|
Romanian Occupation Of Pokuttya
The Romanian occupation of Pokuttia ( ro, Pocuția) took place in early 1919, when, as a result of alliances concluded between Romania and Poland, the former entered the southeastern corner of the former Austro-Hungarian ruled province of Galicia. During the interwar period, Romania was Poland's main ally in Eastern Europe (''see Polish–Romanian alliance''). Both nations were bound by several treaties and history of this alliance dates back to the end of World War I and the Treaty of Versailles. However, to actively cooperate, governments in Bucharest and Warsaw emphasized the necessity of a shared border. Discussions about the border started in Paris some time at the beginning of 1919 and continued during the following months. The proposal for occupation was first advanced by the Romanian government of Ion I. C. Brătianu on May 8, 1919. Brătianu suggested this as a means to separate both Czechoslovakia and Hungary from Soviet influences, thus consolidating the position o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pokuttia
Pokuttia, also known as Pokuttya or Pokutia ( uk, Покуття, Pokuttya; pl, Pokucie; german: Pokutien; ro, Pocuția), is a historical area of East-Central Europe, situated between the Dniester and Cheremosh rivers and the Carpathian Mountains, in the southwestern part of modern Ukraine. Part of the Antean tribal alliance since the 4th century, it joined Kievan Rus' in the 10th century, and was eventually annexed by Poland in the 14th century. The region was involved in a series of wars between Poland and Moldavia, which ceased with the death of Petru Rareș, who failed to conquer the region on two occasions (1531, 1535). A last attempt to seize Pokuttia was made by John III the Terrible in 1572. At times, Polish rule caused discontent among Pokuttians. Many of them were captured and resettled to Moldavia, where they reinforced the Ukrainian element in the country. In the 1490s, a rebellion was started by Petro Mukha, only to be suppressed by 1492. The region remained under P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
First Republic Of Czechoslovakia
The First Czechoslovak Republic ( cs, První československá republika, sk, Prvá česko-slovenská republika), often colloquially referred to as the First Republic ( cs, První republika, Slovak: ''Prvá republika''), was the first Czechoslovak state that existed from 1918 to 1938, a union of ethnic Czechs and Slovaks. The country was commonly called Czechoslovakia (Czech and sk, Československo), a compound of ''Czech'' and ''Slovak''; which gradually became the most widely used name for its successor states. It was composed of former territories of Austria-Hungary, inheriting different systems of administration from the formerly Austrian (Bohemia, Moravia, a small part of Silesia) and Hungarian territories (mostly Upper Hungary and Carpathian Ruthenia). After 1933, Czechoslovakia remained the only ''de facto'' functioning democracy in Central Europe, organized as a parliamentary republic. Under pressure from its Sudeten German minority, supported by neighbouring Nazi Germ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lucjan Żeligowski
Lucjan Żeligowski (; 17 October 1865 – 9 July 1947) was a Polish-Lithuanian general, politician, military commander and veteran of World War I, the Polish-Soviet War and World War II. He is mostly remembered for his role in Żeligowski's Mutiny and as head of a short-lived Republic of Central Lithuania. Biography Lucjan Żeligowski was born on 17 October 1865 in Oszmiana, in the Russian Empire (modern Ashmiany in Belarus) to Polish parents Gustaw Żeligowski and Władysława Żeligowska née Traczewska. Before the Partitions of Poland in the late 18th century the town was part of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth. After graduating from military officers' school located in Riga (1885), Żeligowski joined the Imperial Russian Army, where he served at various staff and command posts. He then married Tatiana Pietrova and had two children. Żeligowski fought in the Russo-Japanese War of 1904-1905. During the First World War he served as a lieutenant colonel and commanding o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
4th Rifle Division (Poland)
The Polish 4th Rifle Division ( pl, 4. Dywizja Strzelców Polskich, russian: Полская 4-я Стрелковая Дивизия) was a Polish military unit, forming, together with the Polish 5th Rifle Division of the Blue Army, the only part of the Polish military which took part in the Russian Civil War. Under the command of General Lucjan Żeligowski, it operated as an ally of the White movement from autumn 1918 to August 1919 in southern Russia and Bessarabia. History and operations The 4th Rifle Division could trace its origins to the Polish 2nd Corps in Russia. The 2nd Corps was formed from various Polish units, but primarily the 2nd Brigade of the Polish Legions in World War I, which rebelled against the Treaty of Brest-Litovsk and decided to join the newly-forming Polish army and help secure the territories inhabited by the Poles in the Kresy region. The Polish 5th Rifle Division found itself fighting in the northern territories of the former Russian Empire; the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kolomyia
Kolomyia, formerly known as Kolomea ( ua, Коломия, Kolomyja, ; pl, Kołomyja; german: Kolomea; ro, Colomeea; yi, ), is a city located on the Prut River in Ivano-Frankivsk Oblast (province), in western Ukraine. It serves as the administrative centre of Kolomyia Raion (district). The city rests approximately halfway between Ivano-Frankivsk and Chernivtsi, in the centre of the historical region of Pokuttya, with which it shares much of its history. Kolomyia hosts the administration of Kolomyia urban hromada, one of the hromadas of Ukraine. The population is . The city is a notable railroad hub, as well as an industrial centre (textiles, shoes, metallurgical plant, machine works, wood and paper industry). It is a centre of Hutsul culture. Until 1925 the city was the most populous city in the region. History The settlement of Kolomyia was first mentioned by the Hypatian Chronicle [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ivano-Frankivsk
Ivano-Frankivsk ( uk, Іва́но-Франкі́вськ, translit=Iváno-Frankívśk ), formerly Stanyslaviv ( pl, Stanisławów ; german: Stanislau), is a city located in Western Ukraine. It is the administrative centre of Ivano-Frankivsk Oblast and Ivano-Frankivsk Raion. Ivano-Frankivsk hosts the administration of Ivano-Frankivsk urban hromada. Its population is Built in the mid-17th century as a fortress of the Polish Potocki family, Stanisławów was annexed to the Habsburg Empire during the First Partition of Poland in 1772, after which it became the property of the State within the Austrian Empire. The fortress was slowly transformed into one of the most prominent cities at the foothills of the Carpathian Mountains. After World War I, for several months, it served as a temporary capital of the West Ukrainian People's Republic. Following the Peace of Riga in 1921, Stanisławów became part of the Second Polish Republic. After the Soviet invasion of Poland at the ons ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polish Army
The Land Forces () are the land forces of the Polish Armed Forces. They currently contain some 62,000 active personnel and form many components of the European Union and NATO deployments around the world. Poland's recorded military history stretches back a millennium – since the 10th century (see List of Polish wars and History of the Polish Army). Poland's modern army was formed after Poland regained independence following World War I in 1918. History 1918–1938 When Poland regained independence in 1918, it recreated its military which participated in the Polish–Soviet War of 1919–1921, and in the two smaller conflicts ( Polish–Ukrainian War (1918–1919) and the Polish–Lithuanian War (1920)). Initially, right after the First World War, Poland had five military districts (1918–1921): * Poznań Military District (Poznański Okręg Wojskowy), HQ in Poznań * Kraków Military District (Krakowski Okręg Wojskowy), HQ in Kraków * Łódź Military District (Łódz ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
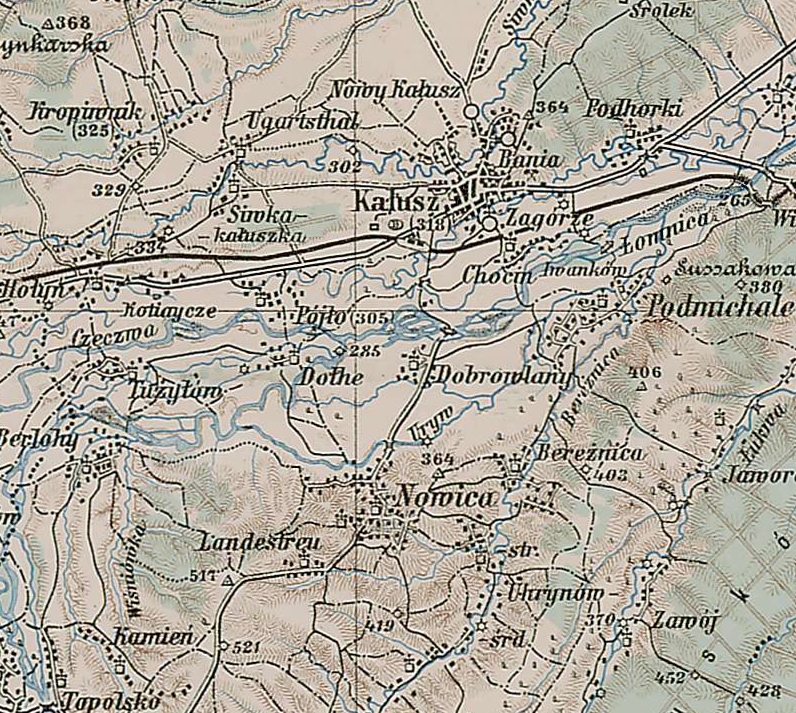
Kalush, Ukraine
Kalush ( uk, Ка́луш, ) is a city set in the foothills of the Carpathian Mountains, in Ivano-Frankivsk Oblast (province) of western Ukraine. It is the administrative centre of Kalush Raion (district) and hosts the administration of Kalush urban hromada, one of the hromadas of Ukraine. Its estimated population was Important local industries include chemicals and concrete. Geography Kalush is in the western portion of Ivano-Frankivsk Oblast, in the region of Western Ukraine at the foothills of the Carpathian Mountains. It stands on the Dniester tributary, the Limnytsia River that begins from the slopes of the Carpathians. The city is at the eastern borders of the ethnographical region of Boyko Land. History The earliest known mention of Kalush is the accounting of a village of that name in a chronicle dated May 27, 1437. At that time, together with all Red Ruthenia, the village belonged to the Kingdom of Poland, and was known under its Polish name, Kałusz. Until th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Romanian Army
The Romanian Land Forces ( ro, Forțele Terestre Române) is the army of Romania, and the main component of the Romanian Armed Forces. In recent years, full professionalisation and a major equipment overhaul have transformed the nature of the Land Forces. The Romanian Land Forces was founded on . It participated in World War I, together with the Imperial Russian Army in actions against the Central Powers and, despite initial setbacks, won the decisive battles of Mărăști and Mărășești. During most of World War II (until August 23, 1944) Romanian forces supported the Axis powers, fighting against the Soviet Union on the Eastern Front. From August 1944 until the end of the war, Romania fought against Germany under the control of the Soviet Union. When the communists seized power after the Second World War, the army underwent reorganisation and sovietization. Following the Romanian Revolution of 1989, due to shortage of funds, many units were disbanded and much equipment was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Józef Piłsudski
), Vilna Governorate, Russian Empire (now Lithuania) , death_date = , death_place = Warsaw, Poland , constituency = , party = None (formerly PPS) , spouse = , children = Wanda, Jadwiga , profession = , signature = Józef Piłsudski Signature.svg , footnotes = , nickname = , allegiance = Austria-HungarySecond Polish Republic , branch = Polish LegionsPolish Army , serviceyears = 1914–19231926–1935 , rank = Marshal of Poland , unit = , commands = , battles = World War IPolish–Ukrainian WarPolish–Lithuanian WarPolish–Soviet War , awards = , resting_place = Józef Klemens Piłsudski (; 5 December 1867 – 12 May 1935) was a Polish statesman who served as the Chief of State (1918–1922) and First Marshal of Poland (from 1920). He was cons ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second Polish Republic
The Second Polish Republic, at the time officially known as the Republic of Poland, was a country in Central Europe, Central and Eastern Europe that existed between 1918 and 1939. The state was established on 6 November 1918, before the end of the First World War. The Second Republic ceased to exist in 1939, when Invasion of Poland, Poland was invaded by Nazi Germany, the Soviet Union and the Slovak Republic (1939–1945), Slovak Republic, marking the beginning of the European theatre of World War II, European theatre of the Second World War. In 1938, the Second Republic was the sixth largest country in Europe. According to the Polish census of 1921, 1921 census, the number of inhabitants was 27.2 million. By 1939, just before the outbreak of World War II, this had grown to an estimated 35.1 million. Almost a third of the population came from minority groups: 13.9% Ruthenians; 10% Ashkenazi Jews; 3.1% Belarusians; 2.3% Germans and 3.4% Czechs and Lithuanians. At the same time, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |