statesman and diplomat. From his origins in the upper class of Junker landowners, Bismarck rose rapidly in Prussian politics, and from 1862 to 1890 he was the Minister President of Prussia, minister president and List of foreign ministers of Prussia, foreign minister of Prussia. Before his rise to the Executive (government), executive, he was the Prussian ambassador to Russian Empire, Russia and Second French Empire, France and served in both houses of the Landtag of Prussia, Prussian Parliament. He masterminded the unification of Germany in 1871 and served as the first Chancellor of Germany#Under the Emperor (1871ŌĆō1918), Chancellor of the German Empire until 1890, in which capacity he dominated European affairs. He had served as the chancellor of the North German Confederation from 1867 to 1871, alon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Florenty Pavlenkov
Florenty Fyodorovich Pavlenkov (Russian: ążą╗ąŠčĆąĄąĮčéąĖą╣ ążčæą┤ąŠčĆąŠą▓ąĖčć ą¤ą░ą▓ą╗ąĄąĮą║ąŠą▓; 20 October 1839 ŌĆō 20 January 1900) was a Russian publisher, librarian A librarian is a person who works professionally in a library providing access to information, and sometimes social or technical programming, or instruction on information literacy to users. The role of the librarian has changed much over time ... and philanthropist, founder of the All-Russian circuit of rural libraries, who compiled and edited the ''Illustrated Reader for Children'' which in 1873 received an honorable commendation at the Vienna Book exhibition. Pavlenkov is best known as a founder and publisher of an epic 200-plus biographical series ' (ą¢ąĖąĘąĮčī ąĘą░ą╝ąĄčćą░č鹥ą╗čīąĮčŗčģ ą╗čÄą┤ąĄą╣) which never ceased after his death and continues in the 21st century. The Pavlenkov Publishing House (which functioned up until 1917) released more than 750 books which sold 3,5 million.Rassudovskaya, N.M. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adam Mickiewicz
Adam Bernard Mickiewicz (; 24 December 179826 November 1855) was a Polish poet, dramatist, essayist, publicist, translator and political activist. He is regarded as national poet in Poland, Lithuania and Belarus. A principal figure in Polish Romanticism, he is one of Poland's "Three Bards" ( pl, Trzej Wieszcze) and is widely regarded as Poland's greatest poet. He is also considered one of the greatest Slavic and European poets and has been dubbed a "Slavic bard". A leading Romantic dramatist, he has been compared in Poland and Europe to Byron and Goethe. He is known chiefly for the poetic drama ''Dziady'' (''Forefathers' Eve'') and the national epic poem '' Pan Tadeusz''. His other influential works include '' Konrad Wallenrod'' and '' Gra┼╝yna''. All these served as inspiration for uprisings against the three imperial powers that had partitioned the PolishŌĆōLithuanian Commonwealth out of existence. Mickiewicz was born in the Russian-partitioned territories of the former G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Stuart Mill
John Stuart Mill (20 May 1806 ŌĆō 7 May 1873) was an English philosopher, political economist, Member of Parliament (MP) and civil servant. One of the most influential thinkers in the history of classical liberalism, he contributed widely to social theory, political theory, and political economy. Dubbed "the most influential English-speaking philosopher of the nineteenth century", he conceived of liberty as justifying the freedom of the individual in opposition to unlimited state and social control. Mill was a proponent of utilitarianism, an ethical theory developed by his predecessor Jeremy Bentham. He contributed to the investigation of scientific methodology, though his knowledge of the topic was based on the writings of others, notably William Whewell, John Herschel, and Auguste Comte, and research carried out for Mill by Alexander Bain. He engaged in written debate with Whewell. A member of the Liberal Party and author of the early feminist work ''The Subjection o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kazimierz Krzywicki
Kazimierz (; la, Casimiria; yi, ū¦ūĢū¢ū×ūÖū©, Kuzimyr) is a historical district of Krak├│w and Krak├│w Old Town, Poland. From its inception in the 14th century to the early 19th century, Kazimierz was an independent city, a royal city of the Crown of the Polish Kingdom, located south of the Old Town of Krak├│w, separated from it by a branch of the Vistula river. For many centuries, Kazimierz was a place where ethnic Polish and Jewish cultures coexisted and intermingled. The northeastern part of the district was historically Jewish. In 1941, the Jews of Krak├│w were forcibly relocated by the German occupying forces into the Krakow ghetto just across the river in Podg├│rze, and most did not survive the war. Today, Kazimierz is one of the major tourist attractions of Krakow and an important center of cultural life of the city. The boundaries of Kazimierz are defined by an old island in the Vistula river. The northern branch of the river (''Stara Wis┼éa'' ŌĆō Old Vistula) was fille ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paul Lacombe (historian)
Paul Lacombe (January 6, 1834 in Cahors ŌĆō July 2, 1919 in Lauzerte) was a French historian and archivist. In a period of intense disciplinary debate among historians and sociologists at the turn of twentieth century Lacombe entered the debate about 'history served by scientific inquiry' through his groundbreaking work, ''De l'histoire consid├®r├®e comme science'' 'The History Considered as Science''(1894) and with his contributions to ''Revue de synth├©se historique'' 'The Journal of Historical Synthesis''of Henri Berr. Refusing an approach to history based on the mere narration of great dates and great men, he invented the concept of 'history of events' (''l'histoire evenementielle'') and insisted on the need for the historian to make strict selections of evidence and to establish a hierarchy among facts. He also laid the foundations of a history which brings social and economic factors to the forefront of investigation. He is, therefore, a precursor to the idea of Fernand Brau ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pierre Paul Leroy-Beaulieu
Pierre Paul Leroy-Beaulieu (9 December 1843 in Saumur – 9 December 1916 in Paris) was a French economist, brother of Henri Jean Baptiste Anatole Leroy-Beaulieu, born at Saumur, Maine-et-Loire on 9 December 1843, and educated in Paris at the Lyc├®e Bonaparte and the ├ēcole de Droit. He afterwards studied at Bonn and Berlin, and on his return to Paris began to write for ''Le Temps'', ''Revue nationale'' and ''Revue contemporaine''. In 1867, he won a prize offered by the Academy of Moral and Political Sciences with an essay entitled ''L'Influence de ├®tat moral et intellectuel des populations ouvri├©res sur le taux des salaires''. In 1870 he gained three prizes for essays on ''La Colonisation chez les peuples modernes, L'Administration en France et en Angleterre'', and ''L'Imp├┤t foncier et ses cons├®quences ├®conomiques''. In 1872, Leroy-Beaulieu became professor of finance at the newly founded ├ēcole Libre des Sciences Politiques, and in 1880 he succeeded his father-in-law, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Max Nordau
Max Simon Nordau (born ''Simon Maximilian S├╝dfeld''; 29 July 1849 ŌĆō 23 January 1923) was a Zionist leader, physician, author, and social critic. He was a co-founder of the Zionist Organization together with Theodor Herzl, and president or vice-president of several Zionist congresses. As a social critic, he wrote ''The Conventional Lies of Our Civilisation'' (1883), '' Degeneration'' (1892), and ''Paradoxes'' (1896). Although not his most popular or successful work whilst alive, ''Degeneration'' is the book most often remembered and cited today. Biography Simon (Simcha) Maximilian S├╝dfeld (later Max Nordau) was born in Pest, Kingdom of Hungary, then part of the Austrian Empire. His father, Gabriel S├╝dfeld, was a rabbi, but earned his livelihood as a Hebrew tutor. As an Orthodox Jew, Nordau attended a Jewish elementary school and earned a medical degree from the University of Pest in 1872. He then traveled for six years, visiting the principal countries of Europe. He changed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hippolyte Carnot
Lazare Hippolyte Carnot (6 October 1801, Saint-Omer ŌĆō 16 March 1888) was a French politician. He was the younger brother of the founder of thermodynamics Sadi Carnot and the second son of the revolutionary politician and general Lazare Nicolas Marguerite Carnot, who also served in the government of Napoleon, as well as the father of French president Marie Fran├¦ois Sadi Carnot. Early life Hippolyte Carnot was born at Saint-Omer, Pas-de-Calais. After the final defeat of Napoleon in 1815, his father went into exile. Hippolyte Carnot lived at first in exile with his father, returning to France only in 1823. Unable to enter active political life, he turned to literature and philosophy, publishing in 1828 a collection of ''Chants hell├®niens'' translated from the German of Wilhelm M├╝ller, and in 1830 an ''Expos├® de la doctrine Saint-Simonienne'', and collaborating in the Saint-Simonian journal ''Le Producteur''. He paid several visits to Britain and travelled in other countri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |