|
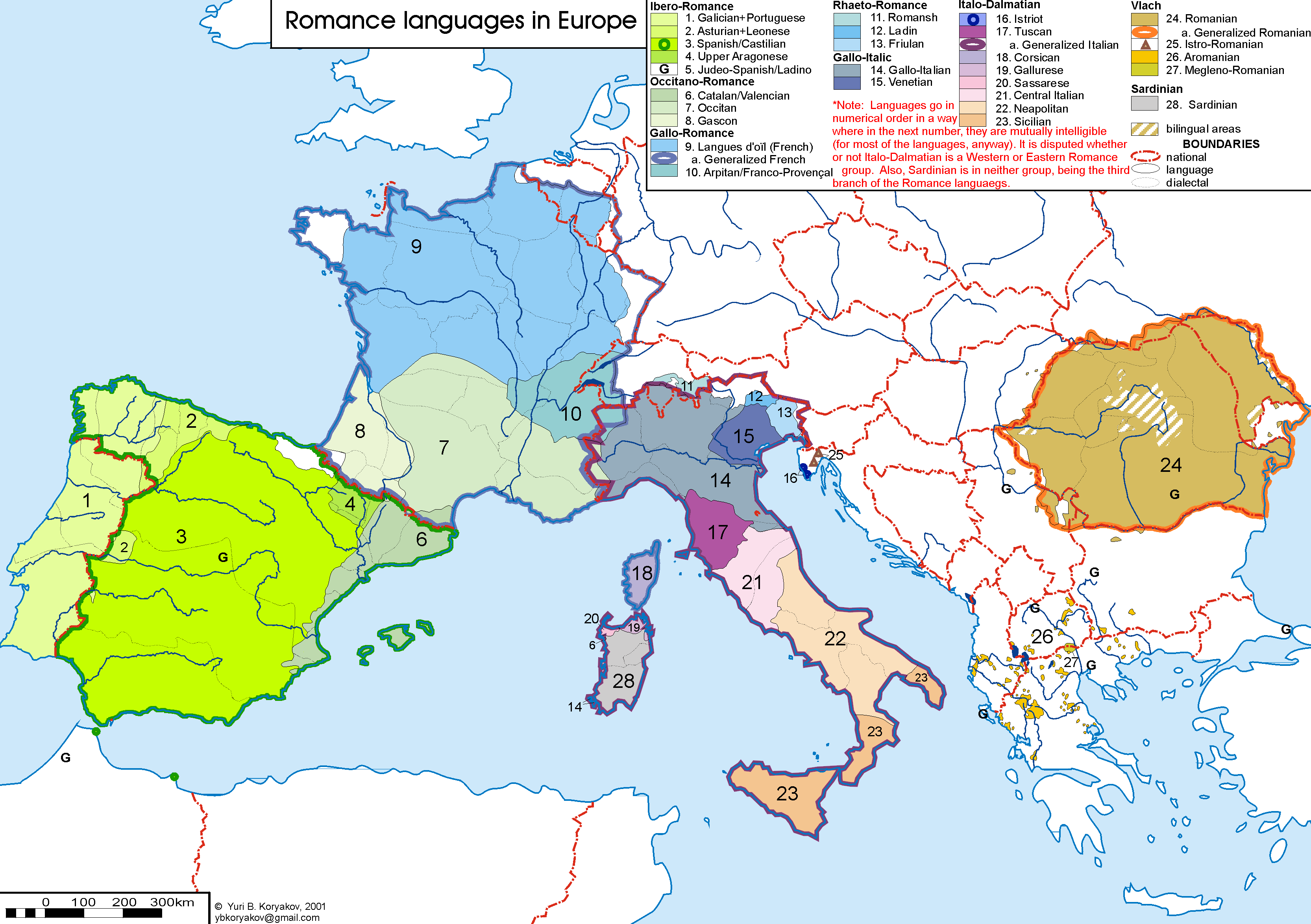
Romance Languages
The Romance languages, also known as the Latin or Neo-Latin languages, are the languages that are Language family, directly descended from Vulgar Latin. They are the only extant subgroup of the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages, Indo-European language family. The five list of languages by number of native speakers, most widely spoken Romance languages by number of native speakers are: Spanish language, Spanish (489 million), official in Spain and most of Central America, Central and South America; Portuguese language, Portuguese (240 million), official in Portugal, Brazil and Portuguese-speaking Africa; French language, French (80 million), Italian language, Italian (67 million), official in Italy, Vatican City, San Marino and Switzerland; and Romanian language, Romanian (30 million), official in Romania and Moldova. There are more than 900 million native speakers of Romance languages found worldwide, mainly in the Americas, Europe, and parts of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Old Latium
Old Latium ( la, Latium vetus or ') is a region of the Italian peninsula bounded to the north by the river Tiber, to the east by the central Apennine mountains, to the west by the Mediterranean Sea and to the south by Monte Circeo. It was the territory of the Latins, an Italic tribe which included the early inhabitants of the city of Rome. Later it was also settled by various Italic tribes such as the Rutulians, Volscians, Aequi, and Hernici. The region was referred to as "old" to distinguish it from the expanded region, Latium, that included the region to the south of Old Latium, between Monte Circeo and the river Garigliano – the so-called Latium adiectum ("attached Latium"). It corresponded to the central part of the modern administrative region of Lazio, Italy, and it covered an area measuring of roughly 50 Roman miles. It was calculated by Mommsen that the region's area was about 1860 square kilometres. Settlement Literary tradition Dionysius of Halicarnassus has preser ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proto-Romance Language
Proto-Romance is the comparatively reconstructed ancestor of all Romance languages. It reflects a late variety of spoken Latin prior to regional fragmentation. Phonology Vowels Monophthongs Diphthong The only phonemic diphthong was /au̯/. Allophony *Vowels were lengthened in stressed open syllables. *Stressed /ɛ, ɔ/ may have yielded the incipient diphthongs ͜ɛ, o͜ɔwhen followed by a syllable containing a close vowel. **Whatever the precise outcome, Maiden argues that this would have been limited, at the Proto-Romance stage, to open syllables. That is, it would have applied only to instances of /ɛ/ and /ɔ/ that had been subject to stressed-open-syllable lengthening. Constraints *Neither a distinct /ɛ/ nor /ɔ/ occurred in unstressed position on account of having merged into /e/ and /o/ respectively.Ferguson 1976: 76; Gouvert 2015: 78–81, 121–122 *Neither a distinct /i/ nor /u/ occurred in the second syllable of words with the structure �σσˈσ� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spanish Language
Spanish ( or , Castilian) is a Romance languages, Romance language of the Indo-European language family that evolved from colloquial Latin spoken on the Iberian peninsula. Today, it is a world language, global language with more than 500 million native speakers, mainly in the Americas and Spain. Spanish is the official language of List of countries where Spanish is an official language, 20 countries. It is the world's list of languages by number of native speakers, second-most spoken native language after Mandarin Chinese; the world's list of languages by total number of speakers, fourth-most spoken language overall after English language, English, Mandarin Chinese, and Hindustani language, Hindustani (Hindi-Urdu); and the world's most widely spoken Romance languages, Romance language. The largest population of native speakers is in Mexico. Spanish is part of the Iberian Romance languages, Ibero-Romance group of languages, which evolved from several dialects of Vulgar Latin in I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Languages By Number Of Native Speakers
This article ranks human languages by their number of native speakers. However, all such rankings should be used with caution, because it is not possible to devise a coherent set of linguistic criteria for distinguishing languages in a dialect continuum. For example, a language is often defined as a set of varieties that are mutually intelligible, but independent national standard languages may be considered to be separate languages even though they are largely mutually intelligible, as in the case of Danish and Norwegian. Conversely, many commonly accepted languages, including German, Italian and even English, encompass varieties that are not mutually intelligible. While Arabic is sometimes considered a single language centred on Modern Standard Arabic, other authors describe its mutually unintelligible varieties as separate languages. Similarly, Chinese is sometimes viewed as a single language because of a shared culture and common literary language. It is also common to descr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indo-European Languages
The Indo-European languages are a language family native to the overwhelming majority of Europe, the Iranian plateau, and the northern Indian subcontinent. Some European languages of this family, English, French, Portuguese, Russian, Dutch, and Spanish, have expanded through colonialism in the modern period and are now spoken across several continents. The Indo-European family is divided into several branches or sub-families, of which there are eight groups with languages still alive today: Albanian, Armenian, Balto-Slavic, Celtic, Germanic, Hellenic, Indo-Iranian, and Italic; and another nine subdivisions that are now extinct. Today, the individual Indo-European languages with the most native speakers are English, Hindi–Urdu, Spanish, Bengali, French, Russian, Portuguese, German, and Punjabi, each with over 100 million native speakers; many others are small and in danger of extinction. In total, 46% of the world's population (3.2 billion people) speaks an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pennsylvania State University Press
The Penn State University Press, also known as The Pennsylvania State University Press, was established in 1956 and is a non-profit publisher of scholarly books and journals. It is the independent publishing branch of the Pennsylvania State University and is a division of the Penn State University Library system. Penn State University Press publishes books and journals of interest to scholars and general audiences. As a part of a land-grant university with a mandate to serve the citizens of the commonwealth of Pennsylvania, it also specializes in works about Penn State University, Pennsylvania, and the mid-Atlantic region. The areas of scholarship the Press is best known for are art history, medieval studies, Latin American studies, rhetoric and communication, religious studies, and Graphic Medicine. In 2016 the Press launched PSU Press Unlocked, an open access platform featuring over 70 books and journals. The Press acquired academic publisher Eisenbrauns, which specializes in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Language Family
A language family is a group of languages related through descent from a common ''ancestral language'' or ''parental language'', called the proto-language of that family. The term "family" reflects the tree model of language origination in historical linguistics, which makes use of a metaphor comparing languages to people in a biological family tree, or in a subsequent modification, to species in a phylogenetic tree of evolutionary taxonomy. Linguists therefore describe the ''daughter languages'' within a language family as being ''genetically related''. According to '' Ethnologue'' there are 7,151 living human languages distributed in 142 different language families. A living language is defined as one that is the first language of at least one person. The language families with the most speakers are: the Indo-European family, with many widely spoken languages native to Europe (such as English and Spanish) and South Asia (such as Hindi and Bengali); and the Sino-Tibetan famil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Language
Language is a structured system of communication. The structure of a language is its grammar and the free components are its vocabulary. Languages are the primary means by which humans communicate, and may be conveyed through a variety of methods, including spoken, sign, and written language. Many languages, including the most widely-spoken ones, have writing systems that enable sounds or signs to be recorded for later reactivation. Human language is highly variable between cultures and across time. Human languages have the properties of productivity and displacement, and rely on social convention and learning. Estimates of the number of human languages in the world vary between and . Precise estimates depend on an arbitrary distinction (dichotomy) established between languages and dialects. Natural languages are spoken, signed, or both; however, any language can be encoded into secondary media using auditory, visual, or tactile stimuli – for example, writing, whi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Merriam-Webster
Merriam-Webster, Inc. is an American company that publishes reference books and is especially known for its dictionaries. It is the oldest dictionary publisher in the United States. In 1831, George and Charles Merriam founded the company as G & C Merriam Co. in Springfield, Massachusetts. In 1843, after Noah Webster died, the company bought the rights to ''An American Dictionary of the English Language'' from Webster's estate. All Merriam-Webster dictionaries trace their lineage to this source. In 1964, Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc. acquired Merriam-Webster, Inc. as a subsidiary. The company adopted its current name in 1982. History Noah Webster In 1806, Webster published his first dictionary, ''A Compendious Dictionary of the English Language''. In 1807 Webster started two decades of intensive work to expand his publication into a fully comprehensive dictionary, ''An American Dictionary of the English Language''. To help him trace the etymology of words, Webster learned ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
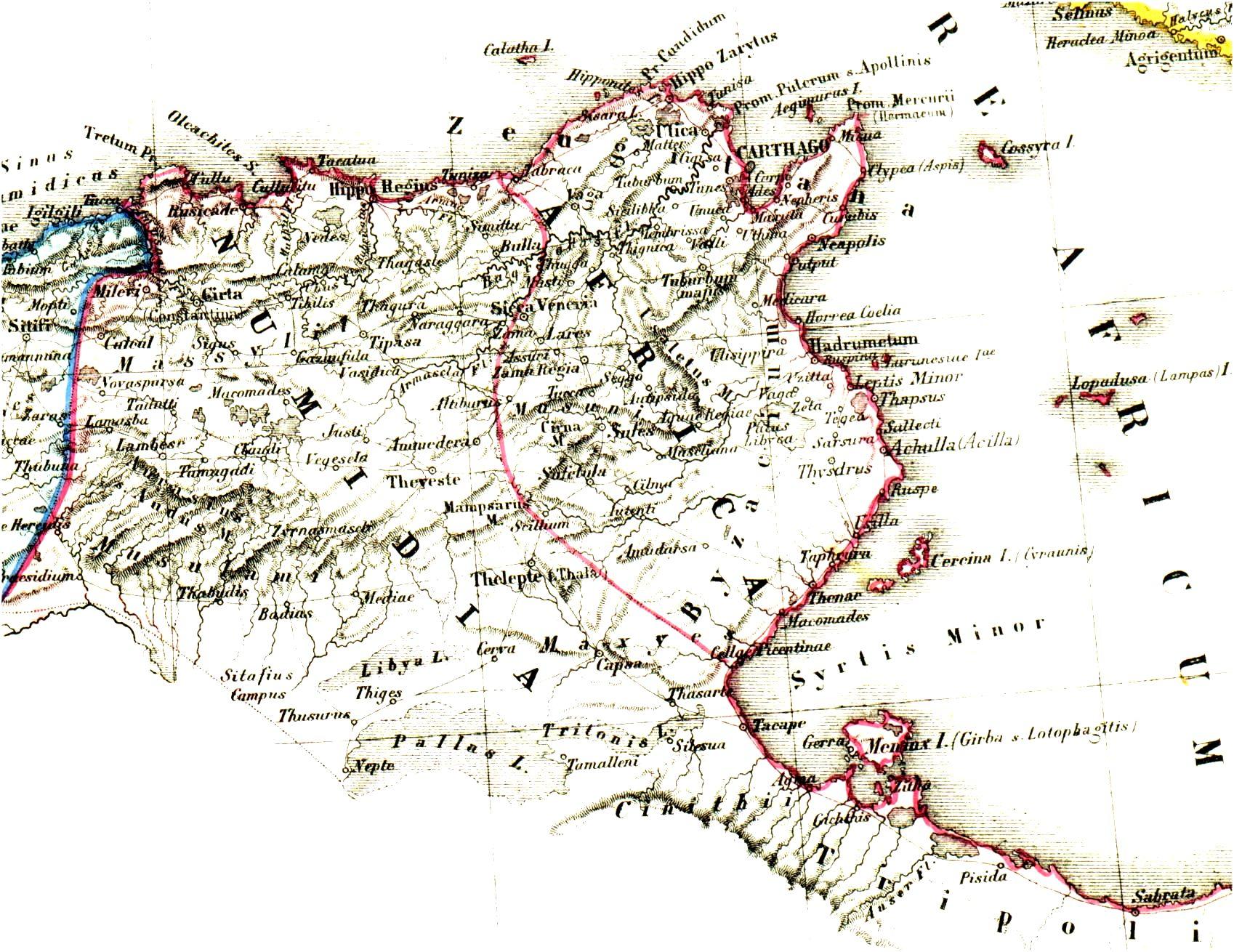
African Romance
African Romance or African Latin is an extinct Romance language that was spoken in the Roman province of Africa by the Roman Africans during the later Roman and early Byzantine Empires, and several centuries after the annexation of the region by the Umayyad Caliphate in 696 AD. African Romance is poorly attested as it was mainly a spoken, vernacular language, a ''sermo rusticus.'' There is little doubt, however, that by the early 3rd century AD, some native provincial variety of Latin was fully established in Africa.' This language, which developed under Byzantine rule, continued through to the 12th century in various places along the North African coast and the immediate littoral,' with evidence that it may have persisted up to the 14th century,' and possibly even the 15th century,' or later' in certain areas of the interior. Background The Roman province of Africa was organized in 146 BC following the defeat of Carthage in the Third Punic War. The city of Carthage, destro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
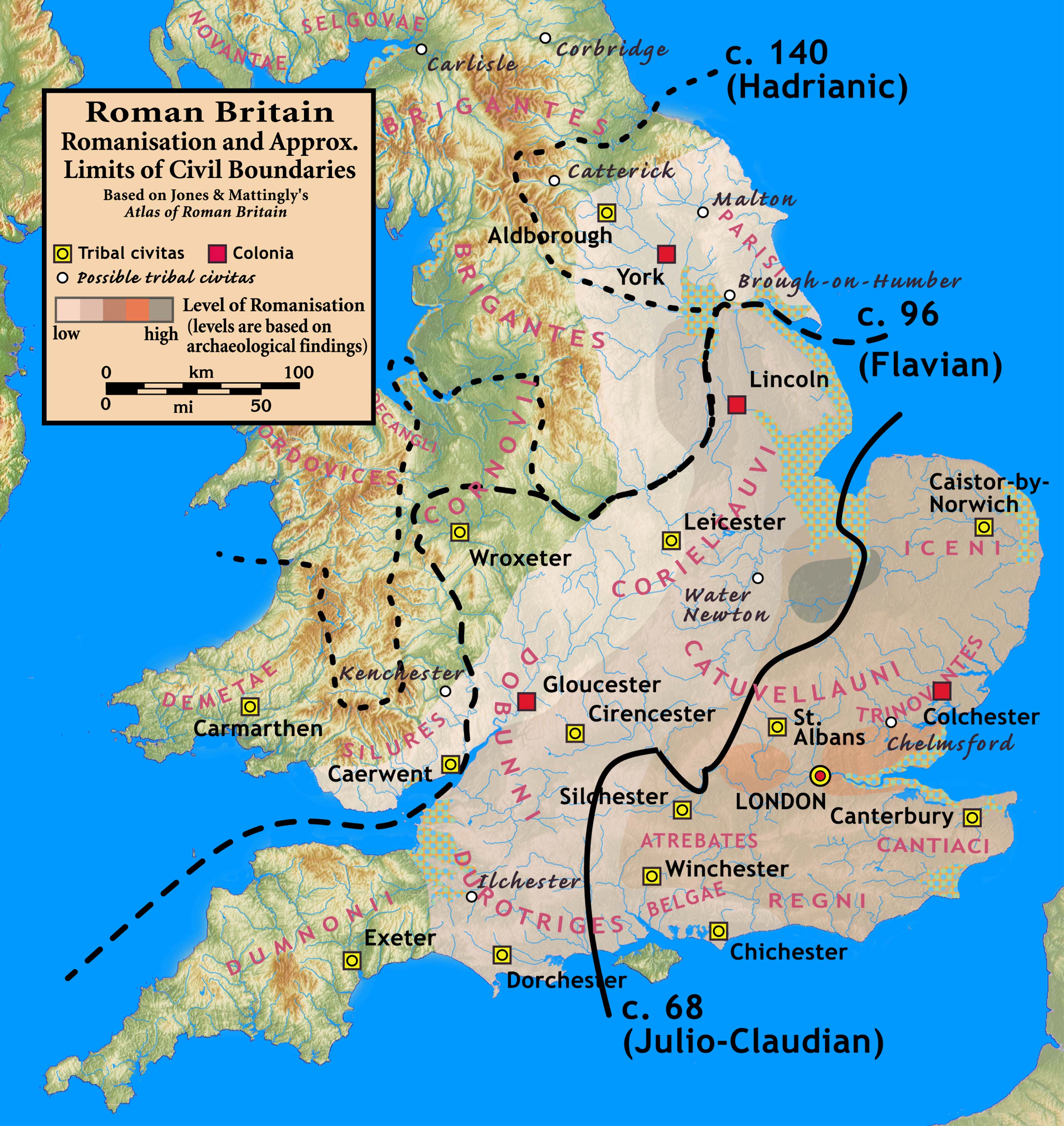
British Latin
British Latin or British Vulgar Latin was the Vulgar Latin spoken in Great Britain in the Roman and sub-Roman periods. While Britain formed part of the Roman Empire, Latin became the principal language of the elite, especially in the more romanized south and east of the island. However, in the less romanized north and west it never substantially replaced the Brittonic language of the indigenous Britons. In recent years, scholars have debated the extent to which British Latin was distinguishable from its continental counterparts, which developed into the Romance languages. After the end of Roman rule, Latin was displaced as a spoken language by Old English in most of what became England during the Anglo-Saxon settlement of the fifth and sixth centuries. It survived in the remaining Celtic regions of western Britain but died out in those regions too by about 700, when it was replaced by the local Brittonic languages. Background At the inception of Roman rule in AD 43, Gr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pannonian Latin
Pannonian Latin (alternatively Pannonian Romance) was a variant of Vulgar Latin that developed in Pannonia, but became extinct after the loss of the province. History Most likely the bigger part of the indigenous population spoke P-Celtic. This was influenced by the neighbouring cultures (eg. Illyrian and Scythian). Unfortunately, the surviving data isn't enough to distinguish their tribes' languages. The conquest of the region by the Roman Empire was completed by 9 BC, and the territory integrated into Illyricum. In 10 AD Pannonia was organized as a separate province. In Pannonia the material culture of the native population showed little sign of Romanization in the first 160 years of Roman rule. In the second half of the second century there were major changes in the composition of the population, but the organic continuity of the Latin language development of the area is unbroken. The particularly destructive Marcomannic Wars changed the ethno-linguistic makeup of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |